SQLAlchemy is a powerful and popular Python library that provides a flexible and efficient way to interact with databases. It uses the Object-Relational Mapping (ORM)tool, which acts as a bridge between the Python objects and the relational database. SQLALchemy provides a wide range of methods to work with databases, It provides a high level of abstraction, allowing you to focus on your application logic while seamlessly interacting with the database using Python. In this article, we see how to update and insert the date, time, and time zone into the database.
Working with DateTime in SQLAlchemy
Date and Time are fundamental aspects of data management, playing a crucial role in organizing and managing the data. The combination of date, time, and time zone in databases enables tasks such as scheduling, historical tracking, compliance auditing, and temporal querying.
Insert the Date, Time, and Time Zone
Step 1: Import the necessary modules
Stary by importing the required functionalities of the SQLAlchemy module and DateTime module
form datetime import datetime
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Step 2: Create the Base class
Create a Base class using the declarative_base(). It serves as the parent class for the model class.
base_class=declarative_base()
Step 3: Establishing the connection
Establish the connection to the database using the create_engine() constructor
Syntax: engine= create_engine("database :// user:password@host:port/database name")
If your using MySql the syntax will be
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://user:pass@host:3306/database name")
pymysql: is a database API module for connecting to MySQL server using the SQLAlchemy. We need to install this module also in order to connect to the MySQL server using the pip command
pip install pymysql
Step 4: Creating a model class
Create a model class that represents the database table. The model class should Inherit the base class and the model class should have one mandatory attribute called __tablename__ which represents the name of the table.
class model_class(base_class):
__tablename__="name of table"
//Attributes
Step 5: Create a Session
Create a session object using the sessionmaker() method and bind it to the database engine
sessionMaker=sessionmaker(bind=engine)
Step 6: Creating a database table
In these step we are creating the database table by using the create_all method. If the database already contains the table no need of these sept
base_class.metadata.create_all(engine)
Step 7: Creating the datetime object:
Create the datetime class object for the required datetime or today’s datetime with the specified time zone. Here we are using the datetime module of Python in order to get the date, time.
dateTimeObj=datetime.datetime(year, month, day, hour, minute, second, tzinfo)
Here tzinfo specifies the time zone which can be obtained from pytz module of the python
Step 8: Creating Table rows (Creating Instance model class)
Create the instance of a Model class with the appropriate attribute values
modelClassObject = model_class(attribute values)
Step 9: Instances of Model
Add the instances of your model class to the session using the add() method(inserting data to the table)
session.add(modelClassObject)
Step 10: Committing Changes
Once you have added the data to the session, commit the changes to the database.
session.commit()
Note: If you’re not using the commit method the changes will not affect the database.
Step 11: Closing Connection
Close the session by using the close().
session.close()
Example: Creating Instances of the SQLAlchemy DateTime Class
In the given example, we create three instances of the DateTime class, each representing a specific date and time with their respective time zones. The first object represents the date and time ‘2020-05-23 10:30:30’ in the time zone ‘Europe/London’. The second object represents the date and time ‘2022-12-30 18:30:30’ in the time zone ‘America/New_York’. The third object represents the current date and time with the time zone set to the current time zone. These instances are then utilized to insert employee data into a table.
Python3
import datetime
import pytz
from sqlalchemy import *
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
base_class = declarative_base()
class Employee(base_class):
__tablename__ = 'employee'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String(50))
age = Column(Integer)
salary = Column(DECIMAL)
hire_date = Column(Date)
hire_time = Column(Time)
time_zone = Column(String(500))
Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
session = Session()
print("connection established...")
base_class.metadata.create_all(engine)
print("table created...")
Obj1 = datetime.datetime(year=2020, month=5, day=23, hour=10,
minute=30, second=30, tzinfo=pytz.timezone("Europe/London"))
Obj2 = datetime.datetime(year=2022, month=12, day=30, hour=18,
minute=30, second=30, tzinfo=pytz.timezone("America/New_York"))
Obj3 = datetime.datetime.now()
todayDate = Obj3.date()
todayTime = Obj3.time()
currentTimeZone = current_timezone = pytz.timezone(
pytz.country_timezones['IN'][0])
print("currnet time zone=", currentTimeZone)
employee1 = Employee(id=1, name="Alice", age=25, salary=50000,
hire_date=Obj1.date(), hire_time=Obj1.time(), time_zone=Obj1.tzinfo)
employee2 = Employee(id=2, name="Bod", age=34, salary=55000,
hire_date=todayDate, hire_time=todayTime, time_zone=Obj1.tzinfo)
employee3 = Employee(id=3, name="Dhoni", age=54, salary=75000,
hire_date=Obj2.date(), hire_time=Obj2.time(), time_zone=Obj2.tzinfo)
employee4 = Employee(id=4, name="Kohli", age=55, salary=150000,
hire_date=todayDate, hire_time=todayTime, time_zone=Obj2.tzinfo)
employee5 = Employee(id=5, name="Raju", age=35, salary=65000, hire_date=Obj1.date(
), hire_time=Obj1.time(), time_zone=currentTimeZone)
employee6 = Employee(id=6, name="Ravi", age=45, salary=25000,
hire_date=todayDate, hire_time=todayTime, time_zone=currentTimeZone)
session.add_all([employee1, employee2, employee3,
employee4, employee5, employee6])
print("successfully data added to session")
session.commit()
print("successfully inserted data")
session.close()
print("DB connection closed")
|
Employee Table:
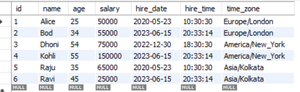
Employee Table
Updating Date, Time, and Time Zone in SQLAlchemy
In SQLAlchemy we can update the DATE and TIME by using the query() method and update() method
By using query()
Please refer SQLAlchemy ORM query() article to know about the query() method.
In this example, we start by creating an engine and session to connect to the database. Then, we retrieve data for employees whose time zone is ‘Europe/London‘ and whose ‘hire_date’ is not equal to today’s date using the query() and filter() methods. Next, we update their ‘hire_date’ and ‘hire_time’ fields to the present date and time.
Python3
import datetime
import pytz
from sqlalchemy import *
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
base_class = declarative_base()
class Employee(base_class):
__tablename__ = 'employee'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String(50))
age = Column(Integer)
salary = Column(DECIMAL)
hire_date = Column(Date)
hire_time = Column(Time)
time_zone = Column(String(500))
Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
session = Session()
dateTimeObj = datetime.datetime.now()
timeZone = pytz.timezone("Europe/London")
date = dateTimeObj.date()
time = dateTimeObj.time()
print(timeZone, date, time)
employeeDate = session.query(Employee).filter(
and_(Employee.time_zone == timeZone, Employee.hire_date != date)).all()
for employee in employeeDate:
employee.hire_date = date
employee.hire_time = time
session.commit()
session.close()
|
After Update:
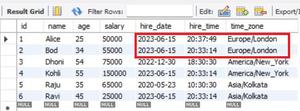
By using update():
update():, It allows you to modify existing records in a database table. It constructs an SQL UPDATE statement to change the values of one or more columns in the table based on specified criteria.
Syntax: update(tableName).where(condition).values(col1=newValue,col2=newValue..)
In the following example, we are performing an update operation to increase the salary of employees by 25000 where their time zone matches the current time zone.
Python3
timeZone=pytz.timezone("Asia/Kolkata")
query=update(Employee).where(Employee.time_zone==timeZone).values(salary=Employee.salary+25000)
session.execute(query)
session.commit()
session.close()
|
After Update:
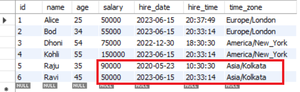
After Updating Employee Table
Filtering Date, Time, and Time Zone in SQLAlchemy
By using query() and filter()
In the following example, we are retrieving the data of all employees whose time zone matches the current time zone or whose hire date is equal to 2022-12-30.
Python3
dateTimeObj = datetime.datetime(year=2022, month=12, day=30)
date = dateTimeObj.date()
currentTimeZone = pytz.timezone("Asia/Kolkata")
empData = session.query(Employee).filter(
or_(Employee.time_zone == currentTimeZone, Employee.hire_date == date)).all()
for emp in empData:
print(emp.id, emp.name, emp.hire_date, emp.time_zone)
session.close()
|
Output:
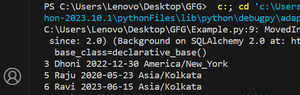
Query output
3 Dhoni 2022-12-30 America/New_York
5 Raju 2020-05-23 Asia/Kolkata
6 Ravi 2023-06-15 Asia/Kolkata
By using the select() and where()
In the following example, we are retrieving the data of employees whose age is greater than or equal to 40 and whose time zone is either Asia/Kolkata or America/New_York.
Python3
timeZone1 = pytz.timezone("Asia/Kolkata")
timeZone2 = pytz.timezone("America/New_york")
statement = select(Employee).where(and_(Employee.age >= 40, or_(
Employee.time_zone == timeZone1, Employee.time_zone == timeZone2)))
result = session.execute(statement).fetchall()
print("By using the select() and where()")
for emp in result:
print(emp[0].id, emp[0].name, emp[0].age, emp[0].salary)
session.close()
|
Output:
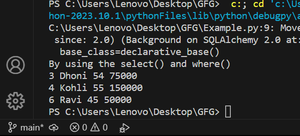
select output
3 Dhoni 54 75000
4 Kohli 55 150000
6 Ravi 45 50000
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...