Count of groups among N people having only one leader in each group
Last Updated :
26 Feb, 2023
Given N number of people, the task is to count the number of ways to form groups of size? N where, in each group, the first element of the group is the leader of the group.
Note:
- Groups with same people having different leaders are treated as a different group. For Example: The group {1, 2, 3} and {2, 1, 3} are treated as different group as they have different leader 1 and 2 respectively.
- Groups with same leader having same people are treated as a same group. For Example: The groups {1, 3, 2} and {1, 2, 3} are treated as same group as they have same leader and same people.
- The answer can be very large, take modulo to (1e9+7).
Examples:
Input: N = 3
Output: 12
Explanation:
Total Groups with leaders are:
Groups with Leader 1:
1. {1}
2. {1, 2}
3. {1, 3}
4. {1, 2, 3}
Groups with Leader 2:
5. {2}
6. {2, 1}
7. {2, 3}
8. {2, 1, 3}
Groups with Leader 3:
9. {3}
10. {3, 1}
11. {3, 2}
12. {3, 1, 2}
Input: N = 5
Output: 80
Approach: This problem can be solved using the concept of Binomial coefficients and modular exponentiation. Below are the observations to this problem statement:
- The number of ways to select one leader among N persons is C(N, 1).
- For every leader we can select a group of size K where 0 ? K ? N-1 to make the possible number of grouping.
- So the total number ways is given by the product of N and the summation of selection K elements from the remaining (N – 1) elements as:
Total Ways = 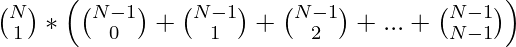
By using Binomial Theorem, the summation of the Binomial Coefficient can be written as:
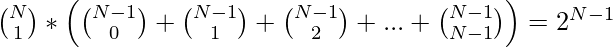
Therefore the number of ways of selecting groups having only one leader is
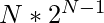
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long mod = 1000000007;
int exponentMod(int A, int B)
{
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
long long y;
if (B % 2 == 0) {
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
else {
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1)
% mod)
% mod;
}
return (int)((y + mod) % mod);
}
void countWays(int N)
{
long long select = exponentMod(2,
N - 1);
long long ways
= ((N % mod)
* (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
cout << ways;
}
int main()
{
int N = 5;
countWays(N);
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static long mod = 1000000007;
static int exponentMod(int A, int B)
{
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
long y;
if (B % 2 == 0)
{
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
else
{
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1) %
mod) % mod;
}
return (int)((y + mod) % mod);
}
static void countWays(int N)
{
long select = exponentMod(2, N - 1);
long ways = ((N % mod) * (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
System.out.print(ways);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5;
countWays(N);
}
}
|
Python3
mod = 1000000007
def exponentMod(A, B):
if (A == 0):
return 0;
if (B == 0):
return 1;
y = 0;
if (B % 2 == 0):
y = exponentMod(A, B // 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
else:
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1) %
mod) % mod;
return ((y + mod) % mod);
def countWays(N):
select = exponentMod(2, N - 1);
ways = ((N % mod) * (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
print(ways)
if __name__=='__main__':
N = 5;
countWays(N);
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static long mod = 1000000007;
static int exponentMod(int A, int B)
{
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
long y;
if (B % 2 == 0)
{
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
else
{
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1) %
mod) % mod;
}
return (int)((y + mod) % mod);
}
static void countWays(int N)
{
long select = exponentMod(2, N - 1);
long ways = ((N % mod) * (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
Console.Write(ways);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5;
countWays(N);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let mod = 1000000007;
function exponentMod(A, B)
{
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
let y;
if (B % 2 == 0) {
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
else {
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1)
% mod)
% mod;
}
return ((y + mod) % mod);
}
function countWays(N)
{
let select = exponentMod(2,
N - 1);
let ways
= ((N % mod)
* (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
document.write(ways);
}
let N = 5;
countWays(N);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...