Count the number of non-reachable nodes
Last Updated :
30 Nov, 2023
Given an undirected graph and a set of vertices, we have to count the number of non-reachable nodes from the given head node using a depth-first search.
Consider below undirected graph with two disconnected components:
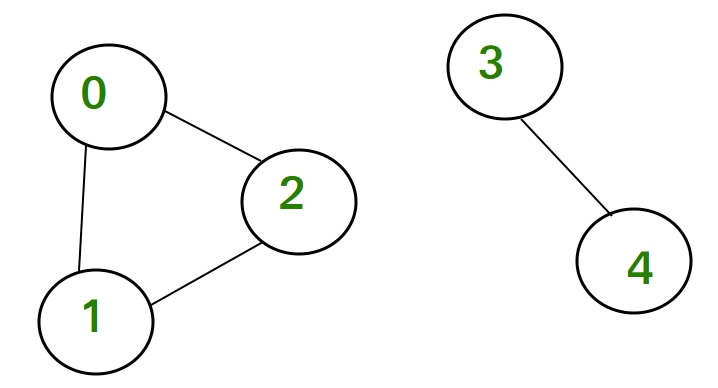
In this graph, if we consider 0 as a head node, then the node 0, 1 and 2 are reachable. We mark all the reachable nodes as visited. All those nodes which are not marked as visited i.e, node 3 and 4 are non-reachable nodes. Hence their count is 2.
Example:
Input : 5
0 1
0 2
1 2
3 4
Output : 2
Here we use BFS:
First we get the src node from user then call for bfs on it for marking all node connected in that component to mark as visited and then calculate the number of unvisited nodes and return the count of it.
Algorithm for
Input : 5
0 1
0 2
1 2
3 4
Output : 2
lookes like. for 1
vector<bool>vis(n,0);
push(1).
while loop run till queue is not empty.
1. mark 1 as visited while pop vis[1]=1.
2. then push all node that are unvisited till now from adjacency list of 1.
3. do this till queue it empty.
after break of while,
count the number of unvisited node from visited vector and return count.
Code implementation :
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int countNotReachusingBFS(vector<int> adj[], int src, int n)
{
vector<bool> vis(n, 0);
queue<int> pq;
pq.push(src);
while (!pq.empty()) {
int start = pq.front();
pq.pop();
vis[start] = 1;
for (auto it : adj[start]) {
if (vis[it])
continue;
else {
pq.push(it);
}
}
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!vis[i])
++cnt;
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
int n = 8;
vector<vector<int> > graph{ { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 }, { 6, 7 } };
vector<int> adj[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++) {
adj[graph[i][0]].push_back(graph[i][1]);
adj[graph[i][1]].push_back(graph[i][0]);
}
cout << "the number of node that are not reachable "
"from 1 are :"
<< endl;
cout << countNotReachusingBFS(adj, 1, n) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static int countNotReachUsingBFS(ArrayList<Integer>[] adj, int src, int n) {
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(src);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int node = queue.poll();
vis[node] = true;
for (int it : adj[node]) {
if (!vis[it]) {
queue.add(it);
}
}
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 8;
ArrayList<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
int[][] graph = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {6, 7} };
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
int from = graph[i][0];
int to = graph[i][1];
adj[from].add(to);
adj[to].add(from);
}
System.out.println("The number of nodes that are not reachable from 1 are:");
System.out.println(countNotReachUsingBFS(adj, 1, n));
}
}
|
Python
from collections import deque
def countNotReachusingBFS(adj, src, n):
vis = [False] * n
pq = deque()
pq.append(src)
while pq:
start = pq.popleft()
vis[start] = True
for it in adj[start]:
if vis[it]:
continue
else:
pq.append(it)
cnt = 0
for i in range(n):
if not vis[i]:
cnt += 1
return cnt
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 8
graph = [[0, 1], [0, 2],
[1, 2], [3, 4],
[4, 5], [6, 7]]
adj = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(len(graph)):
adj[graph[i][0]].append(graph[i][1])
adj[graph[i][1]].append(graph[i][0])
print("the number of node that are not reachable from 1 are :")
print(countNotReachusingBFS(adj, 1, n))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static int CountNotReachableUsingBFS(List<int>[] adj, int src, int n)
{
bool[] vis = new bool[n];
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
queue.Enqueue(src);
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
int start = queue.Dequeue();
vis[start] = true;
foreach (var neighbor in adj[start])
{
if (!vis[neighbor])
{
queue.Enqueue(neighbor);
}
}
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (!vis[i])
count++;
}
return count;
}
static void Main()
{
int n = 8;
List<int>[] adj = new List<int>[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
int[,] graph = {
{ 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 }, { 6, 7 }
};
for (int i = 0; i < graph.GetLength(0); i++)
{
adj[graph[i, 0]].Add(graph[i, 1]);
adj[graph[i, 1]].Add(graph[i, 0]);
}
Console.WriteLine("The number of nodes that are not reachable from 1 are:");
Console.WriteLine(CountNotReachableUsingBFS(adj, 1, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
function countNotReachUsingBFS(adj, src, n) {
const vis = new Array(n).fill(false);
const queue = [];
queue.push(src);
while (queue.length > 0) {
const node = queue.shift();
vis[node] = true;
for (const it of adj[node]) {
if (!vis[it]) {
queue.push(it);
}
}
}
let cnt = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
const n = 8;
const adj = new Array(n).fill().map(() => []);
const graph = [
[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 2], [3, 4], [4, 5], [6, 7]
];
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
const from = graph[i][0];
const to = graph[i][1];
adj[from].push(to);
adj[to].push(from);
}
console.log("The number of nodes that are not reachable from 1 are:");
console.log(countNotReachUsingBFS(adj, 1, n));
|
Output
the number of node that are not reachable from 1 are :
5
Complexity Analysis :
Time Complexity: O(V+E).
Auxiliary Space: O(V).
In the below implementation, DFS is used. We do DFS from a given source. Since the given graph is undirected, all the vertices that belong to the disconnected component are non-reachable nodes. We use the visited array for this purpose, the array which is used to keep track of non-visited vertices in DFS. In DFS, if we start from the head node it will mark all the nodes connected to the head node as visited. Then after traversing the graph, we count the number of nodes that are not marked as visited from the head node.
Implementation:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int V;
list<int>* adj;
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
public:
Graph(int V);
void addEdge(int v, int w);
int countNotReach(int v);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
adj[w].push_back(v);
}
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
visited[v] = true;
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
int Graph::countNotReach(int v)
{
bool* visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
DFSUtil(v, visited);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false)
count++;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
Graph g(8);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 5);
g.addEdge(6, 7);
cout << g.countNotReach(2);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
class Graph{
public int V;
public ArrayList []adj;
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
}
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w);
adj[w].add(v);
}
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean []visited)
{
visited[v] = true;
for(int i : (ArrayList<Integer>)adj[v])
{
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
int countNotReach(int v)
{
boolean []visited = new boolean[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
DFSUtil(v, visited);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
count++;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String []args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(8);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 5);
g.addEdge(6, 7);
System.out.print(g.countNotReach(2));
}
}
|
Python3
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w)
self.adj[w].append(v)
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
visited[v] = True
i = self.adj[v][0]
for i in self.adj[v]:
if (not visited[i]):
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
def countNotReach(self, v):
visited = [False] * self.V
self.DFSUtil(v, visited)
count = 0
for i in range(self.V):
if (visited[i] == False):
count += 1
return count
if __name__ == '__main__':
g = Graph(8)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(3, 4)
g.addEdge(4, 5)
g.addEdge(6, 7)
print(g.countNotReach(2))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Graph{
public int V;
public ArrayList []adj;
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
}
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);
adj[w].Add(v);
}
void DFSUtil(int v, bool []visited)
{
visited[v] = true;
foreach(int i in (ArrayList)adj[v])
{
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
int countNotReach(int v)
{
bool []visited = new bool[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
DFSUtil(v, visited);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
count++;
}
return count;
}
static void Main(string []args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(8);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 5);
g.addEdge(6, 7);
Console.Write(g.countNotReach(2));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let V = 8;
let adj = [];
for(let i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj.push([]);
}
function addEdge(v, w)
{
adj[v].push(w);
adj[w].push(v);
}
function DFSUtil(v, visited)
{
visited[v] = true;
for(let i = 0; i < adj[v].length; i++)
{
if (!visited[adj[v][i]])
DFSUtil(adj[v][i], visited);
}
}
function countNotReach(v)
{
let visited = new Array(V);
for(let i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
DFSUtil(v, visited);
let count = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
count++;
}
return count;
}
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(3, 4);
addEdge(4, 5);
addEdge(6, 7);
document.write(countNotReach(2));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(V+E)
Auxiliary Space: O(V)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...