Convert JSON data Into a Custom Python Object
Last Updated :
16 Dec, 2021
Let us see how to convert JSON data into a custom object in Python. Converting JSON data into a custom python object is also known as decoding or deserializing JSON data. To decode JSON data we can make use of the json.loads(), json.load() method and the object_hook parameter. The object_hook parameter is used so that, when we execute json.loads(), the return value of object_hook will be used instead of the default dict value.We can also implement custom decoders using this.
Example 1 :
Python3
import json
from collections import namedtuple
data = '{"name" : "Geek", "id" : 1, "location" : "Mumbai"}'
x = json.loads(data, object_hook =
lambda d : namedtuple('X', d.keys())
(*d.values()))
print(x.name, x.id, x.location)
|
Output :
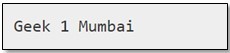
As we can see in the above example, the namedtuple is a class, under the collections module. It contains keys that are mapped to some values. In this case, we can access the elements using keys and indexes. We can also create a custom decoder function, in which we can convert dict into a custom Python type and pass the value to the object_hook parameter which is illustrated in the next example.
Example 2 :
Python3
import json
from collections import namedtuple
def customDecoder(geekDict):
return namedtuple('X', geekDict.keys())(*geekDict.values())
geekJsonData = '{"name" : "GeekCustomDecoder", "id" : 2, "location" : "Pune"}'
x = json.loads(geekJsonData, object_hook = customDecoder)
print(x.name, x.id, x.location)
|
Output :

We can also use SimpleNamespace class from the types module as the container for JSON objects. Advantages of a SimpleNamespace solution over a namedtuple solution: –
- It is faster because it does not create a class for each object.
- It is shorter and simpler.
Example 3 :
Python3
import json
try:
from types import SimpleNamespace as Namespace
except ImportError:
from argparse import Namespace
data = '{"name" : "GeekNamespace", "id" : 3, "location" : "Bangalore"}'
x = json.loads(data, object_hook = lambda d : Namespace(**d))
print(x.name, x.id, x.location)
|
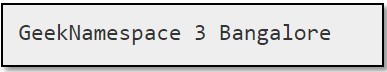
Output :
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...