Compiling with g++
Last Updated :
08 Apr, 2024
g++ command is a GNU c++ compiler invocation command, which is used for preprocessing, compilation, assembly and linking of source code to generate an executable file. The different “options” of g++ command allow us to stop this process at the intermediate stage.
- Check g++ compiler version information:
g++ --version

- Compile a CPP file to generate executable target file: g++ file_name command is used to compile and create an executable file a.out (default target name).
Example: Given a simple program to print “Hello Geek” on standard output with file name hello.cpp
CPP
// hello.cpp file
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello Geek\n";
return 0;
}
g++ hello.cpp

This compiles and links hello.cpp to produce a default target executable file a.out in present working directory. To run this program, type ./a.out where ./ represents present working directory and a.out is the executable target file.
./a.out

- g++ -S file_name is used to only compile the file_name and not assembling or linking. It will generate a file_name.s assembly source file.
Example:
g++ -S hello.cpp

- g++ -c file_name is used to only compile and assemble the file_name and not link the object code to produce executable file. It will generate a file_name.o object code file in present working directory.
Example:
g++ -c hello.cpp

- g++ -o target_name file_name: Compiles and links file_name and generates executable target file with target_name (or a.out by default).
Example:
g++ -o main.exe hello.cpp

- Compile and link multiple files: When -c flag is used, it invokes the compiler stage which translates source code to object code.When -o flag is used it links object code to create the executable file from file_name.o to a.out(default), multiples files may be passed together as arguments.
Example:
CPP
// hello.cpp file
#include "helloWorld.h"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello Geek\n";
helloWorld();
return 0;
}
CPP
// helloWorld.cpp file
#include <iostream>
void helloWorld()
{
std::cout << "Hello World\n";
}
CPP
// helloWorld.h file
void helloWorld();
g++ -c helloWorld.cpp hello.cpp
- It compiles and creates object code for the files helloWorld.cpp and hello.cpp to helloWorld.o and hello.o respectively.
g++ -o main.exe helloWorld.o hello.o
- It links the object codes helloWorld.o and hello.o to create an executable file main.exe
./main.exe
- It runs the executable file main.exe

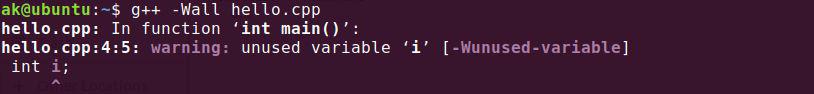
- g++ -Wall file_name: It prints all warning messages that are generated during compilation of file_name.
Example:
CPP
// hello.cpp file
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int i;
std::cout << "Hello Geek\n";
return 0;
}
g++ -Wall hello.cpp
- File extension for c++ files can be .cpp or .c++ , .cpp is widely used but .cpp and .c++ are exactly same and all above functionalities are same for .c++ too

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...