Competitive Benchmarking in product management
Last Updated :
30 Jan, 2024
Competitive Benchmarking in product management involves assessing the strengths and weaknesses of companies offering similar products, which is essential for product managers to make informed decisions about product pricing, marketing, and sales strategies.

competitive benchmarking
What is Competitive Benchmarking?

What is Competitive Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking in Product Management is used by corporations as a strategic management and market analysis tool to assess how well their operations, procedures, goods, and services perform in comparison to those of their main rivals or market leaders. To increase the business’s overall competitiveness, the objective is to identify the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Companies can improve their competitiveness by doing competitive benchmarking to better understand their market position, establish reasonable performance targets, and make well-informed strategic choices. Achieving long-term success, being competitive and adjusting to changes in the industry all depend on this process.
Importance of Competitive Benchmarking:
Here are some points that will cover the importance of competitive benchmarking:

importance of competitive benchmarking
- Assessment of Performance: It enables businesses to evaluate their own performance objectively in comparison to competitors and industry standards.
- Planning Strategically: It provides insights into the strengths and weaknesses of competitors and market trends, which helps in the development of successful business strategies.
- Creating Reasonable Objectives: It allows for the establishment of reasonable and attainable performance targets by taking into account the accomplishments of rivals and industry benchmarks.
- Best Practices and Innovation: It finds best practices employed by rivals and industry leaders, encouraging an innovative and continuous improvement culture.
- Positioning in the Market: It gives information about a company’s place in the market in comparison to its rivals.
- Optimization of Resources: It allows for the effective use of resources by concentrating on areas that have a direct bearing on competitiveness.
- Constant Enhancement: It promotes an organizational culture of ongoing improvement.
Example of Competitive Benchmarking:
- The smartphone maker ABC Tech used competitive benchmarking to evaluate its place in the market.
- After identifying competitors XYZ Communications and WXY Mobile, ABC examined three important metrics: customer satisfaction, pricing and product features.
- ABC found that XYZ had a better pricing strategy and that WXY was more innovative. By putting these findings into practice, ABC improved the characteristics of their products and changed their prices, which raised consumer happiness.
- Ongoing observation guarantees that ABC stays competitive and adjusts to changes in the industry. With the help of this benchmarking method, ABC is better able to set itself apart from rivals, position itself strategically and achieve long-term success in the rapidly evolving smartphone industry.
- Assessment of Performance: Brands can evaluate their own performance against major competitors in a neutral way by using a competitive benchmarking tool. It offers a thorough understanding of the business’s advantages and disadvantages in every aspect.
- Making Strategic Decisions: It gives insights into market dynamics, rival strategies and industry trends to assist brands in making well-informed strategic decisions. To keep ahead of the competition and adjust to changes, you need to know this knowledge.
- Creating Realistic Objectives: It helps in the establishment of reasonable and attainable performance targets based on rivals’ and industry’s performance as benchmarks. This guarantees that objectives are in line with what the market expects.
- Risk Control: It helps in recognizing possible dangers and hazards in the industry. Brands can reduce the risks associated with changes in the industry by proactively addressing difficulties and learning from the experiences of competitors.
- Optimization of Resources: It encourages the effective use of resources by concentrating on areas that have an immediate impact on competitiveness. Brands can cut costs by giving top priority to strategies that have demonstrated effectiveness in competition.
- Adjusting to Shifts in the Industry: It makes it easier to adjust to shifting market conditions and industry changes. By keeping an eye on the actions of their competitors and modifying their strategy accordingly, brands may remain flexible and adaptable.
Easy 4-step process for Competitive Benchmarking:
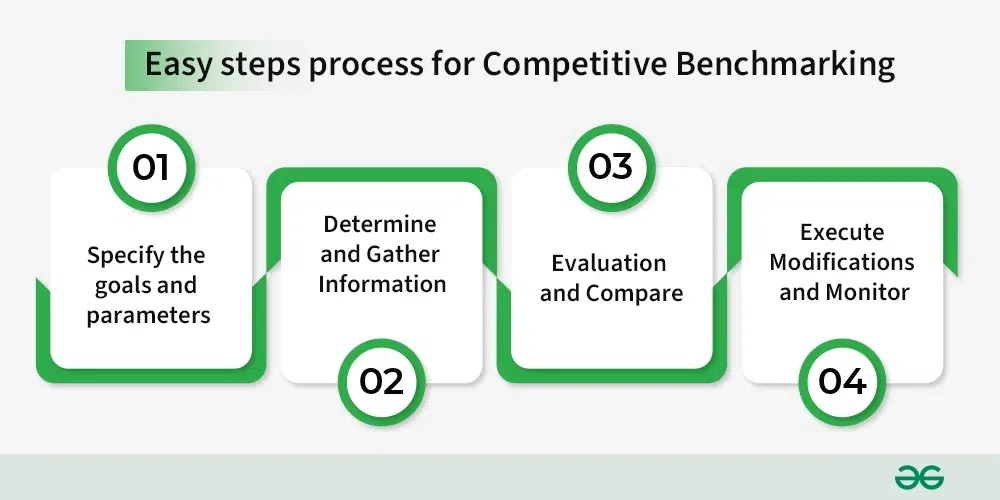
Easy 4-step process for Competitive Benchmarking
- Specify the goals and parameters: Clearly state what you hope to achieve by using competitive benchmarking. Establish the parameters of your benchmarking study, such as the rivals you wish to examine and the KPIs you plan to utilize for assessment.
- Determine and Gather Information: Determine who your main rivals are and obtain pertinent information about their achievements. To provide a foundation for comparison, gather internal data about your own performance in the same areas.
- Evaluation and Compare: Examine the gathered data and compare your performance with that of your rivals. Examine competitor’s strategies and look for best practices. Recognize the factors that lead to their performance in the areas where you are benchmarking.
- Execute Modifications and Monitor: Make adjustments or enhancements where your performance needs work based on your analysis. Review the benchmarking process on a regular basis to stay updated on changes in the competitive environment and to continue making improvements.
Benefits of Competitive Benchmarking:

Benefits of Competitive Benchmarking
- Generating Well-Informed Decisions: Businesses can use benchmarking to make strategic and well-informed decisions by gaining useful insights into market dynamics, rival strategies and industry trends.
- Establishing and Measuring Objectives: It helps in establishing realistic and attainable performance targets based on the accomplishments of rivals and industry benchmarks. It offers an objective standard for assessing achievement.
- Planning Strategically: It helps in developing winning business plans by analyzing market trends, rival’s advantages and disadvantages and client expectations.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: It creates an environment where businesses are encouraged to evaluate performance on a frequent basis, identify areas that need development and carry out continual enhancements.
- Increasing Stakeholder Trust: Stakeholder trust can be increased by exhibiting a commitment to benchmarking and improvement. This is because it demonstrates the company’s commitment to maintaining its competitiveness to consumers, employees and investors.
What Are Different Types of Benchmarking?

Different Types of Benchmarking
- Internal Benchmarking: It involves evaluating how various divisions or departments of the same company perform in terms of procedures, practices and performance. The objective is to find and communicate best practices.
- Functional Benchmarking: It compares certain corporate operations, even those that are not direct competitors with those of other companies. With this kind of benchmarking, best practices in a certain business function are examined.
- Strategic Benchmarking: It investigates the long-term objectives and plans of high-achieving companies, regardless of the industry in which they are active. Adopting strategic ideas that can advance overall success is the goal.
- International Benchmarking: It evaluates an organization’s performance and methods against those of its international competitors. This is especially important for multinational corporations or those thinking about going global.
- Process Benchmarking: It focuses on particular organizational processes. It helps in determining and putting into practice ways to increase the effectiveness and productivity of specific company operations.
- Energy Benchmarking: It evaluates an organization’s energy use and efficiency in comparison to standard practices or recommended procedures. For environmental projects and sustainability, this kind is necessary.
- Performance Benchmarking: It includes comparing key performance indicators (KPIs) between various companies. Companies can assess how they are doing against the standards of the industry with help of this kind of benchmarking.
- Competitive Benchmarking: It compares the performance of the company against that of its direct competitors. It helps in figuring out relative market positioning and highlighting areas in need of development.
How to choose competitors to Benchmark against?
- Comparable Position in the Market: Select rivals who serve a comparable consumer and compete in a comparable market space. In terms of goods, services and target market, this guarantees accuracy.
- Geographic Range: Benchmarking versus local or regional competitors may have greater significance if the majority of your business’s operations are in the region.
- Offerings of Goods and Services: Choose rivals who provide comparable goods or services. This guarantees a comparison of features, procedures and consumer expectations that is more accurate.
- Dimensions and Range: It is possible to compare resources, capabilities and operational efficiency more precisely by benchmarking against businesses of similar size.
- Customer Viewpoint: Think of rivals who are viewed similarly by the public. Comparing your brand against less priced rivals might not be as useful if it is positioned as an elite service.
- Long-Term Success: Examine rivals who have proven to be stable and successful over the long run. Taking a look at companies that have a track record of success might help you understand sustainable methods.
- Industry Patterns: Think about the general trends in your sector. To remain relevant and competitive, set benchmarks against competitors who are embracing or leading these developments.
- Intensity of Competition: Select rivals who are regarded as important participants in your market or sector.
Key methods of Competitive Benchmarking & Analysis:
- Gathering of Data: Compile extensive information about the performance of competitors and your own business.
- KPIs or key performance indicators: The key performance indicators that is used for benchmarking should be identified and defined.
- Customer feedback and surveys: To find out how customers view your goods and services in comparison to those of your rivals, use customer surveys and feedback systems.
- Market Analysis: To learn more about market trends, new technology and customer behavior, conduct market research.
- Frameworks for Competitor Analysis: Use well-known competitor analysis frameworks to systematically evaluate the competitive environment and identify areas that require development, such as Porter’s Five Forces or SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats).
- Industry Standards & Benchmarks: Evaluate your company’s performance in comparison to standard practices and benchmarks.
Competitive Benchmarking vs. Competitive Analysis:

Competitive Benchmarking vs. Competitive Analysis
|
It focuses on evaluating a business’s offerings, operational procedures or performance indicators with those of its rivals or the best companies in the sector.
|
It includes an in-depth examination of the competitive environment, taking into account rivals, market trends and industry characteristics.
|
|
It wants to identify spots where the business may enhance performance and implement best practices from industry leaders.
|
It aims to learn about the competitive landscape, the general state of the market and any prospective advantages or disadvantages.
|
|
It supports strategic decision-making and ongoing development by providing insights from successful rivals.
|
By locating possible fields, market gaps and points of differentiation, it assists in strategic planning.
|
|
As a result of the gaps and possibilities that have been identified, the outcome frequently contains clear, practical insights and recommendations for change.
|
A strategic awareness of the whole competitive environment and insights that guide business initiatives beyond short-term performance are the outcome of this.
|
How can Competitive Benchmarking go wrong?
Some important points to remember while doing competitive benchmarking:
- Inaccurate or incomplete data: Inaccurate, out-of-date or missing data can cause problems in comparisons and conclusions.
- Not appropriate Benchmark Choice: Inappropriate benchmark selection can lead to irrelevant and deceptive comparisons, such as competitors with drastically different sizes, target markets or business models.
- Inability to Establish Goals Clearly: The benchmarking process may lose focus in the absence of precise goals and the learned information may not be useful in supporting strategic decision-making.
- Too much emphasis on metrics: A limited understanding of competitiveness may result from relying exclusively on quantitative indicators and ignoring qualitative aspects. Although they might be disregarded, qualitative factors like brand perception and customer experience are crucial.
- Disregarding Industry Dynamics: Regulatory frameworks, macroeconomic variables and industry-specific dynamics can all be ignored when developing strategies that are inappropriate to the outside world of business.
- Short-term Priority: Neglecting long-term strategic concerns might result from placing too much attention on short-term performance indicators.
Conclusion: Competitive Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking in product management is a powerful strategic instrument that gives companies an organized method to assess how they are doing in comparison to competitors and industry norms. The procedure involves choosing relevant benchmarks with care, analyzing data in-depth and determining best practices. So, it’s important to approach benchmarking with an understanding of the goals and to make sure the data is current and correct. Competitive benchmarking is full with opportunity, but it needs to be executed carefully, quickly and appropriately.
FAQs On Competitive Benchmarking:
1. What are the different types of benchmarking?
- Internal Benchmarking
- Functional Benchmarking
- Strategic Benchmarking
- International Benchmarking
2. What is the difference between strategic benchmarking and competitive benchmarking?
Competitive benchmarking uses methods like reverse engineering to obtain data about direct competitors. Competitive benchmarking with a focus on organisational transformation and strategic action is known as strategic benchmarking.
3. What are the 4 levels of benchmarking?
Internal, external, performance, and practice benchmarking are the four primary categories of benchmarking.
4. What is competitive benchmarking examples?
The smartphone maker ABC Tech used competitive benchmarking to evaluate its place in the market.
5. What is Competitive Benchmarking?
Competitive benchmarking in Product Management is used by corporations as a strategic management and market analysis tool to assess how well their operations, procedures, goods, and services perform in comparison to those of their main rivals or market leaders.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...