Check if digit cube limit of an integer arrives at fixed point or a limit cycle
Last Updated :
14 Jul, 2021
Given an integer N, the task is to check if the Digit Cube limit of an integer arrives at a fixed point or in a limit cycle.
A Digit Cube Limit is a number which repeatedly arrives at a point if its value is computed as the sum of cubes of its digits, i.e. they have the following properties:
- Arrive at a fixed point if it is an Armstrong number.
- Arrive at a limit cycle if it is repeating in a cycle.
Examples:
Input: N = 3
Output: Reached to fixed point 153
Explanation:
F(3) = 3 * 3 * 3 = 27
F(27) = 2*2*2 + 7*7*7 = 351
F(351) = 3*3*3 + 5*5*5 + 1*1*1 = 153
F(153) = 1*1*1 + 5*5*5 + 3*3*3 = 153
Since a fixed point(= 153) was obtained, which is an Armstrong number of order 3. Below is the illustration:

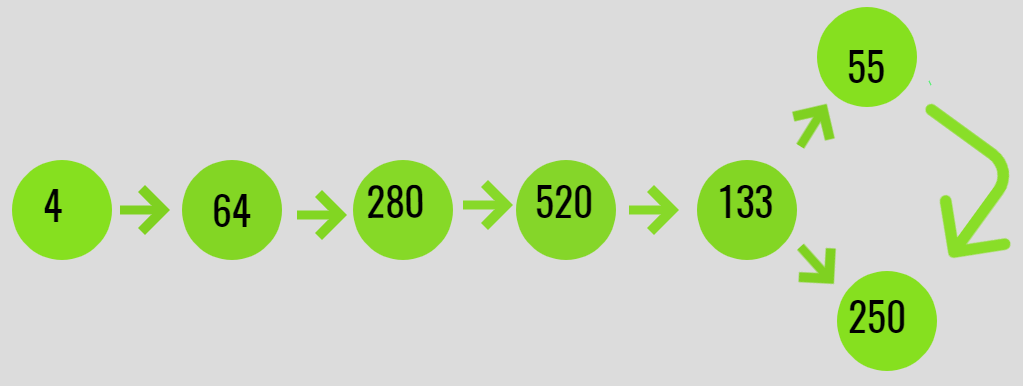
Input: N = 4
Output: Arrived at cycle
Explanation:
F(4) = 4 * 4 * 4 = 64
F(64) = 6 * 6 * 6 + 4 * 4 * 4 = 280
F(280) = 2 * 2 * 2 + 8 * 8 * 8 + 0 * 0 * 0 = 520
F(520) = 5 * 5 * 5 + 2 * 2 * 2 + 0*0*0 = 133
F(133) = 1*1*1 + 3*3*3 + 3*3*3 = 55
F(55) = 5*5*5 + 5*5*5 = 250
F(250) = 5*5*5 + 2*2*2 + 0*0*0 = 133
A cycle between
133 -> 55 -> 250 -> 133 is obtained.
Below is the illustration of the same:
Approach: Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create a hashMap to store the sum of the cube of digits of the number while iteration.
- Iterate for the next values for the sum of cube of digits of a number and Check if the next sum of the cube of digits is already present in the hashMap or not.
- If the number is already in the hash-map then, check if the number is an Armstrong number or not. If found to be true, then the number reaches a fixed point.
- Otherwise, If the number is not Armstrong number then continue.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define limit 1000000000
using namespace std;
long long F(long long N)
{
string str = to_string(N);
long long sum = 0;
for (long long i = 0;
i < str.size(); i++) {
long long val
= int(str[i] - '0');
sum += val * val * val;
}
return sum;
}
long long findDestination(long long N)
{
set<long long> s;
long long prev = N, next;
s.insert(N);
while (N <= limit) {
next = F(N);
auto it = s.find(next);
if (it != s.end()) {
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.insert(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
void digitCubeLimit(long long N)
{
if (N < 0)
cout << "N cannot be negative\n";
else {
long long ans
= findDestination(N);
if (ans > limit)
cout << "Limit exceeded\n";
else if (ans == F(ans)) {
cout << N;
cout << " reaches to a"
<< " fixed point: ";
cout << ans;
}
else {
cout << N;
cout << " reaches to a"
<< " limit cycle: ";
cout << ans;
}
}
}
int main()
{
long long N = 3;
digitCubeLimit(N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int limit = 1000000000;
static int F(int N)
{
String str = String.valueOf(N);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0;
i < str.length(); i++)
{
int val = (int)(str.charAt(i) - '0');
sum += val * val * val;
}
return sum;
}
static int findDestination(int N)
{
HashSet<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
int prev = N, next =0;
s.add(N);
while (N <= limit)
{
next = F(N);
if (s.contains(next))
{
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.add(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
static void digitCubeLimit(int N)
{
if (N < 0)
System.out.print("N cannot be negative\n");
else
{
int ans = findDestination(N);
if (ans > limit)
System.out.print("Limit exceeded\n");
else if (ans == F(ans))
{
System.out.print(N);
System.out.print(" reaches to a" +
" fixed point: ");
System.out.print(ans);
}
else
{
System.out.print(N);
System.out.print(" reaches to a" +
" limit cycle: ");
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3;
digitCubeLimit(N);
}
}
|
Python3
LIMIT = 1000000000
def F(N: int) -> int:
string = str(N)
sum = 0
for i in range(len(string)):
val = int(ord(string[i]) - ord('0'))
sum += val * val * val
return sum
def findDestination(N: int) -> int:
s = set()
prev = N
next = 0
s.add(N)
while (N <= LIMIT):
next = F(N)
if next in s:
return next
prev = next
s.add(prev)
N = next
return next
def digitCubeLimit(N: int) -> int:
if (N < 0):
print("N cannot be negative")
else:
ans = findDestination(N)
if (ans > LIMIT):
print("Limit exceeded")
elif (ans == F(ans)):
print("{} reaches to a fixed point: {}".format(
N, ans))
else:
print("{} reaches to a limit cycle: {}".format(
N, ans))
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 3
digitCubeLimit(N)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static readonly int limit =
1000000000;
static int F(int N)
{
String str = String.Join("", N);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0;
i < str.Length; i++)
{
int val = (int)(str[i] - '0');
sum += val * val * val;
}
return sum;
}
static int findDestination(int N)
{
HashSet<int> s =
new HashSet<int>();
int prev = N, next = 0;
s.Add(N);
while (N <= limit)
{
next = F(N);
if (s.Contains(next))
{
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.Add(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
static void digitCubeLimit(int N)
{
if (N < 0)
Console.Write("N cannot be negative\n");
else
{
int ans = findDestination(N);
if (ans > limit)
Console.Write("Limit exceeded\n");
else if (ans == F(ans))
{
Console.Write(N);
Console.Write(" reaches to a" +
" fixed point: ");
Console.Write(ans);
}
else
{
Console.Write(N);
Console.Write(" reaches to a" +
" limit cycle: ");
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3;
digitCubeLimit(N);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let limit = 1000000000;
function F(N)
{
let str = (N).toString();
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0;
i < str.length; i++)
{
let val = (str[i].charCodeAt(0) - '0'.charCodeAt(0));
sum += val * val * val;
}
return sum;
}
function findDestination(N)
{
let s = new Set();
let prev = N, next =0;
s.add(N);
while (N <= limit)
{
next = F(N);
if (s.has(next))
{
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.add(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
function digitCubeLimit(N)
{
if (N < 0)
document.write("N cannot be negative\n");
else
{
let ans = findDestination(N);
if (ans > limit)
document.write("Limit exceeded\n");
else if (ans == F(ans))
{
document.write(N);
document.write(" reaches to a" +
" fixed point: ");
document.write(ans);
}
else
{
document.write(N);
document.write(" reaches to a" +
" limit cycle: ");
document.write(ans);
}
}
}
let N = 3;
digitCubeLimit(N);
</script>
|
Output:
3 reaches to a fixed point: 153
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...