CBSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Papers for Biology help you to understand the level of questions asked in the previous exams, along with the changes in pattern. The Class 12 board examination is a crucial step in a student’s academic journey. Practicing the CBSE biology class 12 previous question paper enhances time-management skills. It makes you understand the importance of different topics that have been asked previously. It also boosts your confidence level to appear in the examination.
CBSE 12th biology previous year solved paper enhances the understanding of the topic and acts as a checkpoint to see the level of preparation you have done. CBSE 12th Biology Question Paper 2023 is available here. You can also download the CBSE class 12 biology previous year paper with solutions pdf on the official website of Geeks for Geeks.
Overview of CBSE Class 12 Biology Paper
A detailed overview of the CBSE Class 12 Biology paper – 2023 is given below:
|
Number of Questions Asked
|
33
|
|
Maximum Marks
|
80
|
|
Total Time Allotted
|
3 hours
|
|
Paper Section
|
3 Sections (A, B, C, D, and E) – All Compulsory
|
|
Types of Questions Asked
|
Short Answer Types, Long Answer Types, Case Study, and MCQs
|
CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Papers 2023
Question 1: Select the pathogen mismatched with symptoms of diseases caused by it from the list given below:
- Entamoeba histolytica: Constipation, abdominal pain.
- Epidermophyton: Dry scaly lesions on the nail.
- Wuchereria bancrofti: Chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels of the lower limb.
- Haemophilus influenzae: Blockage of intestinal passage.
Answer: Haemophilus influenzae : Blockage of intestinal passage.
Question 2: Important attributes belonging to a population but not to an individual are:
- Birth rate and deathrate
- Male and female
- Birth and death
- Sex-ratio
Select the correct optionfrom the given options:
- (1) only
- (2) only
- (2) and (3)
- (1) and (4)
Answer: (1) and (4)
Question 3: Many copepods live on the body surface of marine fish. This relationship is example of:
- (a) Commensalism
- (b) Parasitism
- (c) Amensalism
- (d) Mutualism
Answer: (b) Parasitism
Question 4: Given below is the restriction site of restriction endonuclease Pst-I and the cleavage sites on a DNA molecule.
Choose the option that gives the correct resultant fragments by the action of the enzyme Pst-I.

Answer: (D)
Question 5: Given below is a sequence of bases in mRNA of a bacterial cell. Identify the amino acid that would be incorporated at codon position 3 and codon position 5 during the process of its translation.
5’ AUC AGG UUU GUG AUG GUA CGA 3’
- (a) Phenylalanine, Methionine
- (b) Cysteine, Glycine
- (c) Alanine, Proline
- (d) Serine and Valine
Answer:- (a) Phenylalanine, Methionine
Question 6: Given below are structural details of a human mammary gland:
- (i)The glandular tissue in the breast has 15-20 clusters of cells called alveoli.
- (ii)The milk is stored in the lumen of alveoli.
- (iii)The alveoli join to form the mammary ducts.
- (iv)Mammary ampulla is connected to lactiferous ducts.
Choose the optionthat gives the correct detailof the human mammary gland.
- (a) (i) and (ii)
- (b) (ii) and (iii)
- (c) (ii) and (iv)
- (d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:- (c) (ii) and (iv)
Question 7: Given below are the list of commercially important products and their source organisms. Select the option which gives correct matches.
|
List A
|
List B
|
|
S. No.
|
Bioactive product
|
S. No.
|
Microbes( Source organism)
|
|
(A)
|
Cyclosporin A
|
(i)
|
Streptococcus
|
|
(B)
|
Statins
|
(ii)
|
Trichoderma polysporum
|
|
(C)
|
Streptokinase
|
(iii)
|
Penicillium notatum
|
|
(D)
|
Penicillin
|
(iv)
|
Monascus purpureus
|
- a.(A)-(i), (B)-(ii), (C)-(iii), (D)-(iv)
- b.(A)-(iii), (B)-(iv), (C)-(ii), (D)-(i)
- c.(A)-(iv), (B)-(iii), (C)-(ii), (D)-(i)
- d.(A)-(ii), (B)-(iv), (C)-(i),(D)-(iii)
Answer:- (d) (A)-(ii), (B)-(iv), (C)-(i), (D)-(iii)
Question 8: Tetanus antitoxin (Tetanus toxoid) when injected into the human body it immediately provides:
- (a) Innate immunity
- (b) Passive immunity
- (c) auto immunity
- (d) Active immunity
Answer:- (b) Passive immunity
Question 9: The primary productivity in an ecosystem is expressed as:
- (a) gm-2 y-1
- (b) gm-2 y
- (c) Kcal m-2 y-1
- (d) Kcal m-2
Answer:- Both (a) and (c) are correct answers
Question 10: Select the option that shows the correctly identified ‘U’, ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ in a developing dicot embryo.

- a.X – Plumule (2n), Y – Suspensor (n), Z – Cotyledon (2n), U – Radicle (2n).
- b.X – Plumule (2n), Y – Suspensor (2n), Z – Radicle (2n), U – Cotyledon (2n).
- c.X – Suspensor (2n), Y – Cotyledon (2n), Z – Radicle (2n), U – Plumule (2n).
- d.X – Cotyledon (2n), Y – Radicle (n), Z – Plumule (n), U – Suspensor (n).
Answer:- (c) X – Suspensor(2n), Y – Cotyledon(2n), Z – Radicle (2n), U – Plumule (2n).
Question 11: The sixth extinction in progress currently is different from all previous extinctions on earth as it is:
- (a) 10-100 times faster
- (b) 100-1000 times faster
- (c) 100-10000 times faster
- (d) 1000-10000 times faster
Answer:- (b) 100-1000 times faster
Question 12: At which stage during evolution did humans use hides to protect their bodies and buried their dead?
(a) Homo habilis
(b) Neanderthal man
(c) Java man
(d) Homo erectus
Answer:- (b) Neanderthal man
Question Nos. 13 to 16 consist of two statements Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
a.Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b.Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c.(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d.(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 13: Assertion (A) : Decomposition process is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and cutin. Reason (R) : Decomposition is largely an oxygen requiring process.
Answer:- (b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 14: Assertion (A) : Determining the sex of an unborn child followed by MTP is an illegal practice. Reason (R) : Amniocentesis is a practice to test the presence of genetic disorders also.
Answer:- (B) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 15: Assertion (A) : In Thalassemia an abnormal myoglobin chain is synthesized due to a gene defect. Reason (R) : α-Thalassemiais controlled by genes HBA1 and HBA2 on chromosome.
Answer:- (d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 16: Assertion (A) : Synthetic oligonucleotide polymers are used during annealing in a PCR. Reason (R) : The primer bind to the double stranded DNA at their complementary regions.
Answer:- (c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
SECTION B
Question 17: (a) Name (i) a GM cerea lcrop having enhanced nutritional value, (ii) the nutrient it is rich in.
(b) State any two benefits of Genetically modified crops.
Answer:
(a) (i) Golden rice
(ii) It is rich in vitamin A content which improves eye vision
(b) Benefits of genetically modified crops: (any two)
- Crops become more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought,salt, heat).
- Reduces reliance on chemical pesticides (pest-resistant crops).
- Helps to reduce post-harvest losses.
- Increased efficiency of mineral usage by plants (this prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil).
Question 18: By using Punnett square, depict the genotypes and phenotypes of test crosses (where green pod colour (G) is dominant over yellow pod colour (g) in Garden pea with unknown genotype.
Answer:
Test Cross: A test cross is formed by crossing a parent with an unknown genotype with parent who has a homozygous recessive genotype. A test cross determines or reveals the original person’s genotype. A test cross can help to determine whether a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous for a specific trait.
Hence we got two cases:
Dominant allele: G, Dominant trait: Green pod color
Recessive allele: g, Recessive trait: yellow pod color

Genotypic ratio: 100% heterozygous dominant i.e., 1:0
Phenotypic ratio: all green
Inference: Unknown is homozygous dominant

Genotypic ratio: 50% heterozygous dominant and 50% homozygous recessive i.e., 1:1 ratio
Phenotypic ratio: 50% Green: 50% Yellow
Inference: Unknown is heterozygous dominant
Question 19: (a) Certain specific bacterial spores are mixed in water and sprayed over Brassica crop to control butterfly caterpillars. Name this bacterium and its mode of action on the butterfly caterpillars.
Answer:
(a) Bacillus thuringiensis is the bacteria that is being used to reduce the action of butterfly caterpillars on Brassica crops.
Mode of Actions
- B. thuringiensis forms protein crystals during a particular phase of their growth. These crystals contain toxic insecticidal protein (inactive protoxin).
- When the butterfly caterpillar (larva) feeds on the plants,the spores, containing inactive protoxins, reach the gut of the larva.
- Inactive protoxinis converted into an active form of toxin due to alkaline pH of the larval gut.
- Activated toxin binds to the surface of the midgut epithelial cells and creates pores. This causes cell swelling and lysis and eventually death of the larva.
OR
(b)Immunotherapy these days is one of the most efficient ways of treatment of cancer. The therapy involved activates the immune system and destroys the tumour.
(i) Write an example of one such biological response modifier used in immunotherapy.
(ii) Why do patients need such substances if the immune system is already working in the body?
(iii) State what is ‘Contact inhibition’.
Answer:
(i) α-interferon is a biological response modifier which activates the immune system of the patient and helps in destroying the tumour.
(ii) Tumor cells have the ability to avoid detection and destruction by the immune system. Hence,patients need a biological response modifier to activate the immune system.
(iii) Contact inhibition is the property shown by healthy cells of the body by virtue of which their contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled cell division. But this property is lost in cancerous cells.
Question 20: The graph given below shows the number of primordial follicles per ovary in women at different ages. Study the graph and answer the questions that follow.
(a) What is the average age of women at the onset of menopause ?
(b) At what age are maximum primordial follicles present in the ovary, according to the giving graph.

Answer:
(a) According to the given graph, the onset of menopause is called perimenopause as the irregular menses begins in this phase. This phase begins between 40 years and 50 years of age. So, the average age of women at the onset of menopause is 45 years, approximately.
(b) The maximum primordial follicles are present at 10 years of age, which indicates puberty.
Question 21: “Some species of insects and frogs have evolved with various specific features that help them from being detected.”
(a) Justify the statement giving reasons.
(b) Mention any two features.
Answer:
(i)
- Frogs and insects can become prey for their respective predators.
- If a predator is too efficient and over exploits its prey, then the prey might become extinct and following it, the predator will also become extinct for lack of food.
- As a result, prey species have evolved various defenses to lessen the impact of predation and go undetectable or uneaten by the predators
(ii)Two such features are given below:
- Some species of insects and frogs have developed cryptically-coloured skin to imitate the neighboring environment. In other words,these organisms camouflage and go undetectable by the predators.
- Monarch butterfly is highly distasteful to its predator (bird) because of a special chemical present in its body. Hence, it is avoided by its predator.
SECTION C
Question 22:
(a) “Plasmodium protozoan needs both a mosquito and a human host for its continuity.” Explain.
OR
(b) We all must work towards maintaining good health because ‘health is wealth’. Enlist any six ways of achieving good health.
Answer:
(a) Malarial parasite Plasmodium requires two hosts – human and mosquitoes – to complete its life cycle.
Female Anopheles mosquito is the vector which transmits the parasite from one individual to another.
Human:
When mosquitoes bite a human, the parasites are introduced into the body. These parasites reach liver through blood.
They reproduces asexually in liver cells,bursting the cells and releasing into the blood. They reproduces asexually in RBCs and are released by the rupturing the RBCs. A few of these parasites undergoes sexual reproduction in RBCs and produces male and female gametocytes, which circulate in the blood.
Mosquito:
When a female mosquito bites an infected human, the male and female gametocytes enter their salivary glands. The male and female gametes fuse in the mosquito’s gut and undergo fertilisation. There they undergo further development to from mature infective stages called sporozoites. Sporozoites escape from the gut and migrate to mosquito’s salivary glands, which is then transmitted into an healthy individual.
OR
(b) We all must work towards maintaining good health because‘health is wealth’.
The following are six ways for achieving good health:
- Balanced diet
- Personal hygiene
- Regular exercise
- Yoga
- Awareness about diseases and their effect on different bodily functions
- Vaccination (immunisation) against infectious diseases
- Proper disposal of wastes
- Control of vectors and maintenance of hygiene in food and water resources
Question 23: “Biodiversity plays a major role in many ecosystem services that nature provides.”
a.Describe any two broadly utilitarian arguments to justify the given statement.
b. State one ethical reason of conserving biodiversity.
Answer:
(a) The broadly utilitarian argument for conserving biodiversity says that the Amazon Forest producing 20 percent of the total oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere through photosynthesis,thus we cannot put an economic value on the services provided by nature.
Similarly, pollination without which plants cannot give fruits or seeds is another service, ecosystems provide through pollinators layer – bees, bumblebees, birds and bats.
Third is the aesthetic pleasures of walking through thick woods,watching spring flowers in full bloom or waking up to a bulbul’s song in the morning.
(b) The ethical argument for conserving biodiversity relates to what we owe to millions of plant, animal and microbe species with whom we share this planet. Philosophically or spiritually, every species has an intrinsic value, even if it may not be of current or any economic value to us. We have a moral duty to care for their well-being and pass on our biological legacy in good order to future generations.
Question 24: Name and explain a surgical contraceptive method that can be adopted by the male partner of a couple.
Answer:
Vasectomy is the surgical contraceptive method in males. In vasectomy, a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up through a small incision on the scrotum. This technique is highly effective but their reversibility is very poor.

Question 25: Human Genome Project (HGP) was a mega projectlaunched in the year 1990 with some important goals.
a. Enlist any four prime goals of HGP.
b. Name any one commonnon human animal modelorganism which has also been sequenced thereafter.
Answer:
(a) The four prime goals of HGP are:
- Identify all the approximately 25000 to 30000 genes present in the Human DNA
- Determine the sequence of 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up the human DNA
- Storing the information about these 25000-30000 genes and 3 billion chemical base pairs in data bases.
- Improve tools for data analysis.
(b) The common non-human animal model organism sequenced after the completion of HGP is Caenorhabditis elegans.
Question 26: One of the major approaches of the crop improvement program is Artificial Hybridization. Explainthe steps involvedin making sure that only the desiredpollen grain pollinate the stigma of a bisexual flower by a plant breeder.
Answer:
Artificial hybridization is one of the major approaches of the crop improvement programme. The steps involved in making sure that only the desired pollen grain pollinate the stigma of a bisexual flower by a plant breeder are:
- Selection of parents: The pure line of male and female plants with desired characters is selected for the process of hybridization and kept in isolation.
- Emasculation: The process of removal of male floral parts from flower of the female plant during the bud stage in the flower.The bud is opened and the undeveloped male floral parts are removed using a forceps. This rules out the chances of pollen from the same flower falling on the stigma.
- Bagging: This is the process of covering up the flower with paper bag or polybag to ensure that no other pollen grain falls on the stigma.
- Collection of pollen from the male parent: The anthers from the flower of the plant chosen as male parent is collected.
- Dusting the pollen grain on stigma: The collected anthers from flowers of the male plant are tapped over the stigma.This results in the pollen grains from these anthers to fall on the stigma.
- Rebagging: The flower bearing the dusted pollen is again covered with paper bag or polybag.
Question 27: Mention Darwin observations made on Finches on his visit to Galapagos island. Write the explanations given by Darwin on his observations?
Answer:
On his visit to Galapagos Island, Darwin made his observations on Finches:
- There were many varieties of small black birds in the same island.
- Each variety had different types of beaks suited for differentdietary habits.
- He observed that all the varieties evolved on the island itself.
Darwin gave the following explanations on his observations
- From the original seed-eating features, many other forms with altered beaks arose.
- The alterations in beak enabled them to become insectivorous and vegetarian finches.
- This process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other geographic areas is called adaptive radiation.
Question 28: “RNA interference has been used to produce transgenic tobacco plants to protect them from the infestation by specific nematodes.” Explain the novel strategy exploited by the biotechnologies.
Answer:
RNA interference is a novel strategy which has been exploited by the biotechnologists to protect the tobacco plant from the infestation by the nematode Meloidogyne incognita. This results in killing the nematode as the infestation starts and protects the plant, benefiting the farmer.
RNA interference involves silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRNA. This is also called mRNA silencing.The complementary comes from an infection by viruses having RNA genomes or transposons that replicate via an RNA intermediate.
To achieve RNA interference, nematode-specific genes are introduced into the host plant using Agrobacterium vectors. The introduced genes are capable of producing both sense and anti-sense RNA in the host cells.These two RNA’s being complementary to each other and can form a double stranded(dsRNA) and silence an essential mRNA of the nematode. As a consequence, parasite could not survive in a transgenic host expressing specific interfering RNA. The transgenic plant therefore got itself protected from the parasite.
SECTION D
Question 29: When a microorganism invades a host, a definite sequence of events usually occur leading to infection and disease, causing suffering to the host. This process is called pathogenesis. Once a microorganism overcomes the defense system of the host, development of the disease follows a certain sequence of events as shown in the graph. Study the graph given below for the sequence of events leading to appearance of a disease and answer the questions that follow:

a. In which period, accordingto the graph there are maximum chancesof a person transmitting a disease/infection and why?
b. Study the graph and write what is an incubation period. Name a sexually transmitted disease that can be easily transmitted during this period. Name the specific type of lymphocytes that are attacked by the pathogen of this disease.
OR
c.Draw a schematic labelled diagram of an antibody.
d.In which period, the number of immune cells forming antibodies will be highest in a person suffering from pneumonia? Name the immune cells that produce antibodies.
Answer:
(a) According to the graph,period of illness is the phase when there is a maximum chance of a person transmitting a disease/infection because at this stage the number of pathogens are high in the host.
(b) The time period between the entry of pathogens in the body and appearance of symptoms is called incubation period. AIDS is a sexually transmitted disease that can be easily transmitted during this period. AIDS is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). HIV enters into helper T- lymphocytes, replicates and produces progeny viruses. The progeny viruses released in the blood attack other helper T-lymphocytes.
(c) The labelled structure of antibody is shown below:
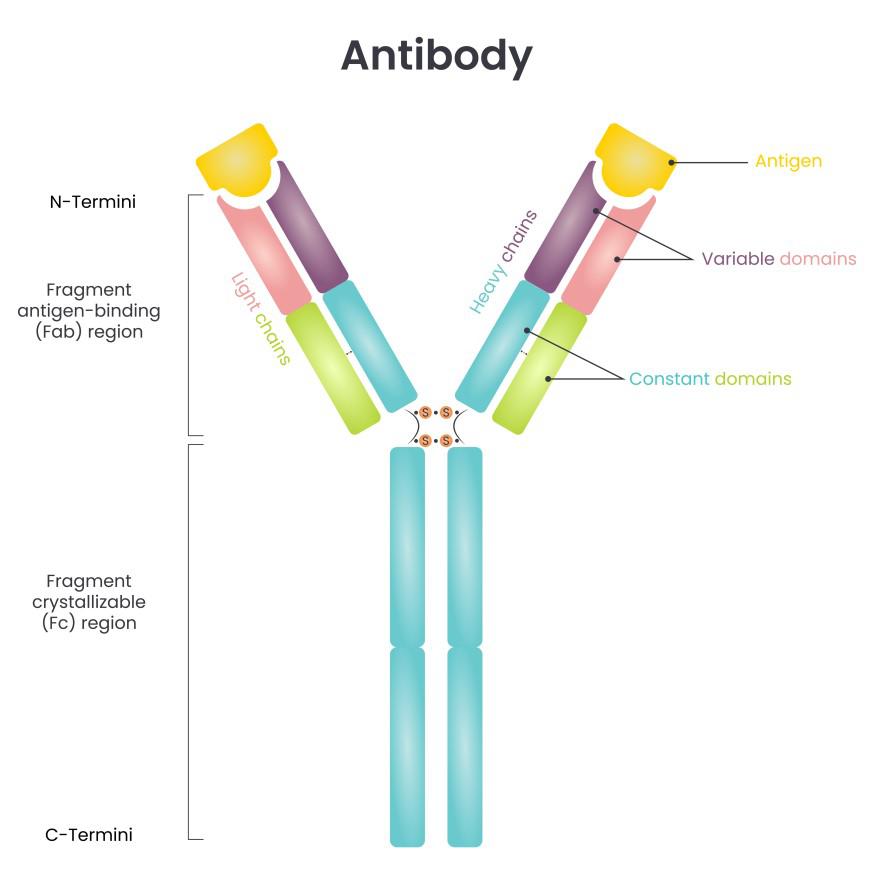
(d) Period of decline is the phase when the number of immune cells forming antibodies will be highest in person suffering from pneumonia. The B-lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to pathogens to fight with them.
Question 30: The chromosome number is fixed for all normal organisms leading to species specification whereas any abnormality in the chromosome number of an organism results into abnormal individuals. For example, in humans 46 is the fixed number of chromosomes both in males and females. In male it is ‘44+XY’ and in female it is ‘44+XX’. Thus, the human male is heterogametic, in other words produces two different types of gametes one with ‘22+X’ chromosomes and other with ‘22+Y’ chromosomes respectively Human female, on the other hand is homogametic i.e. produces only one type of gamete with ‘22+X’ chromosomes only.
Sometimes an error may occur during meiosis of cell cycle, where the sister chromatids fail to segregate called nondisjunction, leading to the production of abnormal gametes with altered chromosome number. On fertilisation such gametes develop into abnormal individuals.
a. State what is aneuploidy.
b. If during spermatogenesis, the chromatids of sex chromosomes fail to segregate during meiosis, write only the different types of gametes with altered chromosome number that could possibly be produced.
c. A normal human sperm (22+Y) fertilises an ovum (22+XX). Name the disorder the offspring thus produced would suffer from and write any two symptoms.
OR
d. Name a best known and most common autosomal aneuploid abnormality in humans and write any two symptoms.
Answer:
(a) Failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division cycle which results in loss or addition of chromosomes in a set of chromosomes is called aneuploidy.
(b) Due to non-disjunction of chromatids during spermatogenesis, some sperm will carry both sex chromosome and some will not carry any sex chromosome. 22 + 0 and 22 + XY

(c) A normal human sperm (22+Y) fertilises an ovum (22+XX).The genetic constitution of the offspring is 44 + XXY and this indicates Klinefelter’s Syndrome. Two symptoms of Klinefelter’s Syndrome are: (i) The affected individual has overall masculine development, how ever the feminine features are also expressed. (ii) Such individuals are sterile.
(d) The best known and most common autosomal aneuploid abnormality in humans is Down’s syndrome.
Two symptoms of Down’s syndrome are:
(i)The affected individual is short statured with a small round head,furrowed tongue and partially open mouth.
(ii)Physical and mental development is retarded.
SECTION E
Question 31: (a)
(i) How and why is charging of tRNA essential in the process of translation?
(ii) State the functionof the ribosome as a catalyst in bacteria during the process of translation.
(iii) Explain the process of binding of ribosomal units to mRNA during
(b) Describe the dihybrid cross upto F2 generation as conducted by Gregor Mendel using pure lines of Garden Pea for characters seed shape and seed colour.
Answer:
(i)The process of activating the inactive amino acids and addition of the activated amino acid to their cognate tRNA is called charging of tRNA. During the charging process, the inactive amino acids in the cytoplasm of a cell are activated in the presence of ATP and is added to the cognate tRNA. This is a crucial step that occurs during the first phase of the translation process because the high energy bond between tRNA and amino acid is used at a later stage in protein synthesis to link the amino acid covalently to the growing polypeptide chain.
(ii) Ribosomes are made up of structural RNAs and several proteins. One such structural RNA known as 23S rRNA acts as a catalyst in bacteria and is known as the enzyme- ribozyme. It helps in the formation of peptide bonds.
(iii) Ribosome exists as two subunits (a large and a small subunit), in its inactive state. When the small subunit encounters an mRNA, the process of translation of the mRNA to protein begins. There are two sites in the large subunit, for subsequent amino acids to bind to and thus, be close enough to each other for the formation of a peptide bond.
(b) The traits in consideration are seed shape and seed colour. Following table shows the various dominant and recessive alleles for these traits.
Pure lines of Garden pea for the characters will have homozygous genotypes. Following is the depiction of the dihybrid cross performed by Gregor Mendel using seed colour and seed shape of the Garden pea as the trait.
In the parent generation, Mendel had performed the cross between homozygous parents (YYRR – yellow and round seeds, yyrr- green and wrinkled seeds). In the first generation, he obtained offsprings which were all heterozygous and exhibited the dominant trait (yellow and round seeds). He performed selfing of the heterozygous offspring.
In the F2 generation he obtained the following ratios:
- Phenotypic ratio: 9:3:3:1
- Genotypic ratio: 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1

|
Trait
|
Dominant
|
Recessive
|
|
Seed Shape
|
Round (R)
|
Wrinkled (r)
|
|
Seed Colour
|
Yellow (Y)
|
Green (y)
|
Question 32: (a) Bioreactors are the containment vehicles of any biotechnology-based production process.For large scale production and for economicreasons the final success of the biotechnological process depends on the efficiency of the bioreactor.
Answer the following questions w.r.t the given paragraph:
(i) List the operational guidelines that must be adhered to so as to achieve optimisation of the bioreactor system. Enlist any four.
(ii) Mention the phase of the growth we refer to in the statement “Optimisation of growth and metabolic activity of the cells”.
(iii) Is the biological product formed in the bioreactor suitablefor the intended immediate use? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b)
(i) ‘EcoRI’ has played very significant role in r-DNA technology.Explain the convention for naming EcoR1. Write the recognition site and the cleavage sites of this restriction endonuclease.
(ii) What are the protruding and hanging stretchesof DNA produced by these restriction enzymes called? Describe their role in formation of r-DNA.
Answer:
(a)
(i) The list of the operational guidelines that must be adhered to so as to achieve optimisation of growth of the bioreactor system are given below:
a) Monitoring and control of the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions (temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen).
b) Maintain a sterile or aseptic environment.
c) Optimisation of mixing and aeration.
d) Regular cleaning and maintenance of the bioreactor.
(ii) The phase of the growth referred to in the statement “Optimisation of growth and metabolic activity of the cells” is the exponential phase of growth.
(iii) The biological product formed in the bioreactor is not suitable for the intended use immediately. It has to further undergo the down streaming process.
This is because the biological product may contain impurities which may hinder the functioning of the product or can cause harmful effects to the consumer. Also if the product is a drug, further clinical trials need to be conducted to ensure the safety and physiological effects of the drug before releasing it into the market.
(b)
(i) The protruding and hanging stretches of DNA produced by EcoRI are called sticky ends. Sticky ends have over hanging stretches of nitrogenous bases which can pair with complementary bases. Hence, the DNA sequence of our interest which is digested by EcoRI can be ligated with specific vector DNA to create a recombinant DNA.
(ii) EcoRI restriction enzyme is isolated from the bacteria Escherichia coli RY 13 strain. Hence, the letter ‘E’ is derived from the first letter of the genus Escherichia and ‘co’ is derived from the species coli. The letter ‘R’ comes from the strain ‘E. Coli RY 13’. It is followed by a Roman letter ‘I’ as it was the first enzyme to be isolated from the given strain. The recognition site of EcoRI is a palindrome having 5′-GAATTC-3′ sequence. It introduces a cut between G and A nucleotides which creates sticky ends.
Question 33: (a) (i) Explain the monosporic development of embryo sac in the ovule of an angiosperm.
(ii) Draw a diagram of the mature embryo sac of an angiospermic ovule and label any four parts in it.
OR
(b) (i) Explain the formation of placenta after the implantation in a human female.
(ii) Draw a diagram showing human foetus within the uterus and label any four parts in it.
Answer:
(a) (i) The process of monosporic development of embryo sac in the ovule of an angiosperm can be divided as:
- Mitotic division of functional megaspore: The nucleus of the functional megaspore undergoes mitotic division to form two nuclei, forming a 2-nucleate embryo sac. This step is followed by two more sequential mitotic nuclear divisions, which result in the 4-nucleate and then the 8-nucleate stages of embryo sac.
- Cell wall formation: Out of eight nuclei, cell walls form around six nuclei and are organised into cells.
- Distribution of cells in embryo sac: The egg apparatus consisting of two synergids and one egg cell are grouped together at the micropylar end. The antipodals consisting of three cells are at the chalazal end. The two nuclei called the polar nuclei are located in the large central cell.
(ii) The labelled diagram of the mature embryo sac of an angiospermic ovule is given below:

(a) (i) The placenta develops during the first three months of the pregnancy:
- After implantation, finger-like projections called chorionic villi appear on the trophoblast.
- This chorionic villi is surrounded by the uterine tissue and maternal blood.
- The uterine tissue and chorionic villi become interdigitated with each other and jointly form a structural and functional unit between developing embryo (foetus) and maternal body. This structure is called placenta.
(ii) The labelled diagram of human foetus within the uterus is given below

Points to Remember While Solving Class 12 CBSE Biology Previous Year Question Paper
Some points to focus on while practising CBSE Class 12 previous year question papers for biology are:
- Understand the question paper format and marking scheme.
- Review important concepts and topics covered in the syllabus.
- Practice time management to answer all questions within the allotted time.
- Read each question carefully and understand what is being asked.
- Answer questions using appropriate diagrams, if necessary.
- Double-check answers for accuracy and clarity before submission.
- Seek clarification from teachers or peers if any doubts arise during solving.
- Use Class 12 previous year question papers as a tool for revision and understanding exam patterns.
Conclusion – CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2023
The CBSE 12th biology previous year solved paper are an important tool while preparing for class 12 board examinations. You can score high in CBSE class 12 biology using previous year question papers as it gives you a chance to judge your preparations before examinations. The main purpose of providing the biology class 12 previous year question paper is to give an idea about exam pattern and the types of questions asked in exam. Questions are often repeated in exams as well. Hence, solving CBSE Previous Year Question Papers for Class 12 biology is important while studying.
Also Read:
FAQs – CBSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper for Biology (2023)
Does CBSE repeat questions class 12 biology?
Yes, CBSE repeat question of class 12 biology
Which Type of Questions Comes in Board Exam 2023 Class 12?
Starting this year, CBSE Class 12 board exams will include 20% multiple-choice questions (MCQs). The remaining 80% of the exam paper will be structured into two distinct formats. Forty percent of the questions will be competency-based, encompassing MCQs, source-based, and case-study-based questions.
Is CBSE Released Sample Paper for 2023?
The CBSE board published the CBSE Sample Paper 2023-24 in PDF format on April 6th, 2023. As per the CBSE board exam timetable, the CBSE Board exams are slated to occur in February 2024.
What is the Passing Marks Out of 80?
The minimum pass marks out of 80 are 26 marks.
Is Previous Year Questions Enough for CBSE Class 12?
Yes, solving the last 5-7 years previous question paper of Class 12 is enough for CBSE board exams but it is advisable to understand the topics before starting to solve the questions.
Is it Necessary to Solve the CBSE Biology Previous Year Papers of Class 12?
Yes, solving CBSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Papers for Biology after completing topics from NCERT textbook helps in gaining in-depth knowledge of the chapter that will ultimately help in scoring good marks in the exams.
Where can we Study for CBSE Board Exam 2023-24?
NCERT Books are sufficient for the Class 12 Board exam. Supplement with Sample Papers, Question Banks, and video notes for comprehensive preparation, focusing on important topics and revising weaker areas strategically.
How to Score 90+ in CBSE Class 12 Biology Using Previous Papers?
To score 90+ in CBSE Class 12 Biology, study previous papers to understand exam patterns, focus on core concepts, and practice solving previous year question papers under timed conditions for efficient preparation.
Where can I Find Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2023 Solved PDF?
You can download the Class 12 biology question paper 2023 solved pdf from the official website of Geeks for Geeks.
What are the Best Books for CBSE Class 12 Biology Preparation with Previous Papers?
Pairing NCERT with any reference books along with solving previous year paper is a good way to prepare for the Class 12 biology board examinations.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...