Benchmarking: Concept, Advantages and Drawbacks
Last Updated :
07 May, 2024
What is Benchmarking?
Benchmarking is a strategic management approach that organisations use to gain a competitive edge by comparing their practices, processes, and performance metrics with those of their industry counterparts or top performers. It’s a powerful tool that allows companies to identify areas for improvement, set performance targets, and implement effective strategies to enhance overall organisational performance.
By analyzing data and information obtained from benchmarking partners, businesses can pinpoint performance gaps and discover best practices that can be adopted. This knowledge enables organisations to establish ambitious yet achievable targets, create well-defined action plans, and closely monitor progress. With a strong emphasis on continuous learning, innovation, and collaboration, benchmarking empowers businesses to enhance their competitiveness, streamline operations, and make well-informed strategic decisions.
Definitions of Benchmarking
- “Benchmarking is the continuous process of measuring products, services, and practices against the toughest competitors or those companies recognised as industry leaders.” – David Kearns of Xerox Corporation
- “A process of identifying, understanding and adopting outstanding practices from within the same organisation or from other organisations to help improve performance.” – Sarah Cook
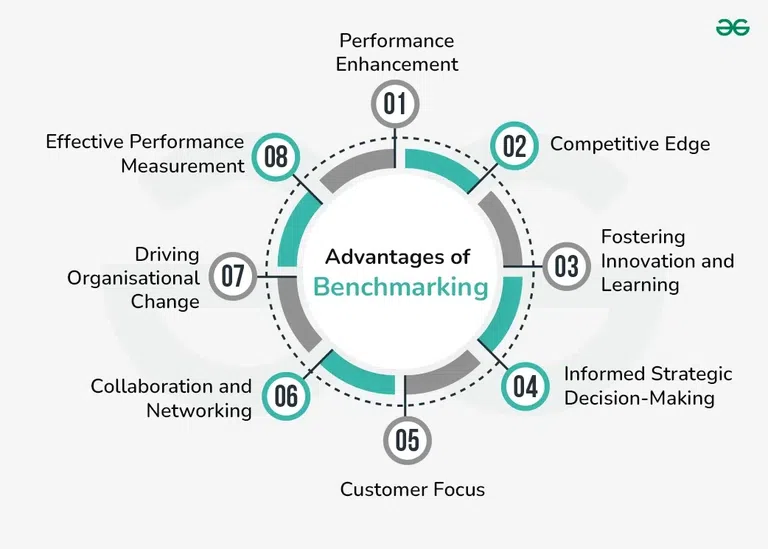
Advantages of Benchmarking
Benchmarking offers numerous advantages for organisations striving to improve their performance and gain a competitive edge. Some key benefits of benchmarking are:
- Performance Enhancement: Benchmarking enables organisations to compare their practices, processes, and performance metrics against industry leaders or competitors. This analysis highlights areas for improvement, allowing organisations to implement best practices and enhance their operational efficiency, product quality, customer satisfaction, and overall performance.
- Competitive Edge: By benchmarking, organisations can identify unique strategies and practices that provide a competitive advantage. Learning from the successes of others and incorporating industry-leading approaches enables organisations to differentiate themselves in the market and stay ahead of competitors.
- Fostering Innovation and Learning: Benchmarking nurtures a culture of continuous improvement, learning, and innovation within organisations. By studying best practices and emerging trends, businesses can generate fresh ideas, drive innovation, and improve their processes and products.
- Informed Strategic Decision-Making: Benchmarking provides objective data and insights that inform strategic decision-making. It helps organisations allocate resources effectively, prioritize process improvement initiatives, and position themselves in the market based on industry best practices.
- Customer Focus: Benchmarking allows organisations to understand customer expectations and evaluate their performance in delivering products or services. By benchmarking customer service practices and satisfaction levels, organisations can identify areas for improvement and enhance the overall customer experience, leading to increased loyalty.
- Collaboration and Networking: Benchmarking often involves collaboration and networking with external organisations. By engaging in benchmarking initiatives, organisations can build valuable networks, establish partnerships, and share knowledge with industry peers. Such collaborations foster innovation and provide insights through shared experiences.
- Driving Organisational Change: Benchmarking challenges the status quo and promotes a culture of continuous improvement within organisations. It encourages organisational change by presenting tangible evidence and demonstrating the benefits of adopting new practices or processes.
- Effective Performance Measurement: Benchmarking provides a framework for measuring performance against industry standards and key performance indicators (KPIs). It enables organisations to establish meaningful performance metrics and track progress over time, ensuring they stay on course to achieve their goals.
Drawbacks of Benchmarking
While benchmarking can be a valuable tool for organisations, it’s important to be aware of potential pitfalls and challenges that can arise. Here are some common pitfalls of benchmarking:
- Inappropriate or Irrelevant Comparisons: One key pitfall is selecting benchmarking partners or metrics that are not directly applicable to the organisation’s specific context. It’s crucial to ensure that the comparisons being made are meaningful and aligned with the organisation’s goals and industry.
- Lack of Internal Assessment: Before engaging in benchmarking, organisations must conduct a thorough internal assessment of their own processes and practices. Failing to understand and address internal issues can lead to misguided benchmarking efforts and ineffective improvements.
- Blind Adoption of Best Practices: While benchmarking aims to identify best practices, blindly adopting them without considering the organisation’s unique circumstances can be problematic. Each organisation has its own culture, resources, and objectives, and it’s crucial to evaluate and adapt best practices to fit these specific factors.
- Inaccurate or Flawed Data: Reliable and accurate data is the foundation of effective benchmarking. If the data used for comparisons is incomplete, outdated, or flawed, it can result in inaccurate conclusions and misguided improvement efforts. Ensuring data accuracy and integrity is essential for meaningful benchmarking outcomes.
- Neglecting Organisational Culture: Benchmarking involves more than just replicating processes or practices. It’s essential to consider and align benchmarking efforts with the organisation’s unique culture, values, and ways of operating. Failing to do so can lead to resistance, low adoption rates, and ineffective improvements.
- Lack of Continual Improvement: Benchmarking is an ongoing process that requires a commitment to continuous improvement. Organisations should not view it as a one-time exercise. Sustaining benchmarking efforts over time, adapting to industry trends, and continually evolving is necessary to maximize the long-term benefits.
- Excessive Competitor Focus: While understanding and learning from competitors is important, becoming overly fixated on them can limit the perspective. It’s valuable to explore benchmarking partners from different industries or sectors who may offer innovative practices and insights.
- Absence of Clear Action Plans: Benchmarking should not stop at identifying performance gaps or best practices. It’s essential to develop clear and actionable plans for implementing improvements. Without a well-defined action plan, the benchmarking exercise may yield limited or no tangible results.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...