Applications of Electromagnetic Spectrum
Last Updated :
26 Apr, 2024
Electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type of radiation has different frequencies and wavelengths. These waves carry energy and can travel through a vacuum at the speed of light. They play a very important role in various fields like communication, medicine, technology, etc. In this article, we are going to learn some of the most common applications of electromagnetic spectrum in real life.
What is Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum refers to the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of energy that travels through space in waves. It includes a wide range of waves, from low-frequency radio waves to high-energy gamma rays.
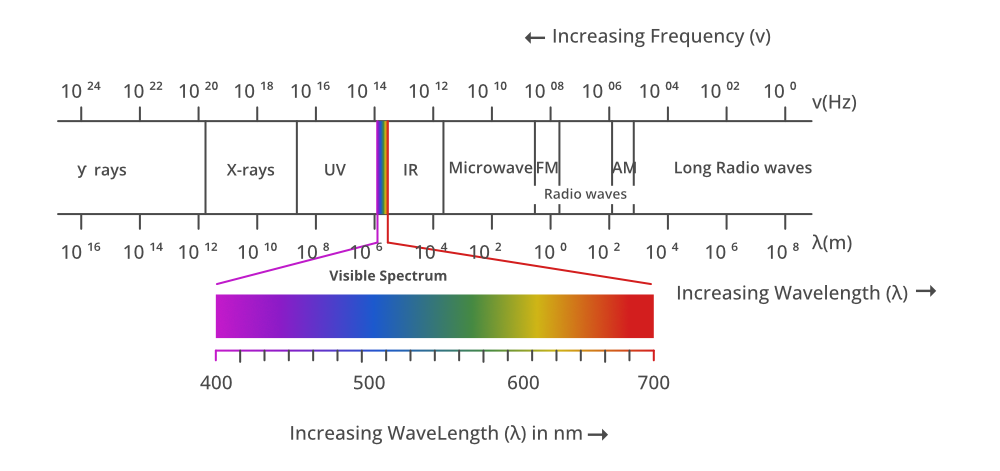
- There are no clear boundaries between different types of waves. They blend seamlessly into one another. It is a continuous spectrum.
- Different types of waves have different wavelengths and frequencies, inversely related to each other.
- All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, approximately 299,792 kilometers per second.
- Electromagnetic waves propagate perpendicular to the direction of their oscillation.
- Electromagnetic radiation shows both wave-like and particle-like behavior, known as wave-particle duality.
Here’s the range of the electromagnetic spectrum with their corresponding wavelengths and frequencies:
| Region |
Wavelength Range |
Frequency Range |
| Radio Waves |
Greater than 1 mm |
Less than 300 GHz |
| Microwaves |
1 mm to 1 meter |
300 GHz to 300 MHz |
| Infrared Radiation |
1 micrometer to 1 mm |
300 THz to 300 GHz |
| Visible Light |
400 to 700 nanometers |
750 THz to 430 THz |
| Ultraviolet |
10 nanometers to 400 nm |
30 PHz to 750 THz |
| X-rays |
0.01 to 10 nanometers |
30 EHz to 30 PHz |
| Gamma Rays |
Less than 0.01 nanometers |
Greater than 30 EHz |
What are Applications of Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is useful in real life for communication, medical imaging, and technology. It enables wireless connectivity and energy production. Here are some of the most common applications of electromagnetic spectrum in real life.
Medical Imaging
Electromagnetic radiation is very useful in medical imaging. It helps doctors see inside the body.
- X-rays use high-energy electromagnetic waves to capture images of bones.
- MRI scans use radio waves and magnetic fields to produce detailed images of organs.
- These technologies help in diagnosing diseases and monitoring treatments.
- Medical imaging is non-invasive, making it safer for patients.
- It provides critical information that guides medical decisions.
Communication Systems
Electromagnetic waves are the backbone of modern communication. They transmit data over long distances.
- Radio and microwaves are used for broadcasting and mobile phone signals.
- Satellites use microwaves to relay communication signals worldwide.
- This technology enables internet, television, and radio services.
- It has made global connectivity and information sharing faster.
- Communication systems are continually evolving to increase their speed and reliability.
Solar Energy
Solar panels convert light from the sun into electricity. This process uses the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Photovoltaic cells absorb sunlight and generate power.
- Solar energy is renewable and helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- It is used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
- Solar power is essential for sustainable development.
- It reduces carbon emissions and combats climate change.
Food Processing
Electromagnetic energy is used to process and preserve food. This enhances safety and shelf life.
- Microwaves are used in ovens to cook food quickly.
- Radiation sterilizes food by killing bacteria and other pathogens.
- This technology extends the shelf life without chemical preservatives.
- It ensures food safety and reduces waste.
- Electromagnetic treatment helps maintain nutritional value and freshness.
Forensic Analysis
Forensic scientists use the electromagnetic spectrum to solve crimes. It helps in evidence analysis.
- UV light can reveal hidden blood and fingerprints.
- Infrared spectroscopy identifies substances by their chemical composition.
- This technology aids in authenticating documents and artworks.
- It is important for gathering accurate and detailed evidence.
- Forensic applications of the electromagnetic spectrum are essential in law enforcement.
Weather Forecasting
Meteorologists use electromagnetic waves to monitor weather and forecast changes.
- Radar uses microwaves to detect rain, storms, and other weather patterns.
- Satellites monitor weather systems and collect data over large areas.
- This information predicts weather accurately and timely.
- It is vital for planning and disaster response.
- Accurate weather forecasting saves lives and property.
Sterilization in Healthcare
Electromagnetic radiation is used for sterilization in healthcare settings. It ensures equipment safety.
- UV light is commonly used to sterilize medical instruments and surfaces.
- Gamma rays kill bacteria and viruses on a variety of tools.
- This method is effective and fast, reducing the risk of infections.
- It’s critical in maintaining sterile environments in hospitals.
- Sterilization helps prevent the spread of diseases.
Night Vision Technology
Night vision devices use the infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum to see in the dark. They detect heat emitted by objects.
- These devices are essential for wildlife research, security, and military operations.
- Infrared light is invisible to the naked eye but can be captured by special sensors.
- Night vision helps users see in complete darkness or through smoke and fog.
- It enhances safety and operational capabilities in low-light conditions.
- The technology is also used in various automotive and surveillance applications.
Non-Destructive Testing
Electromagnetic methods are used in non-destructive testing to inspect materials and structures. This technique ensures safety without damaging the object.
- Eddy current testing uses electromagnetic induction to find flaws in metal structures.
- Ultraviolet fluorescence can detect cracks or leaks on surfaces.
- These methods are critical in aerospace, manufacturing, and construction.
- They help in maintaining the integrity of critical infrastructure.
- Non-destructive testing saves time and costs by preventing failures.
Art Restoration and Analysis
Art historians and restorers use the electromagnetic spectrum to examine and preserve artworks. Techniques vary based on the wavelength used.
- Infrared reflectography can see under the surface paint to reveal sketches and changes.
- X-rays identify earlier compositions and the structure of an artwork.
- These methods uncover hidden layers and authenticate old masterpieces.
- They provide insights without harming the valuable pieces.
- Electromagnetic analysis has revolutionized art restoration and research.
Pest Control
Electromagnetic waves are used in agricultural pest control to target and eliminate pests without chemicals.
- Radio frequency waves can kill insects and pests residing within crops.
- This method is environmentally friendly and leaves no toxic residues.
- It’s used to preserve grain and other stored products.
- Electromagnetic pest control contributes to sustainable agriculture.
- It ensures healthier food products and reduces the use of pesticides.
Space Exploration
The electromagnetic spectrum is crucial in space exploration for communication and observation.
- Radio waves transmit data between spacecraft and Earth.
- Infrared telescopes help astronomers discover celestial bodies that are too cool to emit visible light.
- This technology maps planets, stars, and galaxies.
- It aids in the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Space exploration relies heavily on the electromagnetic spectrum for navigation and research.
Also, Check
FAQs on Applications of Electromagnetic Spectrum
What is electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum refers to the entire range of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What role does the electromagnetic spectrum play in medical imaging?
The electromagnetic spectrum, especially X-rays and gamma rays, is essential for creating detailed images of the body’s internal structures, aiding in diagnosis and treatment.
How does the electromagnetic spectrum facilitate communication?
Radio waves, a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, are crucial for transmitting data over airwaves, enabling everything from TV broadcasts to mobile phone connectivity.
Can the electromagnetic spectrum be used in solar energy?
Yes, solar panels utilize the visible light portion of the spectrum to convert sunlight into electricity, providing a renewable energy source.
What is the use of the electromagnetic spectrum in weather forecasting?
Weather radars use microwave radiation to detect atmospheric conditions, helping meteorologists predict weather patterns and issue warnings.
How does the electromagnetic spectrum improve automotive safety?
In automotive safety, radar systems use microwave radiation to detect nearby objects, assisting in collision avoidance and adaptive cruise control.
What is the use of electromagnetic spectrum in space exploration?
The spectrum is used for communication between spacecraft and Earth, and for observing celestial objects in different wavelengths to gather data on the universe.
How does the electromagnetic spectrum contribute to food safety?
Radiation from the electromagnetic spectrum, such as gamma rays, is used for sterilizing food products, effectively eliminating bacteria and extending shelf life without chemicals.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...