What is the Service Marketing Mix?
Service Marketing is a type of marketing that focuses on promoting and selling services instead of physical goods. It uses specific strategies to increase demand, highlight the benefits, and provide excellent customer service experiences. This kind of marketing puts a strong emphasis on understanding customer needs, providing customized services, ensuring customer satisfaction, and keeping customers engaged to build loyalty and encourage repeat business. The main goal is to make customers feel valued and give them a positive and unforgettable experience that sets the business apart from its competitors.
Key Takeaways:
- The service marketing mix offers a comprehensive framework for businesses to consider all aspects of marketing their services.
- Services are inherently customer-centric, involving direct interactions between service providers and customers.
- Effectively utilizing the service marketing mix allows businesses to differentiate their offerings and create a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
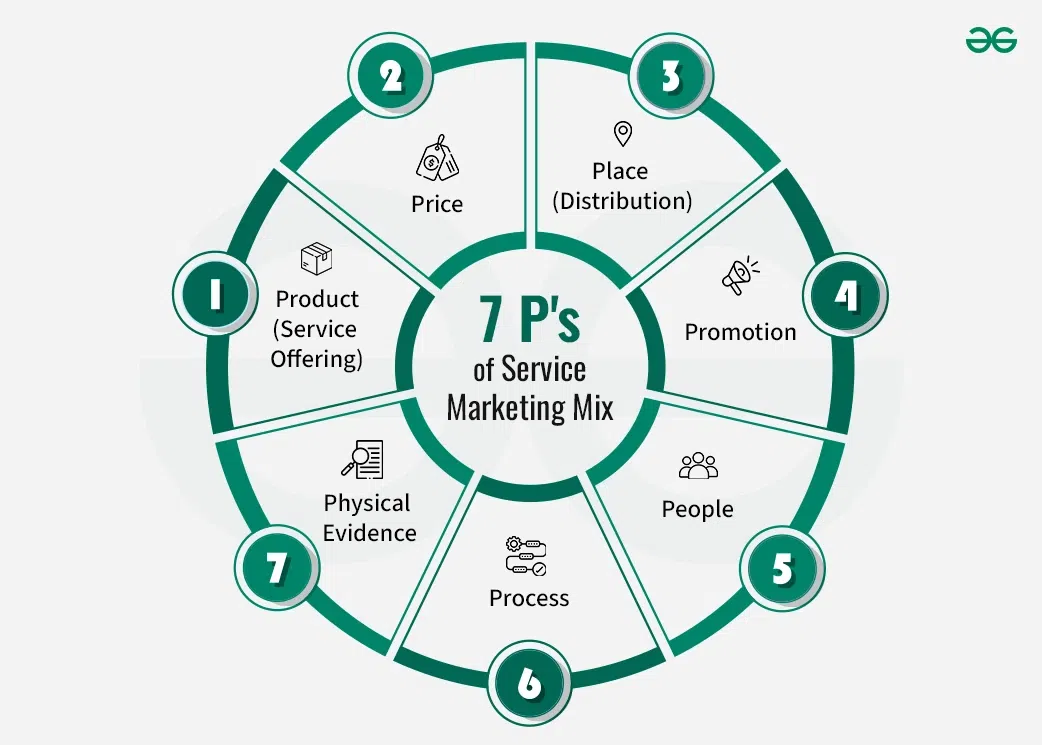
7 P’s of Service Marketing Mix
The 7 P’s of service marketing mix is an extension of the traditional 4 P’s (Product, Price, Place, and Promotion) specifically tailored for service marketing. These additional three P’s focus on the unique aspects of services, which are intangible, perishable, variable, and inseparable from their providers. Each of them is explained below,
1. Product (Service Offering)
Product includes the core service or offering that the business provides to its customers. It encompasses both tangible and intangible aspects of the service, such as features, benefits, quality, branding, and customization options.
Example: A software company offering a cloud-based project management tool. Features include task management, file sharing, team collaboration, and customizable project dashboards.
2. Price
Price refers to the amount customers are charged for the service. Pricing strategies in services marketing may involve considerations, such as value-based pricing, dynamic pricing, bundling, or subscription models.
Example: A streaming service offering different subscription tiers, such as basic, standard, and premium, with corresponding prices based on the level of access, streaming quality, and number of simultaneous streams allowed.
3. Place (Distribution)
In services marketing, place refers to the channels through which the service is delivered to customers. This includes physical locations, online platforms, distribution partners, and any other touchpoints where customers interact with the service.
Example: A food delivery service using a mobile app and website to connect customers with local restaurants. Customers can place orders online, and the service coordinates delivery through its network of drivers
Promotion involves all the activities used to communicate the value of the service to the target audience and persuade them to purchase or use it. Promotion strategies in services marketing may include advertising, public relations, personal selling, sales promotions, and digital marketing tactics.
Example: A hotel chain running a targeted digital advertising campaign promoting special vacation packages for families during the holiday season. The campaign includes display ads, social media posts, and email newsletters.
5. People
When we talk about “People” in service marketing, we’re highlighting how important the workers are in providing the service. This includes everyone from the folks you see up front helping you, like waiters or cashiers, to the managers making sure things run smoothly behind the scenes, and even the support staff helping out in different ways. Basically, how you feel about the service often depends on how friendly, skilled, and helpful these people are.
Example: A luxury spa resort prides itself on hiring highly trained and friendly staff. The spa therapists, concierge, and other employees are attentive to guests’ needs, providing personalized recommendations and ensuring a relaxing experience.
6. Process
Refers to the procedures, systems, and workflows involved in delivering the service. A well-defined and efficient service process is crucial for ensuring consistency, quality, and customer satisfaction. Process design may involve aspects such as service blueprinting, automation, standardization, and continuous improvement efforts.
Example: An online retailer has a streamlined order fulfillment process. Customers can easily browse products, add items to their cart, and complete the checkout process within a few clicks. The retailer offers multiple payment options and provides order tracking updates to keep customers informed.
7. Physical Evidence
“Physical Evidence” means the stuff you can see, touch, or notice when you’re using a service. It’s like the things around you that give you an idea of what the service is like. For example, when you walk into a restaurant, you might notice how clean and comfy it looks, or you might see the menus and signs they have. All these things—like the decorations, furniture, signs, and even the uniforms people wear—help you decide if the service is good or not.
Example: A car rental company maintains a fleet of modern vehicles, all cleaned and well-maintained. The rental locations are equipped with clear signage, comfortable waiting areas, and professional staff uniforms, creating a positive impression for customers.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...