India has plenty of different lifestyles, beliefs, languages, and customs. It means that many different people and thoughts come together for a common goal of democracy. Do you know what Indian democracy is based on? It’s the Indian Constitution!
The Indian Constitution is the most important rule book of India.
- This text tells us about the government and its rules.
- It also explains what rights and responsibilities people have.
- It is the basics of treating everyone equally, being democratic, and being fair for everyone in society.
The Constitution of India was made official on January 26, 1950, replacing the old Government of India Act from 1935. The Indian Constitution is very long and has many parts, articles, and schedules. It has more articles than any other written constitution in the world.
There are many different sets of rules for the government, similar to the ones in Britain, America, and Ireland, all mixed. The idea also comes from the beliefs of freedom, equality, and friendship that were made important during the French Revolution.
5 Provisions That Make India a Full-fledged Constitution
Preamble
The Preamble of the Indian Constitution is like a short introduction that explains the important beliefs and ideas our country is built upon.
The Preamble to the Indian Constitution reads as follows –
"WE, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA having solemnly resolved to constitute India into a SOVEREIGN SOCIALIST SECULAR DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC and to secure to all its citizens:
JUSTICE, social, economic and political;
LIBERTY of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship;
EQUALITY of status and of opportunity; and to promote among them all
FRATERNITY assuring the dignity of the individual and the unity and integrity of the Nation;"
.webp)
Preamble of Indian Constitution
The Preamble is very important for the Indian Constitution, like its soul.
The Preamble covers the four most important pillars of democracy i.e. liberty, justice, equality, and also fraternity.
- Justice – Being fair and unbiased is important in the legal system so that everyone can have equal access to it.
- Liberty – Liberty means everybody can say what they think without being punished for it.
- Equality – This means giving equal opportunities to everyone without treating anyone unfairly based on their religion, caste, gender, etc.
- Fraternity – In simpler terms, fraternity means that everyone should feel like they are brothers and sisters, and should work together even if they are not the same.
Fundamental Rights
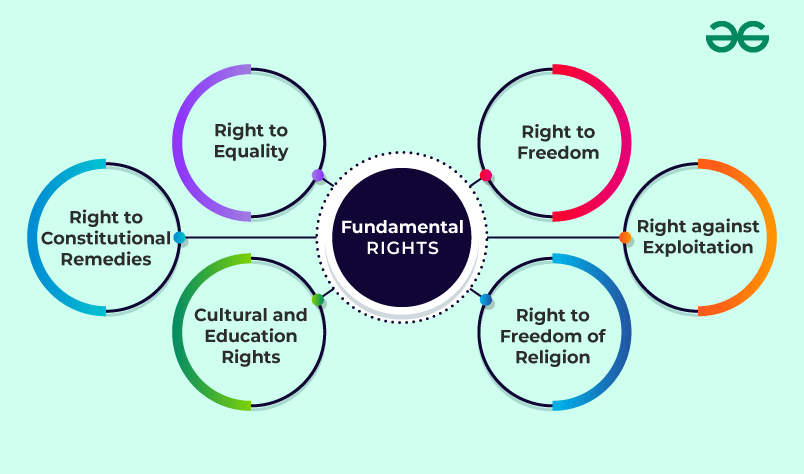
Do you know about Fundamental Rights? They are very important for Indian people! These rights are six things that every citizen can do, as written in the Indian Constitution. They give us basic protections and freedoms.
There are six basic rights that everyone has.
- The Right to Equality
- The Right to Freedom
- The Right against Exploitation
- Freedom of Religion
- Cultural and Educational Rights
- The Right to Constitutional Remedies
Fundamental Rights
Directive Principles of State Policy
Do you know about the Directive Principles of State Policy? They help the Indian state work towards making things fairer for everyone. Directive Principles cannot be enforced by law. However, the DPSPs still play an important role in the Constitution.
The Directive Principles talk about many things like helping people in society and making sure everyone gets the same pay for doing the same job. They have rules for:
- Promotion of social welfare
- Economic justice
- Health and Education
- Protection of the environment
- Gender equality
The Indian government is doing things to follow the rules they set and helping people who are not treated fairly, giving everyone free education and free healthcare, and taking care of the environment as well. They help the state make fair decisions and treat everyone equally.
Parliamentary System
Indian governments work based on the parliamentary system. In a parliamentary system, the leaders responsible for making decisions in the government called the executive branch, must answer to the group of lawmakers who make up the legislature, also known as the parliament. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the president of India and two houses –
- the Rajya Sabha (Council of States)
- the Lok Sabha (House of the People)
Parliament of India
People in India directly vote for the Lok Sabha members, but the Rajya Sabha members are elected by the State Legislative Assemblies by proportional representation. This is called the parliamentary system.
The parliamentary system of India also makes sure that the Executive, Legislature, and Judiciary are kept separate in their roles and powers which means no one can interfere in other organs’ functioning. Each organ of the government has its job to do, so no part becomes too strong or no part becomes too weak and everyone has equal power.
Separation of Powers
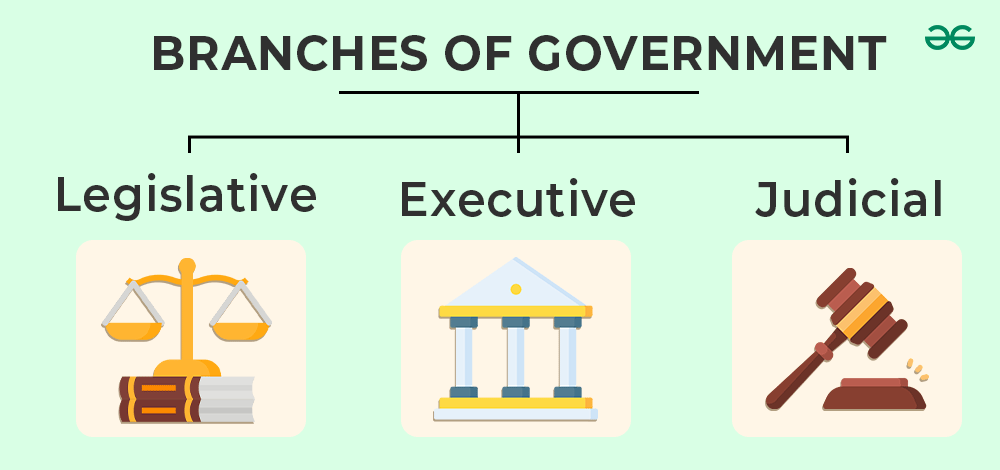
Do you want to know how power is shared by the different parts of government in India? The Indian Constitution has the separation of powers which is very important. India’s power is split into three parts called the executive, the legislature, and the judiciary. The separation of powers simply means that no single organ of the government has too much power means power imbalance does not exist and they all keep an eye on each other. It is important for the functioning of democracy that the government is transparent about its works and decisions.
Branches of Government
Executive – The group that enforces laws is called the executive branch. The executive branch makes sure rules from the government are followed and put into action.
Legislature – The group that creates laws is called the legislative branch. The Lok Sabha members are chosen by the people of India. But, the Rajya Sabha members are chosen by people who work in the State Legislative Assemblies. The lawmakers make rules and check if the leaders are doing their job properly.
Judiciary – The group that explains laws and settles arguments is called the judiciary. India’s most important court is called the Supreme Court and it leads the judiciary branch. The judiciary makes sure laws are understood and helps settle problems between people and the government. The Supreme Court can say if a law or action by the government is not okay with the Constitution. This is called “judicial review”.
Conclusion
We finished learning about the Provisions that make India a full-fledged constitution. It was an exciting journey! We studied the preamble, the freedoms that everyone should have, how the government should assist its citizens, and how leaders in power make decisions. These rules are very important for Indian democracy and for keeping people’s rights and freedoms safe.
The Constitution changes to match what society needs over time. The Constitution shows what Indian people want and hope for. We must all make sure it stays a symbol of democracy and freedom. Let’s keep studying the Constitution and work together to make a fairer world for everyone.
Never stop learning and discovering new things!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...