What is “Lean Product Development”? Principles and Benefits
Last Updated :
21 Mar, 2024
The goal of lean product development is to create goods more quickly while generating less waste. By doing away with the communication barriers that usually divide departments, it enhances conventional product development procedures. Lean organisations enable the product to develop and get better because every team works on it from start to finish. Five guiding concepts are used in lean development.
What is lean product development?
Lean product development prioritizes efficiency by minimizing resource use and focusing on delivering value to customers promptly. It avoids extensive upfront investments and lengthy planning phases common in conventional development approaches. Instead, Lean emphasizes iterative improvements based on continuous customer feedback, ensuring that the final product meets user needs effectively.
Here are a few important points of Lean Product Development:
- Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop: The product is built in small pieces, tested with real customers, and improved based on their feedback. This iterative process ensures that the product meets customer needs effectively.
- Agile development: Flexible and adaptive processes in Lean product development allow for quick adjustments based on new information or feedback. This agility helps teams stay responsive to customer needs and market changes, leading to more successful and customer-centric products.
- Data decision-making: In Lean product development, decisions are made by gathering feedback and data directly from customers. This approach ensures that the product meets their needs and preferences effectively. It also allows for continuous improvements based on real-world usage and customer insights.
How Does Lean Product Development Work
Lean development follows a core cycle:
- Ideate and prioritize: The process includes brainstorming ideas, identifying customer preferences, and prioritizing features based on their perceived value to customers. This helps ensure that the most important and beneficial features are developed first to meet customer needs effectively.
- Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Lean product development involves creating a simplified version of the product with essential features to gather feedback from users quickly. This early input helps refine the product and ensures that it meets customer needs effectively, leading to a more successful final product.
- Observe and learn: The Minimal Viable Product (MVP) involves observing how users engage with the product and gathering their feedback and comments. This data helps teams understand user behaviour and preferences, enabling them to make informed decisions about further product development and improvements.
- behaviourIterate and improve: The MVP helps identify what users like and dislike, leading to improvements such as adding valuable features and removing less useful ones. This continuous cycle of feedback and refinement ensures that the product aligns with user needs and preferences effectively.
How to Get Started with Lean Product Development
Here are some initial steps:
- Assemble a cross-functional team: Collaborating with team members from engineering, marketing, and design ensures a holistic approach to product strategy. By incorporating diverse perspectives, the strategy can address technical, market, and user experience aspects effectively, leading to a more successful product launch and development process.
- Clearly define your target audience: Understanding your target client helps in creating a product that specifically addresses their needs and preferences. This knowledge enables you to tailor the product features and design to better meet customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and success in the market.
- Identify the core problem you are solving: Identifying and highlighting our product’s value proposition and the problem it solves is crucial for attracting customers. This clear communication helps them see how your product can address their needs and why they should choose it over alternatives, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
How to Use Lean Product Development
Here are some key principles are includes:

How to Use Lean Product Development
- Prioritize user feedback: Consistently seek and incorporate user feedback during the project to ensure the product aligns with their needs. This iterative approach allows for continuous improvements and helps create a product that resonates with users, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Embrace experimentation: Stay flexible in trying out different ideas and adjusting them based on new information and feedback. This adaptable approach enables continuous improvement and leads to a product that better meets user needs, ultimately driving success and satisfaction.
- Focus on continuous improvement: Where you continuously improve and evolve your skills and knowledge. This mindset helps you stay adaptable and open to new ideas, leading to better outcomes and success in your projects.
Five principles of lean product development
Here are five principles of lean product development:
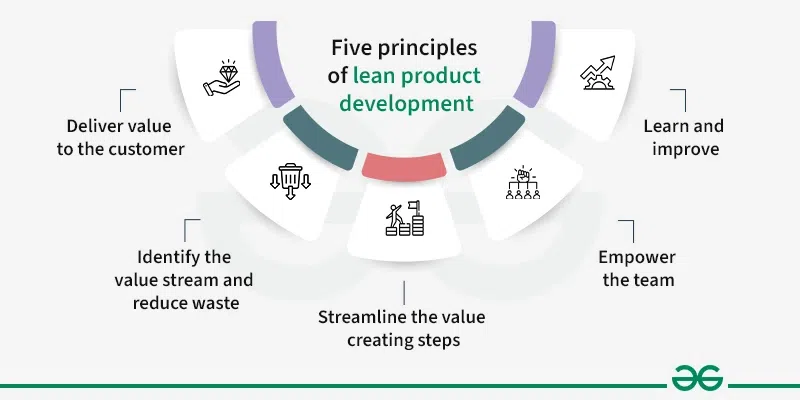
Five principles of lean product development
- Deliver value to the customer: Always prioritize meeting customer needs above all else in the development process. Every decision and choice should focus on creating a product that addresses their specific needs and resolves any issues they may have. This customer-centric approach ensures that the final product is tailored to their preferences, leading to higher satisfaction and success in the market.
- Identify the value stream and reduce waste: Design and the flowchart that outlines the development journey, focusing on steps that directly add value for customers. Remove any processes or tasks that don’t contribute to improving the product or meeting customer needs. This optimization effort aims to streamline operations, reduce unnecessary work, and allocate resources more effectively, resulting in a more efficient and customer centric development process that delivers higher quality products.
- Streamline the value creating steps: Traditional development involves passing work between teams, leading to communication problems and lack of accountability. In contrast, lean development includes all stakeholders from the start, allowing for diverse perspectives and early issue anticipation. Teams manage workflow to prevent bottlenecks and maintain focus, with a SCRUM Master overseeing this in SCRUM methodology. Lean teams start working early, even with incomplete information, to speed up development. This approach, inspired by Toyota, emphasizes parallel work to reduce overall project timelines effectively.
- Empower the team:In lean development, teams are trusted to organize themselves and given clear goals to achieve. This is because those who directly engage with customers understand their needs better and can manage projects more effectively. These teams often comprise members from different departments, such as designers, engineers, and marketers, working together on specific projects. They work independently in short cycles called sprints, lasting two to four weeks, to deliver tangible results. This approach allows for faster iteration and adaptation to customer feedback, leading to more successful and customer centric products. .
- Learn and improve: In lean product development, learning plays a crucial role, and organizations prioritize capturing and sharing knowledge to prevent redundant efforts. Techniques such as Knowledge centered Service (KCS) advocate for creating knowledge bases or internal wikis where lessons learned can be documented and shared. Digital product companies leverage user analytics to track user actions within their products, identifying areas for improvement in user experience. For instance, a fitness app team may analyze user screenflow to enhance button placement and overall usability. This continuous learning and improvement cycle ensures that products evolve to better meet user needs and preferences over time, leading to higher satisfaction and success in the market.
Benefits of Lean Product Development
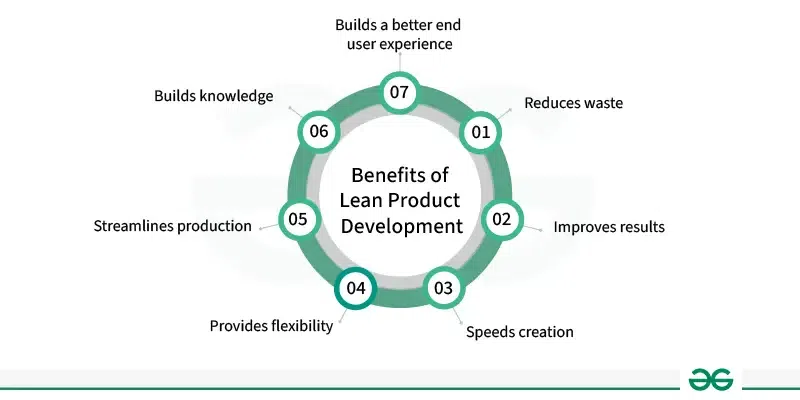
Benefits of Lean Product Development
- Reduces waste: The Lean methodology aims to minimize waste in materials and labor hours. This involves using technology and materials efficiently and following a structured process to finish designs. The goal is to reduce the number of steps in the process and constantly find ways to be more efficient.
- Improves results: Designs are tested and refined to improve both the product and production process. Benchmarking, which compares a business to its competitors, helps identify areas for improvement and gain a competitive advantage. This continuous improvement approach ensures that the final product meets customer needs effectively and keeps the business ahead in the market.
- Speeds creation: Lean methodology focuses on cutting down unnecessary process stages to make production faster and simpler. This streamlining drastically reduces the time required to create a product. By eliminating anything that doesn’t add value to the process, production becomes more efficient and effective, leading to better outcomes.
- Provides flexibility: In today’s dynamic economy, businesses need to adapt swiftly to changing conditions. Lean methodology offers testing and assessment options to ensure products meet evolving customer needs. This flexibility allows companies to make quick adjustments and remain competitive in the market.
- Streamlines production: Designing and manufacturing is a key aspect of lean product development. It involves creating products that are easy to reproduce during production. This improves productivity by refining and optimizing procedures for efficient manufacturing processes.
- Builds knowledge: In lean methodology, learning from errors and waste is essential. This knowledge is used to improve the current product and also refine the design process for future products. It enables creators to continuously enhance their approach, leading to better products and processes over time.
- Builds a better end user experience: Continuous improvement is central to lean philosophy, with user feedback driving enhancements in product design. This iterative approach is particularly effective in dynamic markets where customer preferences can change quickly. It enables businesses to stay agile and responsive to customer needs, ensuring competitiveness and long-term success.
Conclusion: Lean Product Development
In conclusion, Lean Product Development optimises workflows to quickly produce valuable goods that satisfy consumer demands. Teams can improve product-market fit and optimise operations by implementing Agile methodologies, prioritising user feedback, and iterating through Build-Measure-Learn cycles. By embracing cross-functional cooperation, concentrating on key challenges, and addressing targeted audiences, organisations guarantee effective, customer-focused development. The advantages encompass decreased waste, better outcomes, quicker output, adaptability, efficient procedures, acquisition of information, and improved user experiences. Lean implementation promotes competitiveness and adaptability, which leads to long-term success in dynamic marketplaces.
FAQs: Lean Product Development
What do you mean by lean development?
Lean development refers to a methodology focused on maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste in product development processes, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer value.
What is the lean approach to product development?
The lean approach to product development involves streamlining processes, eliminating waste, and prioritizing customer value through iterative cycles of Build-Measure-Learn, Agile practices, and data-driven decision-making.
What are the 3 types of lean?
The three types of lean are Lean Manufacturing, Lean Services, and Lean Product Development, each tailored to optimize specific processes within manufacturing, service industries, and product development, respectively.
What are the 5 principles of lean?
The five principles of lean are: Deliver value to the customer, Identify the value stream and reduce waste, Streamline the value-creating steps, Empower the team, and Learn and improve continuously. These principles guide organizations in optimizing processes, maximizing efficiency, and delivering value to customers effectively.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...