What is Demiltarized Zone?
Last Updated :
21 Aug, 2022
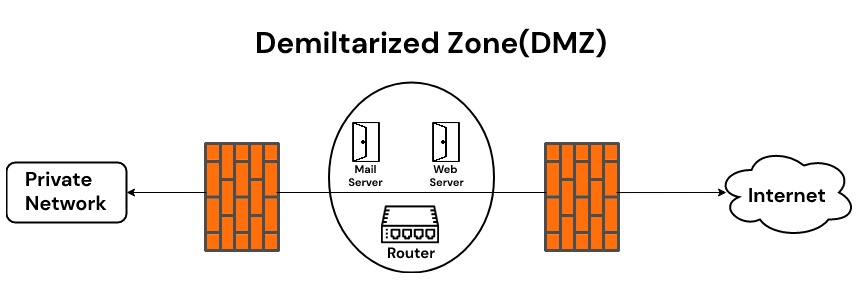
Demilitarized zones, or DMZ for short, are used in cybersecurity. DMZs separate internal networks from the internet and are often found on corporate networks. A DMZ is typically created on a company’s internal network to isolate the company from external threats. While the name might sound negative, a DMZ can be a helpful tool for network security.
The DMZ is a network barrier between the trusted and untrusted network in a company’s private and public network. The DMZ acts as a protection layer through which outside users cannot access the company’s data. DMZ receives requests from outside users or public networks to access the information, website of a company. For such type of request, DMZ arranges sessions on the public network. It cannot initiate a session on the private network. If anyone tries to perform malicious activity on DMZ, the web pages are corrupted, but other information remains safe.
The goal of DMZ is to provide access to the untrusted network by ensuring the security of the private network. DMZ is not mandatory, but a better approach to use it with a firewall.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| It provides access to external users by securing the internal sensitive network. |
Various vulnerabilities can be found in DMZ System’s services. |
| A DMZ can be used with a combination of a firewall & router, which as a result provide high security. |
If an attacker successfully cracks the DMZ system, they may access your confidential information. |
| By implementing DMZ, only the data that is intended to be visible publicly is displayed. the rest is hidden and secured. |
An attacker having are authenticated data can access the system as an authorized user. |
| DMZ enables web server, email servers etc. to be accessible on the internet simultaneously protecting it with a firewall. |
The data provided on a public network to the external networks can be leaked or replicated. |
Key features:
- A DMZ provides a buffer from the outside world for your computer systems. When you create a network, you must decide where your computer systems will reside.
- Creating a buffer zone between your systems and the internet allows you to function normally without being susceptible to external attacks. Keeping your internal systems inside a DMZ also makes it difficult for hackers to steal data or cause disruptions on company networks. For this reason, most organizations use a DMZ when creating secure computer systems.
- A DMZ provides a target for ethical hackers. Hackers often seek out companies with weak computer security; this is why many organizations use a DMZ to protect their internal systems.
- Companies that have strong security measures typically don’t create vulnerabilities in their networks by demilitarizing zones on their own computers or in their IT environments.
- The DMZ makes it easy for ethical hackers to find vulnerabilities and gain access to designated targets once they’re inside the buffer zone. By knowing which systems have weak security and then targeting them, ethical hackers can perform necessary maintenance without damaging company networks further.
Conclusion:
Demilitarized zones provide buffers between internal computers and the internet. They can also be used as targets when performing hacking tasks such as pentesting or social engineering. Finally, demilitarized zones may also be used for physical penetration tests.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...