Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the total cost a business incurs to acquire a new customer. It encompasses all expenses related to marketing, advertising, and sales efforts aimed at bringing a customer to your doorstep. Calculating CAC is like taking the pulse of your customer acquisition strategy, and it’s an indispensable metric for any business.
In the dynamic landscape of business and product management, understanding and effectively managing your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is paramount. CAC is a metric that can make or break your venture, and in this article, we’ll delve into what CAC is, why it’s important, how it affects your business, how to calculate it with an example, the relationship between Lifetime Value (LTV) and CAC, strategies to reduce CAC, and tips for improving this critical metric.

What is Customer Acquisition Cost
What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)?
What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the total cost a business incurs to acquire a new customer. It encompasses all expenses related to marketing, advertising, and sales efforts aimed at bringing a customer to your doorstep. Calculating CAC is like taking the pulse of your customer acquisition strategy, and it’s an indispensable metric for any business.
Importance of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) in Product Management

Importance of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Cost Efficiency
Product managers may carefully evaluate the cost-effectiveness of their client engagement tactics according to the crucial statistic known as CAC. It is crucial in determining the effectiveness of different marketing channels and strategies. Product managers may decide which strategies are most effective in acquiring new customers by understanding the CAC associated with various techniques. Additionally, CAC supports the most effective utilisation of resources by allowing product managers to allocate marketing and sales expenditures to strategies and channels with the lowest CAC, maximising return on investment (ROI).
Budget Allocation
Product managers may allocate budget funds wisely by using CAC data as guidance. Product managers may easily set priorities and allocate resources thanks to the helpful data provided by CAC. They can allocate financial resources to the channels and methods that produce the greatest returns by determining the most cost-effective client acquisition strategies. As a result, this allocation technique enables businesses to maximise ROI and guarantee that marketing and sales expenditures are fully utilised, having significant effects.
Pricing Strategy
Within the context of product management, CAC is a crucial variable that affects pricing tactics. It encourages establishing prices for products and services to take into account the expense of obtaining each consumer. This guarantees that pricing both pays for the costs invested during client acquisition and boosts the total profitability of the business. Maintaining competitiveness and attaining sustained profitability in a dynamic market environment depend on finding the correct balance between acquisition costs and revenue generation.
The CAC offers useful insights into the expenses related to obtaining and keeping consumers. Product managers can prioritise products and improvements targeted at increasing consumer satisfaction after taking this data into consideration. It is important to do this because happy consumers are more likely to stick around, make repeat purchases, and lower turnover. Product managers may guarantee that their product development efforts are in line with customer expectations and are crucial in maintaining existing customers while justifying the price of acquisition by making data-driven decisions based on CAC.
Scaling
Scalability is the primary concern for product managers, and CAC is essential to ensuring long-term growth. To preserve long-term profitability as a firm grows, CAC must be maintained or decreased. To support this expansion, product managers are leading the charge to optimise the user acquisition process. Companies may grow successfully and show that they can attract clients at a low cost by controlling CAC correctly. This effectiveness is a defining characteristic of carefully planned growth plans, providing both ongoing development and long-term success.
What does Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) include?
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) comprises various expenses directly associated with acquiring new customers. These expenses typically include:

What does Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) include
- Marketing Expenses: Costs related to marketing efforts aimed at attracting and converting potential customers. This includes advertising costs across various platforms (online, print, TV, radio), content creation, social media marketing, email campaigns, search engine marketing, and influencer partnerships.
- Sales Costs: Expenses tied to the sales process, such as salaries, commissions, bonuses, and training for the sales team, as well as the cost of sales tools and software used for customer acquisition.
- Promotional Costs: Any promotional activities specifically aimed at acquiring new customers, such as discounts, special offers, referral programs, or free trials.
- Campaign Costs: Expenses associated with specific marketing campaigns or initiatives, including costs for events, sponsorships, partnerships, or other targeted promotional activities aimed at customer acquisition.
- Technology and Tools: Costs related to customer relationship management (CRM) systems, marketing automation tools, analytics software, and other technologies used to manage and track customer acquisition efforts.
- Content Creation: Costs incurred in creating marketing materials, such as website content, blog posts, videos, graphics, and other content designed to attract and engage potential customers.
- Testing and Optimization: Expenses related to A/B testing, market research, and other optimization efforts aimed at improving the effectiveness of customer acquisition strategies.
How Does Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) Affect Your Business?
CAC affects your business in several ways:
- Profitability : CAC has a direct impact on your profitability. If your CAC is too high, it may take a long time for each customer to become profitable, affecting your bottom line. Conversely, a low CAC can lead to quicker profitability.
- Financial Health: CAC directly affects your company’s financial health. Higher CAC means you’re spending more to acquire each customer, which can strain your cash flow. In contrast, a lower CAC ensures that you’re efficiently using your resources to attract customers.
- Scaling: A well-optimized CAC allows you to scale your business more effectively. When you have a low CAC, you can invest more in customer acquisition without significantly increasing your marketing budget. This is crucial for businesses looking to expand.
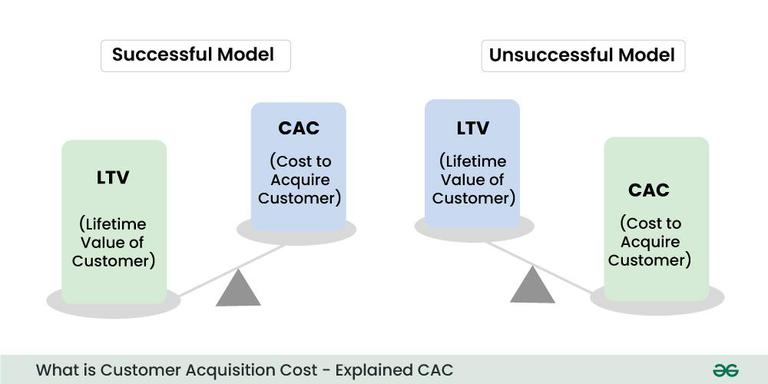
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): The relationship between CAC and LTV is pivotal. To remain profitable, the cost of acquiring a customer should be lower than the revenue that customer generates during their relationship with your business. Calculating and optimizing this ratio is key to long-term success.
- Competitive Advantage: A lower CAC can be a competitive advantage. You can either offer more competitive prices to your customers or allocate resources to other aspects of your business, such as product development or customer support.
- Investor Attraction: Startups and businesses seeking investment need to demonstrate a clear understanding of their CAC. Investors often look for companies with a reasonable CAC and solid growth potential.
To calculate CAC, use this formula:
-Formula-01.webp)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC = (Cost of Sales and Marketing) / (Number of New Customers Acquired)
Example : Let’s say you spent $10,000 on marketing and acquired 100 new customers. Your CAC would be $100.
What is Customer Lifetime Value(LTV)?
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) is a metric that represents the total value a customer is expected to generate for a business over the entire duration of their relationship. It calculates the potential revenue a customer will bring in throughout their engagement with the company.
LTV takes into account various aspects, including:
- Purchase History: The total amount a customer spends on products or services over their entire relationship with the business.
- Repeat Purchases: If customers tend to make multiple purchases, the LTV incorporates these additional transactions.
- Retention Period: The duration a customer typically stays engaged with the business. This can vary significantly between industries and businesses.
How to Calculate LTV/CAC and why it’s useful?
The LTV/CAC ratio is a valuable metric used to assess the health of a business by comparing the Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) to the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). This ratio helps in evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of acquiring and retaining customers relative to the cost incurred in acquiring them.
To calculate the LTV/CAC ratio:
- Calculate Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): Determine the LTV using a formula that estimates the total value a customer will bring to the business over their entire relationship, as discussed earlier.
- Calculate Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Determine the cost associated with acquiring a customer. This includes marketing, sales, and other expenses related to customer acquisition within a specific period.
- Divide LTV by CAC: Once you have both values, divide the Customer Lifetime Value by the Customer Acquisition Cost.
LTV/CAC Ratio=Customer Lifetime Value/ Customer Acquisition Cost
The LTV/CAC ratio offers several benefits:
- Assessment of Efficiency: A ratio above 1 indicates that the value a customer brings over their lifetime is higher than the cost incurred in acquiring them. A higher ratio generally indicates more efficient customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- Health of Business Model: It helps assess the overall health of a business by providing insights into the balance between the cost of acquiring customers and the value they bring. A ratio that’s steadily improving or consistently above a certain threshold is indicative of a healthy business model.
- Decision-Making: The ratio guides decisions regarding resource allocation, marketing budgets, and strategies. It helps in optimizing spending on customer acquisition and retention efforts by focusing on channels or strategies that yield higher returns relative to their costs.
- Investor Confidence: For startups and businesses seeking investment, a strong LTV/CAC ratio can boost investor confidence. It demonstrates the company’s ability to acquire and retain customers efficiently, potentially influencing valuation and investment decisions.
Steps to Reduce Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
.jpg)
Steps to Reduce Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
1. Refine Target Audience
Identify and focus on the specific customer segments that are most likely to convert. Understanding their demographics, behaviors, and preferences allows you to tailor your marketing efforts more efficiently.
Benefits: By using this technique, you may more effectively customise your marketing efforts. Understanding your target audience’s demographics, behaviours, and preferences can help you develop marketing efforts that are highly relevant to, highly targeted, and more likely to ring true with potential consumers.
2. Optimize Conversion Paths
Ensure that the journey from a potential customer’s first interaction with your brand to conversion is as straightforward as possible. By streamlining this process, you increase the chances of converting at a lower cost.
Benefits: You may boost the likelihood of converting new clients at a reduced cost by optimising the conversion process. This is essential for enhancing the overall user experience and maximising the return on investment for marketing initiatives.
3. Leverage Content Marketing
High-quality, valuable content can attract customers at a lower cost. By addressing the pain points and questions of your target audience, you can establish your brand as a helpful resource.
Benefits: Your target audience will get attracted to high-quality content. You may position your brand as a beneficial and reliable resource by answering their concerns, inquiries, and interests. Potential consumers are drawn in by this, and over time, brand loyalty and authority are developed as well.
4. Customer Retention
Investing in keeping existing customers happy can reduce the need for acquiring new ones. Satisfied customers are more likely to make repeat purchases and refer others.
Benefits: It may be economical to make an investment in client retention. Customers who are satisfied are more likely to make subsequent purchases, increasing the customer lifetime value. They may also turn into brand promoters, spreading the word about you and growing your clientele through word-of-mouth advertising.
Top Tips to Reduce Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
-01.webp)
Top Tips to Reduce Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
1. Efficient Use of Channels
Identify the marketing channels that deliver the most cost-effective customer acquisition. By concentrating your efforts on these channels, you can maximize the return on investment.
2. Customer Advocacy
Encourage satisfied customers to refer new customers to your business. Word-of-mouth marketing from happy customers can be a highly effective and low-cost method for acquisition.
3. Data-Driven Decisions
Use data and analytics to continuously refine your customer acquisition strategy. Data-driven insights allow you to optimize your marketing efforts for the best results and lowest costs.
4. Build Strong Google Ads Campaigns
To attract clients economically, efficient Google Ads campaigns are crucial. It entails thorough keyword research, persuading ad text, and calculated bidding. Your advertising budget will be used effectively if these campaigns are routinely changed.
5. Prioritize appropriate audiences
Target the most promising consumer categories to cut acquisition expenses. To ensure effective resource allocation, use audience targeting in your marketing efforts to concentrate on the characteristics or actions that are most likely to result in conversions.
6. Improve Your Conversion Rate
Conversion rate optimisation is essential for cost-effective acquisition. By improving the user experience, optimising landing pages, and using A/B testing to determine what generates higher conversion rates, you may increase client acquisition without raising marketing costs.
Examples of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) varies significantly across industries, businesses, and marketing strategies. Here are a few examples to provide a range of CAC:
- E-commerce Company
- Software as a Service (SaaS) Company
- Subscription-based Business
- Retail Chain
Conclusion: Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a pivotal metric in business and product management. Understanding its importance, measuring and comparing it to Lifetime Value (LTV), and implementing strategies to reduce CAC can help businesses thrive. In the competitive world of customer acquisition, efficiently managing your CAC can make all the difference. It’s not just a metric; it’s a roadmap to sustainable growth and long-term success.
FAQs on Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
1. What is meant by customer acquisition cost?
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) refers to the total cost a business incurs to acquire a new customer. It encompasses all expenses related to marketing, sales, and other activities aimed explicitly at bringing in new customers within a specific period.
2. Why is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) important?
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a important for businesses due to several key reasons:
- Profitability Assessment
- Resource Allocation
- Performance Measurement
- Business Growth Strategies
3. What is the goal of CAC in marketing?
The goal of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) in marketing is to optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of acquiring new customers while maintaining profitability and maximizing the long-term value these customers bring to the business.
4. What are good customer acquisition costs?
The notion of a “good” customer acquisition cost (CAC) can vary widely based on factors such as industry, business model, target market, and the specific goals of a company. However, generally speaking, a lower CAC is often considered more favorable as it implies more cost-efficient customer acquisition.
5. How is CAC calculated?
To calculate CAC, use this formula:
CAC = (Cost of Sales and Marketing) / (Number of New Customers Acquired)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...