Ways To Save Python Terminal Output To A Text File
Last Updated :
26 Feb, 2024
Python provides various methods for redirecting and saving the output generated in the terminal to a text file. This functionality can be useful for logging, debugging, or simply capturing the results of a script. In this article, we’ll explore different ways to save Python terminal output to a text file.
Save Python Terminal Output to a Text File in Python
Below are some of the ways by which we can save Python terminal output to a text file in Python:
Using the > Operator in the Terminal
The > operator is used in the terminal to redirect the standard output to a file. This approach is simple and effective for quickly saving the output.
Python3
for i in range(10):
print("printing line ", i)
|
Command
python script.py > output.txt
Output:
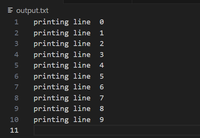
Using the tee Command
The tee command is used to redirect output to both the terminal and a file. This approach is useful for real-time monitoring in the terminal while saving the output to a file.
Python3
for i in range(10):
print("printing line ", i)
|
Command
python script.py | tee output.txt
Output:
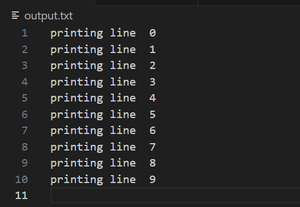
Redirecting sys.stdout in the Python Script
The sys.stdout stream is redirected to a file using the with open(...) block. This approach allows programmatically controlling where the output goes within the script.
Python3
import sys
original_stdout = sys.stdout
with open('output.txt', 'w') as f:
sys.stdout = f
for i in range(10):
print("printing line ", i)
|
Output:
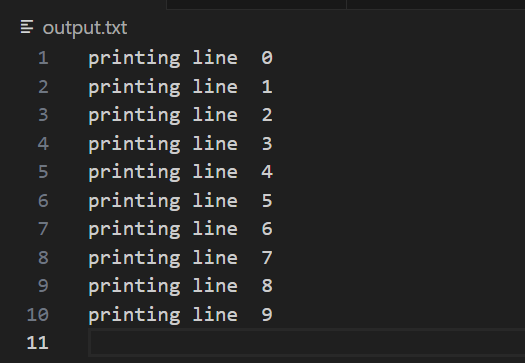
Using the logging Module
The logging module is used to configure a log file. This approach is beneficial for more extensive projects where logging is a standard practice.
Python3
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='output.log', level=logging.INFO)
for i in range(10):
logging.info("printing line %d", i)
|
Output:
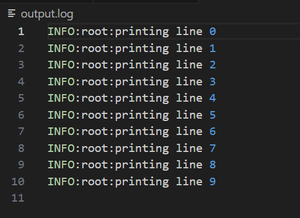
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...