Vindhya Range : River, Climate, & Important Landforms
Last Updated :
20 Mar, 2024
The Vindhya range is a lengthy series of mountains in central India that forms the southern edge of the central uplands. The river spans more than 675 miles, beginning in Gujarat in the west, passing through Madhya Pradesh, and ending in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, where it merges into the Ganges River.
Towards Bihar, the range breaks into two sections: one section runs north of the Son River, and the other section runs between the Son and Narmada Rivers, finally reaching the Satpura Range at the Maikala Range or the Amarkantak Plateau.
In this article, we will discuss the Vindhyan Range in detail.
Let’s start.
Overview Of Vindhya Range
| Aspect |
Description |
| Location |
Central India, spanning across several states including Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra. |
| Length |
Approximately 1,050 kilometers (650 miles) long. |
| Width |
Varies, with an average width of about 300 kilometers (190 miles). |
| Highest Peak |
Dhupgarh, located in the Satpura Range (a part of the Vindhya Range), with an elevation of approximately 1,350 meters. |
| Geology |
Made up of sedimentary rocks, including sandstone, limestone, and shale. |
| Biodiversity |
Rich biodiversity, with forests, grasslands, and numerous wildlife species. |
| Cultural Significance |
Historically significant region with mentions in ancient Indian texts and mythology. |
Vindhya Range
- Situated in west-central India, the Vindhya Range, additionally referred to as Vindhyachal, is made up of plateaus, hills, highlands, and mountain ridges.
- The Vindhyas comprise a varied and widespread collection of landforms, in contrast to a conventional mountain range.
- The range holds significant importance in Indian mythology and history.
- The Vindhyas include various hill systems, historically including parts now identified as the Satpura Range.
- The escarpment and its hills expansions in Madhya Pradesh to the north of the Narmada River are commonly referred to as the “Vindhya Range”.
- With varying heights, the range crosses many states: Chhattisgarh to the east, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar to the north, and Gujarat to the west.
- The name “Vindhya” comes from the Sanskrit “vaindh,” meaning to obstruct, reflecting a mythological legend.
- Similarly, “Vindhyachala” comes from “achala,” meaning “mountain” in Hindi.
- Ancient texts describe the Vindhyas as the southern boundary of Āryāvarta, the early home of the Indo-Aryan people.
- Today, the range still marks a division between northern and southern India, even though Indo-Aryan languages have spread beyond it.
- There’s some disagreement on how high the Vindhyas are, with estimates ranging from 300 to 650 meters across 1,200 kilometers, and the tallest point never going over 700 meters.
- The highest spot is Sad-bhawna Shikhar (Goodwill Peak), which is 752 meters high, near Singrampur in the Damoh district.
- Amarkantak was once considered part of the Vindhyas but is now seen as belonging to the Maikal Range, which is an extension of the Satpuras
Vindhya Range Map
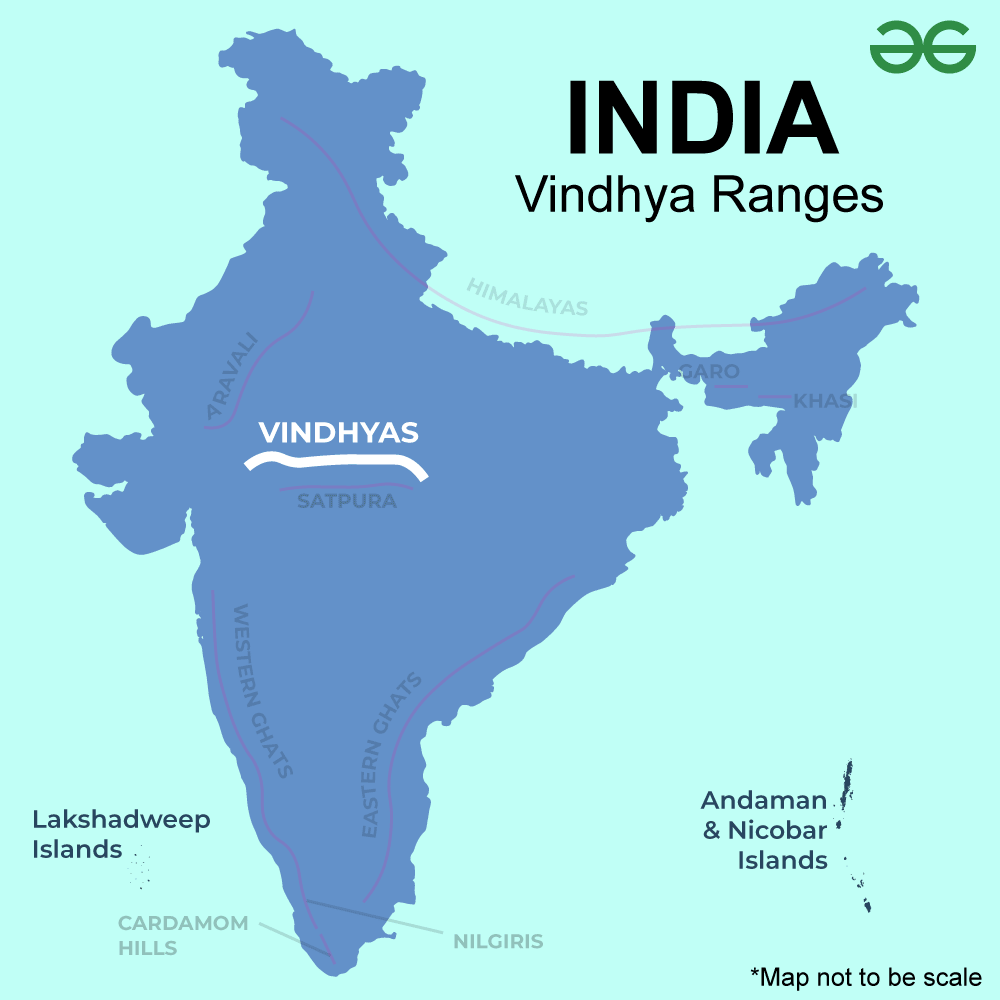
Vindhya Range
Vindhya Range – Rivers
- The Vindhya Range is really important because it’s the starting point for many rivers, including the Narmada and Son, which people rely on for water to farm, drink, and even for electricity.
- The Narmada River flows towards the west and separates North and South India, while the Son River flows east and helps farmers in Bihar and Uttar Pradesh since it joins the Ganges River.
- Other rivers like the Chambal, Betwa, Dhasan, Sunar, Ken, Tamsa, Kali Sindh, and Parbati also start in the Vindhyas and are important for the area around the Ganga and Yamuna rivers.
- These rivers from the north side of the Vindhyas meet many needs of the people living there.
- The south side of the Vindhyas has the Narmada and Son rivers starting from the Maikal hills, which are part of the Satpuras but used to be considered part of the Vindhyas.
Vindhya Range – Climate
- The weather near the Vindhya Mountains changes a lot from one place to another.
- It gets hotter in the lower areas and valleys close to the Deccan Plateau and cooler up in the mountains.
- Thanks to the good amount of rain from the monsoon winds, the mountains have a lot of different plants and animals.
- Most of the area is covered with forests that lose their leaves, which happens because of the seasonal rains followed by a long dry period.
- Trees like teak, sal, and bamboo are pretty common here.
- The wildlife includes big brown deer, bison, spotted deer, wild buffalo, leopards, and blackbucks. So, there’s a rich variety of life in the Vindhya Mountains. However, the environment there is getting worse because of things people do.
- The Vindhya Range is home to the UNESCO World Heritage site known as the Bhimbetka rock shelters, which include over 30,000-year-old cave paintings.
- The landscape additionally features plateaus, gorges, and valleys.
- Some famous sites are the Amarkantak Plateau, which is the source of the Narmada and Son rivers, and Raneh Falls, which is renowned for its limestone gorge.
- The range splits into branches east of Malwa, with the eastern Vindhyas comprising numerous chains.
- The southern chain links the Son and Narmada rivers to the Satpura Range at the Maikal Hills in Amarkantak.
- The northern chain, including the Bhander Plateau and Kaimur Range, stretches north of the Son River.
- This area spans from the former Vindhya Pradesh to the Kaimur district in Bihar.
- The Panna range, part of the Vindhya, crosses Bundelkhand.
- The central northern part of the range is known as the Vindhyan tableland or the Rewa-Panna plateau.
Significance of Vindhya Range
- The Vindhya Range is important for many reasons.
- It separates North and South India and is known for its diverse languages, cultures, and natural surroundings.
- The mountains are also rich in minerals, boosting the mining industry.
- With a wide range of animals and plants, the Vindhya Range offers various types of landscapes, from scrublands to forests.
- It’s considered one of India’s seven sacred mountain ranges and marks a division between the Deccan plains to the south and the Indo-Gangetic plains to the north, although it’s smaller and not as rugged as other mountain ranges.
- The mountains influence the local weather by blocking winds, which can make the climate tougher.
- Rivers that flow into the Ganges and the Narmada start in the Vindhyas. The area is known for its sandstone, used in building ancient Buddhist structures in Sanchi and temples in Khajuraho.
Conclusion on Vindhyan Range
The Vindhya Range in India is famous for its stunning landscapes, lots of animals, and rich history. It attracts all kinds of visitors, from those who love history and adventure to those who just want to soak in nature’s beauty. This range is home to beautiful rivers, has a variety of weather, and its physical features stand out, making it a key part of India’s nature. More than just a place on a map, the Vindhyas are important for culture and the environment, affecting many people’s lives. They show how different things can come together in harmony, which is a big part of what makes India special. The Vindhyas are where many rivers start and they are a safe place for lots of different animals.
People Also View:
- 7 Major Mountain Ranges in India
- Types of Mountain : Formation, Characteristics, Diagram
- Plateaus in India – Meaning, Types & Importance
FAQs on Vindhya Range
Where are Vindhya Range located?
The Vindhya Range stretches across central India from Gujarat to the edge of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, separating the area with its hills and plateaus and lying next to the Narmada River.
Which is the highest peak in Vindhya Range in India?
The highest peak in the Vindhya Range in India is Sad-bhawna Shikhar (Goodwill Peak), which reaches an elevation of 752 meters (2,467 feet) above sea level.
Is Vindhya range in Maharashtra?
No, the Vindhya Range is not located in Maharashtra. It primarily stretches across central India, covering parts of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Gujarat.
What is the Vindhya range famous for?
The Vindhya Range is known for its beautiful hills and plateaus full of different plants and animals, and it’s historically and mythically important as it marks the boundary between north and south India.
Which river is located in Vindhya Range?
The Narmada River is one of the prominent rivers flowing near the Vindhya Range, running roughly parallel to it in the northern part of the range in central India.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...