Total number of different staircase that can made from N boxes
Last Updated :
22 Aug, 2022
Given N boxes of unit dimension, i.e. (1×1 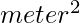 ). The task is to find the total number of different staircases that can be made from those boxes with the following rules:
). The task is to find the total number of different staircases that can be made from those boxes with the following rules:
- The staircase must be in strictly descending order.
- Each staircase contains at least two steps. ( The total steps are equal to the breadth of the staircase.)
Examples:
Input : N = 5
Output : 2
The two staircases are the following :

Input : N = 6
Output : 3
The three staircases are the following :

If we consider total steps = 2, we can observe the fact that the number of staircases is incremented by 1 if N is incremented by 2. We can illustrate the above things from the following image:

Now, if the total steps are greater than 2 (assume, total steps = K), then we can take this thing as first create a base (base requires boxes equal to the total steps) for the staircase and put another staircase on it of steps size K and K – 1 have boxes N – K. (because K boxes already used to create base). Thus, we can solve this problem using bottom-up dynamic programming.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int countStaircases(int N)
{
int memo[N + 5][N + 5];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j++) {
memo[i][j] = 0;
}
}
memo[3][2] = memo[4][2] = 1;
for (int i = 5; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 2; j <= i; j++) {
if (j == 2) {
memo[i][j] = memo[i - j][j] + 1;
}
else {
memo[i][j] = memo[i - j][j] +
memo[i - j][j - 1];
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
answer = answer + memo[N][i];
return answer;
}
int main()
{
int N = 7;
cout << countStaircases(N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int countStaircases(int N)
{
int [][] memo=new int[N + 5][N + 5];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j++) {
memo[i][j] = 0;
}
}
memo[3][2] = memo[4][2] = 1;
for (int i = 5; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 2; j <= i; j++) {
if (j == 2) {
memo[i][j] = memo[i - j][j] + 1;
}
else {
memo[i][j] = memo[i - j][j] +
memo[i - j][j - 1];
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
answer = answer + memo[N][i];
return answer;
}
public static void main(String [] args)
{
int N = 7;
System.out.println(countStaircases(N));
}
}
|
Python 3
def countStaircases(N):
memo = [[0 for x in range(N + 5)]
for y in range(N + 5)]
for i in range(N + 1):
for j in range (N + 1):
memo[i][j] = 0
memo[3][2] = memo[4][2] = 1
for i in range (5, N + 1) :
for j in range (2, i + 1) :
if (j == 2) :
memo[i][j] = memo[i - j][j] + 1
else :
memo[i][j] = (memo[i - j][j] +
memo[i - j][j - 1])
answer = 0
for i in range (1, N + 1):
answer = answer + memo[N][i]
return answer
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 7
print (countStaircases(N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int countStaircases(int N)
{
int [,] memo = new int[N + 5, N + 5];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j++)
{
memo[i, j] = 0;
}
}
memo[3, 2] = memo[4, 2] = 1;
for (int i = 5; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 2; j <= i; j++)
{
if (j == 2)
{
memo[i, j] = memo[i - j, j] + 1;
}
else
{
memo[i, j] = memo[i - j, j] +
memo[i - j, j - 1];
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
answer = answer + memo[N, i];
return answer;
}
public static void Main()
{
int N = 7;
Console.WriteLine(countStaircases(N));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function countStaircases($N)
{
for ($i = 0; $i <= $N; $i++)
{
for ($j = 0; $j <= $N; $j++)
{
$memo[$i][$j] = 0;
}
}
$memo[3][2] = $memo[4][2] = 1;
for ($i = 5; $i <= $N; $i++)
{
for ($j = 2; $j <= $i; $j++)
{
if ($j == 2)
{
$memo[$i][$j] = $memo[$i - $j][$j] + 1;
}
else
{
$memo[$i][$j] = $memo[$i - $j][$j] +
$memo[$i - $j][$j - 1];
}
}
}
$answer = 0;
for ($i = 1; $i <= $N; $i++)
$answer = $answer + $memo[$N][$i];
return $answer;
}
$N = 7;
echo countStaircases($N);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function countStaircases(N)
{
let memo=new Array(N + 5);
for(let i=0;i<N+5;i++)
{
memo[i]=new Array(N+5);
for(let j=0;j<N+5;j++)
{
memo[i][j]=0;
}
}
for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j <= N; j++) {
memo[i][j] = 0;
}
}
memo[3][2] = memo[4][2] = 1;
for (let i = 5; i <= N; i++) {
for (let j = 2; j <= i; j++) {
if (j == 2) {
memo[i][j] = memo[i - j][j] + 1;
}
else {
memo[i][j] = memo[i - j][j] +
memo[i - j][j - 1];
}
}
}
let answer = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++)
answer = answer + memo[N][i];
return answer;
}
let N = 7;
document.write(countStaircases(N));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(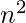 ).
).
Auxiliary Space: O(n ^ 2)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...