Sum of sum-series of first N Natural numbers
Last Updated :
25 Jul, 2022
Given a natural number n, find the sum of the sum-series of the first N natural number.
Sum-Series: is sum of first N natural numbers, i.e, sum-series of 5 is 15 ( 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 ).
| Natural number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Sum of natural number (sum-series) | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 21 |
| Sum of sum-series | 1 | 4 | 10 | 20 | 35 | 56 |
Example:
Input: N = 5
Output: 35
Explanation:
Sum of sum-series of {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} i.e. {1 + 3 + 6 + 10 + 15} is 35.
Input: N = 2
Output: 4
Explanation:
Sum of sum-series of {1, 2} i.e. {1 + 3} is 4.
Simple approach:
Find sum series for every value from 1 to N and then add it.
- Create a variable Total_sum to store the required sum series.
- Iterate over the number from 1 to N
- Find sum-series of every value by using the formulae sum = (N*(N + 1)) / 2
- Add the value to Total_sum
- In the end, print the value stored in Total_sum.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
static long sumOfSumSeries(int N)
{
long sum = 0L;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
sum = sum + (i * (i + 1)) / 2;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int N = 5;
cout << sumOfSumSeries(N);
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static long sumOfSumSeries(int N)
{
long sum = 0L;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
sum = sum + (i * (i + 1)) / 2;
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5;
System.out.println(sumOfSumSeries(N));
}
}
|
Python3
def sumOfSumSeries(N):
_sum = 0
for i in range(N + 1):
_sum = _sum + (i * (i + 1)) // 2
return _sum
N = 5
print(sumOfSumSeries(N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static long sumOfSumSeries(int N)
{
long sum = 0L;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
sum = sum + (i * (i + 1)) / 2;
}
return sum;
}
public static void Main()
{
int N = 5;
Console.Write(sumOfSumSeries(N));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function sumOfSumSeries(N)
{
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
sum = sum + (i * (i + 1)) / 2;
}
return sum;
}
let N = 5;
document.write(sumOfSumSeries(N));
</script>
|
Time complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Efficient approach:
Total_sum of the above series can be calculated directly by using the below formulae:
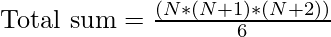
where N is the natural number
Proof of the above formula:
Lets assume N = 5
- Then the sum is sum of all the below elements in the table, let’s call this “result”
let’s populate the empty cells with the same value in other columns, lets’s call this “totalSum“
-
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
As sum of N numbers is repeated N times
totalSum = N * [(N*(N + 1))/2]
populated data = (1 times * 2) + (2 times * 3) + (3 times * 4) + (4 times * 5)
= 1*2 + 2*3 + 3*4 ……… +(N-1)*N
=[(N-1) * (N) * (N+1)]/3
- Since,
result = totalSum – populatedData
= N * [(N*(N+1))/2] – [(N-1) * (N) * (N+1)]/3
= (N*(N+1)*(N+2))/6
- Therefore
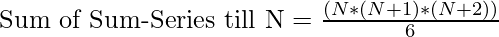
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
long sumOfSumSeries(int n)
{
return (n * (n + 1) * (n + 2)) / 6;
}
int main ()
{
int N = 5;
cout << sumOfSumSeries(N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static long sumOfSumSeries(int n)
{
return (n * (n + 1) * (n + 2)) / 6;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5;
System.out.println(sumOfSumSeries(N));
}
}
|
Python3
def sumOfSumSeries(n):
return (n * (n + 1) * (n + 2)) // 6
N = 5
print(sumOfSumSeries(N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static long sumOfSumSeries(int n)
{
return (n * (n + 1) * (n + 2)) / 6;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5;
Console.Write(sumOfSumSeries(N));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function sumOfSumSeries(n)
{
return (n * (n + 1) * (n + 2)) / 6;
}
let N = 5;
document.write(sumOfSumSeries(N));
</script>
|
Time complexity: O(1), considering multiplication, addition & division takes constant time.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...