Solanaceae, Fabaceae, Liliaceae: Family Description
Last Updated :
23 Apr, 2024
Solanaceae, Fabaceae, and Liliaceae belong to the flowering plant group. Fabaceae and Solanaceae are dicotyledon plants whereas Liliaceae are monocot plants. Solanaceae and Fabaceae are dicotyledon plants with tap root systems, whereas the Liliaceae plants are monocotyledons with fibrous root systems. Fabaceae occupies the third largest family position in the Plant Kingdom and it is one of the economically important families also called the legume family. Solanaceae known as the nightshade or potato family is most commonly used by humans. Liliaceae is called the lily family and is mostly known for its decorative and beautiful flowers.
Solanaceae Family
The name Solanaceae comes from the genus Solanum. The other name of Solanaceae is Nightshades. These are flower-bearing plants that can be perennial, biennial, or annual. These plants are found all over South and Central America, there are about 2000 species of plants under this family. Some of these plants that belong to the Solanaceae family are tomatoes, Eggplants, chilies, Capsicum, potatoes, Petunia, and Datura. These plants have significant agricultural and culinary importance, as well as some with notable medicinal properties.
Read For More Information: Solanaceae – Characteristics, Importance, Examples
Scientific Classification of Solanaceae
The taxonomic classification of Solanaceae is:
| Rank |
Scientific Name |
| Kingdom |
Plantae |
| Subkingdom |
Tracheobionta |
| Superdivision |
Spermatophyta |
| Division |
Magnoliophyta |
| Class |
Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass |
Asteridae |
| Order |
Solanales |
|
Family
|
Solanaceae
|
Solanaceae Floral Formula and Floral Diagram
The floral formula of Solanaceae is given below:

- ⊕ – Actinomorphic (radial symmetry)
- ⚥- Bisexual
- K(5) – Calyx – 5 sepals, gamosepalous (united)
- C(5) – Corolla – 5 petals, gamopetalous
- A5 – Androecium – 5 stamens, polyandrous (free), epipetalous (attached to petals)
- G(2) – Gynoecium – Bicarpellary, syncarpous (united), superior ovary

Solanaceae Family Characteristics
The various characteristics of solanaceae family including vegetative, floral, and economic importance are as follows:
Vegetative Characters
The vegetative characteristics of plants of the Solanaceae Family are stated below:
- The family comprises different types of plants like vines, shrubs, epiphytes, lianas, and trees
- Root System is Tap root System
- The leaves are simple and arranged alternately. It is exstipulate and has reticulate venation
Also Read: Root System in Plants
Floral Characters
The floral characteristics of plants of the Solanaceae Family are as follows:
- The inflorescence is racemose which is either terminal or axillary
- The flowers of this family are complete, bisexual, actinomorphic, and hypogynous
- The calyx has five sepals, gamosepalous with valvate aestivation
- The corolla has five petals, gamopetalous with valvate aestivation
- Androecium has 5 stamens, epipetalous, and the anthers are basifixed
- The gynoecium is syncarpous, bi-carpellary , bilocular, superior ovary with axile placentation
- The fruits are either berry or capsule
- The fruits have numerous seeds that are endospermous
Economic Importance
Many plants of Solanaceae Family have significant economic value. Some of them are:
- Plants are important sources of food e.g. potatoes, tomatoes, brinjal
- Important sources of spices e.g. chili
- The leaves of the plant Nicotiana tobacum are used as a major source of tobacco
- Plants like petunia are used for ornamental purposes
- Certain plants like ashwagandha and belladonna are used for medicinal purpose.
Also Read: Parts of a Flower and their Functions
Fabaceae Family
The family Fabaceae is commonly called legumes or beans and it is the third-largest family in the plant kingdom containing more than 20,000 species of flowering plants and are widely distributed across the world. The fruit of the plant is characterized by the presence of a pod and the plants contain rhizobium bacteria in their root nodules. The bacteria helps in fixing atmospheric nitrogen in the soil. Peas, lentils, peanuts, soybeans, beans, and acacia are some of the types of plants in the Fabaceae family.
Also Read: Biological Nitrogen Fixation
Scientific Classification of Fabaceae
The taxonomic classification of Fabaceae is:
| Rank |
Scientific Classification |
| Kingdom |
Plantae |
| Subkingdom |
Tracheobionta |
| Superdivision |
Spermatophyta |
| Division |
Magnoliophyta |
| Class |
Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass |
Rosidae |
| Order |
Fabales |
| Family |
Fabaceae |
Fabaceae Floral Formula and Floral Diagram
The floral formula of Fabaceae is given below:
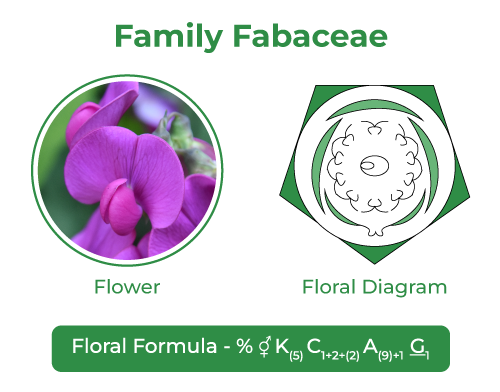
- % – Zygomorphic
- ⚥ – Bisexual
- K(5) – Calyx – 5 sepals, gamosepalous
- C1+2+(2) – Corolla – 5 petals, polypetalous
- A(9)+1 – Androecium – 10 stamens, diadelphous
- G1 – Gynoecium – monocarpellary, predominant ovary
Characteristics of Fabaceae Family
Let us see the vegetative, floral characters and economic importance of the Fabaceae family.
Vegetative Characters
The vegetative characteristics of plants of the Fabaceae Family are stated below:
- The root system is a tap root system with root nodules
- The stems of the plants are either erect or climbers and the plants of this family include shrubs, herbs, trees, and mostly climbers
- The leaves are petiolate, either simple or pinnately compound with pulvinus leaf base, stipulating that can be a thorn or leaf and reticulate venation
- The leaflets of certain plants like Vicia are modified into tendrils
Floral Characters
The floral characteristics of plants of the Fabaceae Family are as follows:
- The inflorescence of the Fabaceae plants is racemose; where the main axis is grown indefinitely without terminating into flowers
- The flowers are complete, zygomorphic, hypogynous and bisexual
- Five sepals in the calyx are gamosepalous with valvate aestivation
- The corolla has five petals, polypetalous with vexillary aestivation
- The androecium has ten stamens (9+1), diadelphous and the anther is dithecous
- The ovary is superior, monocarpellary, unilocular, and single with a short flat style and hairy stigma
- The fruits are generally leguminous
- It has one or more seeds that are npn-endospermic
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Economic Importance
Many plants of Fabaceae Family have significant economic value. Some of them are:
- The root nodules of the leguminous plants contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria that help to fix the atmospheric nitrogen to the soil and enrich it
- Certain pulses like chickpeas, soybeans, and lentils are the primary sources of food
- Oils extracted from peanuts and soybeans are used for cooking
- The licorice plant has medicinal value
- Sweet pea and Lupin are ornamental plants
- Indigofera plant produces indigo dye
- Sunn hemp is used as fiber and timber
- Sesbian and Trifolium are used as fodder for livestock
Also Read: The Structure and Functions of Pistil
Liliaceae Family
Family Liliaceae belongs to the order Liliales which has more than 250 genera and 4075 species that are distributed globally mainly in the temperate regions of the northern hemisphere. Liliaceae is a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the lily family. Onions, lilies, Hyacinths, tulips daylilies, and Snake plants belong to the Liliaceae family. Liliaceae members contribute to horticulture, providing ornamental plants and cultivated crops, and some species have historical or cultural significance.

Characteristics of Liliaceae Family
Let us see a few vegetative, floral, and economic importance of the Liliaceae family.
Vegetative Characteristics
The vegetative characteristics of plants of the Liliaceae Family are stated below:
- The plants of this family are perennials, herbaceous and monocotyledons
- The root is fibrous root system
- The stems propagate through bulbs or rhizomes
- Leaves are simple, exstipulate with parallel venation and arranged alternatively
Floral Characters
The floral characteristics of plants of the Liliaceae family are as follows:
- The inflorescence is cymose, solitary and umbellate clusters
- Flowers are complete, hupogynous, actinomorphic with the presence of perianth.
- Perianth have indistinctive sepals and petals with six tepals that are often united
- The six stamens are arranged in two rows in androceium
- The gynoecium has a superior ovary that are syncarpous ,tricarpellary with axile placentation
- The fruits are usually capsules but at times berry
- The seeds are endospermic
Economic Importance
The plants of the Liliaceae family have certain economic importance:
- The plants of the Liliaceae family have certain economic importance like:
- Aloe vera, Colchine and Smilax plants have medicinal importance
- Tulips, lilium, Ruscus and Gloriosa are used as ornamental plants
- Roots of various plants and bulbs of allium are used as flavoring agents
- Asparagus is used as a source of food
Difference Between Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae
Here are some differences between Solanaceae, Fabaceae, and Liliaceae:
|
Characteristics
|
Solanaceae
|
Fabaceae
|
Liliaceae
|
|
Number of Cotyledons
|
Dicotyledons
|
Dicotyledons
|
Monocotyledons
|
|
Root System
|
Tap root system
|
Tap root system
|
Fibrous root system
|
|
Common Name
|
Potato Family
|
Pea Family
|
Lily Family
|
|
Placentation
|
Axile Placentation
|
Marginal Placentation
|
Axile Placentation
|
|
Importance
|
Produce medicinal compounds like atropine, nicotine and hyoscine
|
Legumes fix atmospheric nitrogen to the soil with the help of the bacteria present in the root nodules
|
The flowers are generally used for decorative purpose
|
|
Examples
|
Potato, Capsicum, Tomato, Eggplant, Chilly
|
Chickpeas, Pea and Soyabean
|
Tulip, Asparagus, Onion and Lily
|
Conclusion – Solanaceae, Fabaceae, Liliaceae
Solanaceae, Fabaceae plant species are dicots whereas Liliaceae family species are monocots. In the Plant Kingdom, the Fabaceae family is the third biggest. Sometimes referred to as the legume family, Fabaceae is one of the most significant families commercially. The Solanaceae family is the one that humans use the most. Solanaceae Family is sometimes referred to as either the nightshade or potato family and include foods such as tomatoes, potatoes, bell peppers, gooseberries, and so on. Lilies and tulips are among the lovely and ornamental flowers that belong to the Liliaceae family. All the species of the three families are of great economic importance like they are good source of food, medicinal value and are also used as ornamental plants.
Also Read:
FAQs on Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae
Which Plant is a Member of the Solanaceae Family?
Solanaceae is also known as the nightshade plant and the plants that belong to the Solanaceae family are tomatoes, potatoes, capsicum, chilies, petunia, and egg plants.
What are the Similarities Between Solanaceae, Fabaceae, and Liliaceae Family?
Solanacea and Fabaceae plants are dicotyledons with taproot systems and the members of the Liliaceae are monocotyledons with a fibrous root system. The similarities between these three families are they are economically very important plants.
What is the Economic Importance of the Fabaceae Family?
The Fabaceae family commonly known as the pea family has various species that are economically important. Various plants yield oil, legumes are rich in proteins and some plants are used as fodder for livestock.
What Kind of Plants Fall Under the Fabaceae Family?
The types of plants under the Fabaceae family include soybeans, peas, chickpeas, broad beans, peanuts, and alfalfa.
Solanaceae is Included Under the Order?
The family Solanaceae is included under the order Polymoniales mainly based on the vegetative and floral characters.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...