Retained Earnings : Meaning, Features, Advantages and Limitations
Last Updated :
19 Jan, 2024
What are Retained Earnings?
Retained Earnings are that part of the profits of an organisation, which remains with it after meeting all its operating expenses and paying out dividends to all the shareholders. The organization intends to keep this surplus amount with itself in the form of reserves and surplus to meet any contingency, carry out research work, expansion projects, etc.

Usually, the profits earned by a business are distributed as dividends among its shareholders. However, a business may decide not to distribute all of its profits to its shareholders in the form of dividends, instead, it keeps a portion of the net income for future use. This method of raising funds using own profits by a firm is called retained earnings or ploughing back of profits. This method of raising funds serves as a means of internal funding, self-financing, or profit-sharing. It is a hassle-free method of raising funds since the firm does not have to depend upon any external sources. It is to be noted that the amount of profit that can be reinvested in a company depends upon the earnings made by the company during a particular year, the dividend policy adopted by the firm and the company’s age.
Features of Retained Earnings
The features of Retained Earnings are as follows:
- Cushion of Security: Retained earnings are considered as a cushion of security because they provide support in times of adversity when it becomes difficult for a firm to raise funds from other projects.
- Funds for Innovative Projects: Retained earnings are a common source of funds for financing risky and innovative projects. These are generally used for research work, expansion projects, etc.
- Medium and Long-term Finance: Retained earnings are considered as ownership funds and serve the purpose of medium and long-term finance.
- Conversion into Ownership Securities: Surplus retained earnings can be converted into ownership funds by way of issue of bonus shares. No cash outflow is involved in issuing bonus shares. Investors too are benefitted from the issue of shares free of cost.
Advantages of Retained Earnings
The advantages of Retained Earnings are as follows:
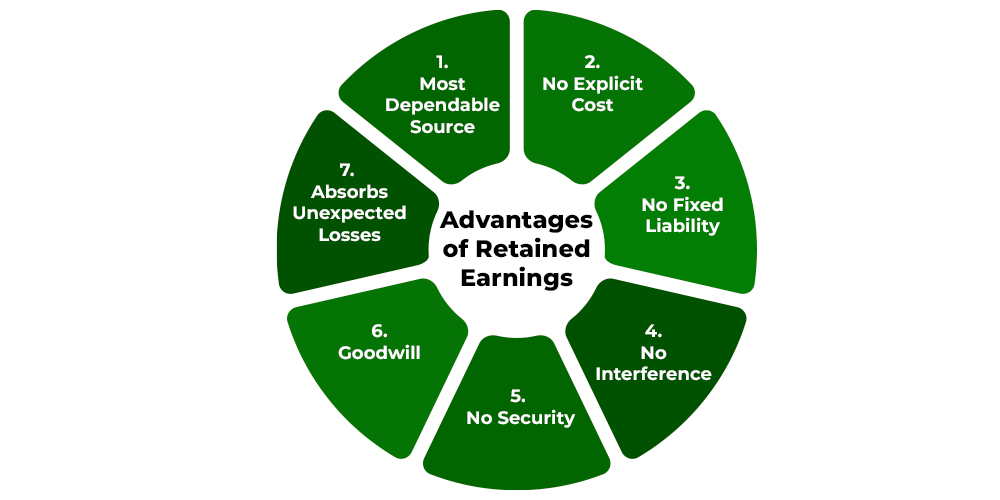
- Most Dependable Source: Being an internal source, retained earnings are a more dependable and permanent source of finance than external sources of funds. This is because all external sources depend upon market conditions, the preference of the creditors, etc.
- No Explicit Cost: Using retained earnings does not involve any costs to be incurred as no expenditure is to be made on issuing prospectus, advertising, floatation costs, etc.
- No Fixed Liability: There is no fixed liability to pay dividends or interest on this source of funds as retained earnings are a company’s own money.
- No Interference: When a company utilizes its retained profits, it does not need to issue any new shares. As a result, there is no risk of dilution of control in the organization.
- No Security: Unlike debentures, no charge is created on the assets of the company. As a result, the company is free to use its assets for raising loans in the future.
- Goodwill: Retained earnings add to the financial strength and credibility of the company. Large reserves enable businesses to respond with ease to any crisis or unforeseen contingency. Retained earnings may lead to an increase in the market price of the equity shares.
- Absorbs Unexpected Losses: If a business has retained earnings, then it is in the position to absorb unexpected losses.
Limitations of Retained Earnings
Retained Earning has the following limitations:
- Dissatisfaction: In cases of excessive ploughing back of profits, i.e., where a major portion of the profits has been kept in the form of reserves, the shareholders might be disappointed by the lower amounts of dividends paid to them.
- Uncertainty: Retained earnings are a highly uncertain method of raising funds since the profits of a business are always fluctuating.
- Opportunity Cost: The opportunity cost associated with the usage of retained profits is often overlooked or sometimes, not even recognized by a lot of firms, which leads to sub-optimal usage of the funds.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...