Python Program For Finding The Length Of Loop In Linked List
Last Updated :
18 May, 2022
Write a function detectAndCountLoop() that checks whether a given Linked List contains loop and if loop is present then returns count of nodes in loop. For example, the loop is present in below-linked list and length of the loop is 4. If the loop is not present, then the function should return 0.
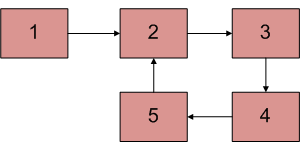
Approach:
It is known that Floyd’s Cycle detection algorithm terminates when fast and slow pointers meet at a common point. It is also known that this common point is one of the loop nodes. Store the address of this common point in a pointer variable say (ptr). Then initialize a counter with 1 and start from the common point and keeps on visiting the next node and increasing the counter till the common pointer is reached again.
At that point, the value of the counter will be equal to the length of the loop.
Algorithm:
- Find the common point in the loop by using the Floyd’s Cycle detection algorithm
- Store the pointer in a temporary variable and keep a count = 0
- Traverse the linked list until the same node is reached again and increase the count while moving to next node.
- Print the count as length of loop
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def AddNode(self, val):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(val)
else:
curr = self.head
while(curr.next):
curr = curr.next
curr.next = Node(val)
def CreateLoop(self, n):
LoopNode = self.head
for _ in range(1, n):
LoopNode = LoopNode.next
end = self.head
while(end.next):
end = end.next
end.next = LoopNode
def detectLoop(self):
if self.head is None:
return 0
slow = self.head
fast = self.head
flag = 0
while(slow and slow.next and fast and
fast.next and fast.next.next):
if slow == fast and flag != 0:
count = 1
slow = slow.next
while(slow != fast):
slow = slow.next
count += 1
return count
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
flag = 1
return 0
myLL = LinkedList()
myLL.AddNode(1)
myLL.AddNode(2)
myLL.AddNode(3)
myLL.AddNode(4)
myLL.AddNode(5)
myLL.CreateLoop(2)
loopLength = myLL.detectLoop()
if myLL.head is None:
print("Linked list is empty")
else:
print(str(loopLength))
|
Output:
4
Complexity Analysis:
- Time complexity:O(n).
Only one traversal of the linked list is needed.
- Auxiliary Space:O(1).
As no extra space is required.
Please refer complete article on Find length of loop in linked list for more details!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...