Python Continue Statement
Last Updated :
09 May, 2023
Python Continue Statement skips the execution of the program block after the continue statement and forces the control to start the next iteration.
Python Continue Statement
Python Continue statement is a loop control statement that forces to execute the next iteration of the loop while skipping the rest of the code inside the loop for the current iteration only, i.e. when the continue statement is executed in the loop, the code inside the loop following the continue statement will be skipped for the current iteration and the next iteration of the loop will begin.
Python continue Statement Syntax
while True:
...
if x == 10:
continue
print(x)
Flowchart of Continue Statement
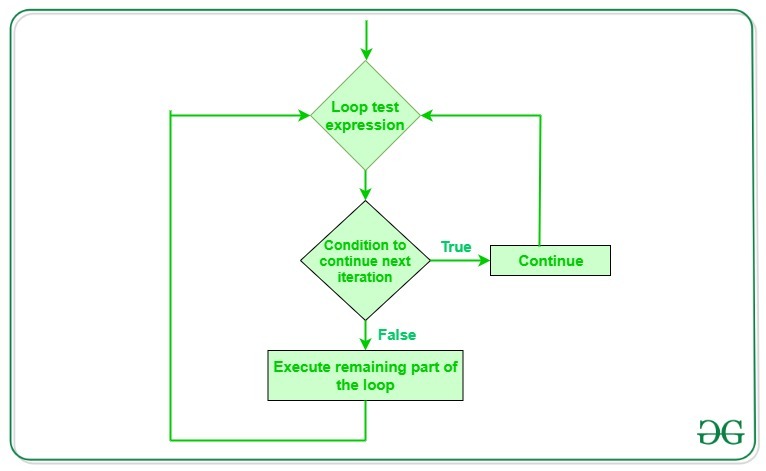
flowchart of Python continue statement
Continue statement in Python Examples
Demonstration of Continue statement in Python
In this example, we will use continue inside some condition within a loop.
Python3
for var in "Geeksforgeeks":
if var == "e":
continue
print(var)
|
Output:
G
k
s
f
o
r
g
k
s
Explanation: Here we are skipping the print of character ‘e’ using if-condition checking and continue statement.
Printing range with Python Continue Statement
Consider the situation when you need to write a program that prints the number from 1 to 10, but not 6.
It is specified that you have to do this using a loop and only one loop is allowed to use. Here comes the usage of the continue statement. What we can do here is we can run a loop from 1 to 10 and every time we have to compare the value of the loop variable with 6. If it is equal to 6 we will use the continue statement to continue to the next iteration without printing anything, otherwise, we will print the value.
Python3
for i in range(1, 11):
if i == 6:
continue
else:
print(i, end=" ")
|
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 10
Note: The continue statement can be used with any other loop also like the while loop, similarly as it is used with for loop above.
Continue with Nested loops
In this example, we are creating a 2d list that includes the numbers from 1 to 9 and we are traversing in the list with the help of two for loops and we are skipping the print statement when the value is 3.
Python3
nested_list = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
for i in nested_list:
for j in i:
if j == 3:
continue
print(j)
|
Output
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
Continue with While Loop
In this example, we are using a while loop which traverses till 9 if i = 5 then skip the printing of numbers.
Python3
i = 0
while i < 10:
if i == 5:
i += 1
continue
print(i)
i += 1
|
Output
0
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
Usage of Continue Statement
Loops in Python automate and repeat tasks efficiently. But sometimes, there may arise a condition where you want to exit the loop completely, skip an iteration or ignore that condition. These can be done by loop control statements. Continue is a type of loop control statement that can alter the flow of the loop.
To read more on pass and break, refer to these articles:
- Python pass statement
- Python break statement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...