Product Segmentation: Definition, Importance and Examples
Last Updated :
30 Jan, 2024
Product segmentation is defined as an essential tactic that has the power to make or break the success of your company. There exist multiple strategies to enhance your market share. First, by providing them with outstanding service, you should strengthen your bonds with your clients.
If you differentiate your business from the competition and offer your customers something they can only get there, you’ll attract more customers regularly. But it can be difficult when every other company is making the same effort.

What is Product Segmentation?
Product segmentation in Product Management is a crucial part of any successful marketing strategy. To create specialized goods or marketing campaigns for these segments, the market must be divided into smaller groups of consumers with comparable demands or characteristics.
Personality influences the demands and preferences of customers. Product segmentation can accommodate the preferences of every niche market. Businesses can focus on the specific needs of certain clientele to increase customer satisfaction, which will increase sales and give them a competitive edge.
Importance of Product Segmentation:
Any marketing strategy must include product segmentation because it helps companies identify and target specific customer demographics with tailored products and advertising campaigns. The following justifies the importance of product segmentation:
- Cost-effective: By concentrating on particular market segments rather than the total market, businesses can create more cost-effective products.
- Improved product development: Companies can create goods that have a higher chance of being successful in the market by understanding the unique needs of different industries.
- Product pricing: By dropping a single product, businesses can do away with one-size-fits-all pricing. Because the product is divided into different target markets, companies can use a pricing strategy that suits each of them.
- Increased customer satisfaction: By knowing the specific needs of different market segments, businesses can develop products and marketing strategies that are more likely to satisfy the needs of their customers. Customer satisfaction will rise as a result.
- Improved customer insights: Product segmentation helps companies gain a deeper understanding of the requirements, preferences, and behavior of their clients. This knowledge can then be used to inform future pricing, marketing strategies, and product development.
- Performance of individual products: Analyzing the performance of individual products enables you to evaluate the performance of consumer segments. You can find out how each customer group responds to your product by keeping an eye on the one that is most closely associated with them.
In today’s competitive business market, it is more crucial than ever to comprehend and target particular customer categories. Businesses can do this more successfully thanks to product segmentation, which boosts customer satisfaction, and sales, and gives them a competitive edge in the marketplace.
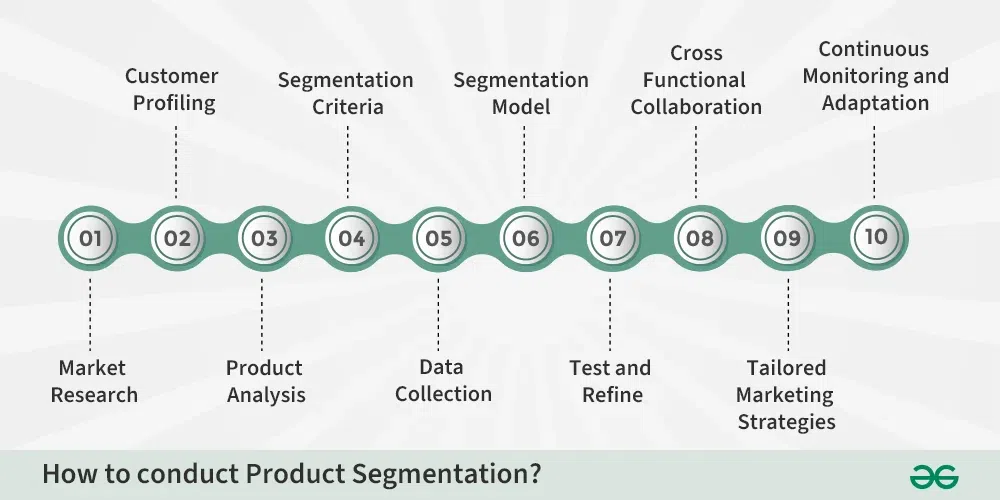
How to conduct Product Segmentation?
- To begin, conduct thorough market research to learn about customer demographics, preferences, and behaviors..
- Consider factors like age, income, location, or psychographics to identify potential segments.
2. Customer Profiling:
- Foster point by point profiles for every possible fragment, illustrating their necessities, inclinations, and buying conduct.
- Consider factors like way of life, values, and buying inspirations.
3. Product Analysis:
- Assess your current item portfolio to distinguish elements, advantages, and qualities of every item.
- Think about whether some products are better suited to particular types of customers.
4. Segmentation Criteria:
- Decide the measures for item division, for example, use designs, value awareness, or explicit item includes.
- Guarantee that the measures line up with the distinguished client portions.
How to conduct Product Segmentation
5. Data Collection:
- Assemble pertinent information on client conduct, buying history, and item execution.
- Use reviews, interviews, or investigation instruments to gather quantitative and subjective information.
6. Segmentation Model:
- Foster a division model that sorts items in view of the laid out measures.
- This model ought to be sufficiently adaptable to oblige changes on the lookout or client inclinations.
7. Test and Refine:
- Put the segmentation model into practice and evaluate its performance.
- Gather input, evaluate the results, and make any necessary adjustments to the segmentation models.
8. Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Engage in the segmentation process with various departments, such as product development, sales, and marketing.
- Make coordination and cooperation a priority in order to effectively apply segment-particular tactics.
9. Tailored Marketing Strategies:
- Foster designated showcasing systems for each acknowledge portion, accentuating item highlights and benefits that resound with their specific necessities.
10. Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation:
- Timely monitor customer opinions, product performance, and market developments.
- Change item division strategies as compulsory to maintain long-term sufficiency and importance.
What is Customer Segmentation?
Client division is the method engages with differentiating organization’s consumer base into discrete gatherings according to qualities, propensities, or necessities in like manner. The aim is to perceive and fathom different client grouping to form tweaked promoting plans, individualized item contributions, and redid correspondences. This acknowledges that consumers are different, and businesses may improve their capacity to please a wide range of tastes and expectations by batch them into distinct segments.
Client segmentation require considering the client’s values, profits, shopping habits (including what they buy and how they use goods), preferences, and basic demographic data (age, gender, and income). People that share characteristic are grouped together so that companies may create more quirky and successful marketing strategies for each group.
Customer segmentation has certain profits, superior better customer satisfaction and corporate performance, enhanced customer loyalty, and more successful marketing attempts. By knowing the distinctive traits of different customer category, organisations may change their services to appeal to certain consumers. In the long run, this strategy may stronger bonds and improve client loyalty.
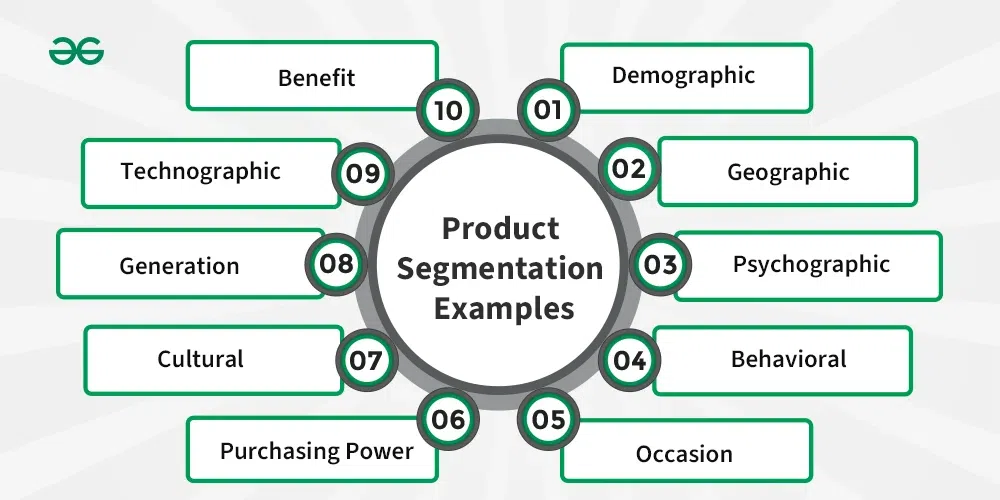
Product Segmentation Examples:
1. Technology:
- Classify based on purpose, like computers designated for gaming, business, or productivity.
- Develop smartphones considering various needs, offering options between budget-friendly models with advanced features and premium, high-end models.
2. Automobiles:
- Cars categorized by size (compact, sedan, SUV), addressing diverse consumer preferences.
- Electric vehicles targeting environmentally conscious consumers in contrast to conventional fuel options.
3. Apparel:
- Clothing collections tailored for specific demographics, such as activewear for fitness enthusiasts or professional business attire.
- Fashion brands providing distinct lines to cater to a wide range of individuals.
4. Food and Beverages:
- Breakfast oats categorized based on age groups or health preferences.
- Caffeinated beverages designed for sports enthusiasts and individuals focused on wellness.
Product Segmentation Examples
5. Financial Services:
- Credit cards tailored to specific lifestyles, like those with cashback or travel rewards features.
- Banking services providing a range of account types categorized based on income levels.
6. Cosmetics:
- Skin care products addressing particular skin issues, such as anti-aging or acne-prone items, illustrate examples in this category.
- Cosmetic lines created to cater to diverse skin tones or preferences, including options for normal or bold appearances, serve as another instance in the cosmetic product range.
7. Fitness Equipment:
- Home fitness center equipment designed for health-conscious students versus high-quality equipment for seasoned customers
- Innovation in wearable health care caters to a variety of interests, including smartwatches for general health monitoring and specialized gaming devices.
8. Travel and Hospitality:
- Hotel chains provide a wide range of lodging choices, ranging from economical to luxurious.
- Hotel chains provide a wide range of lodging choices, ranging from economical to luxurious.
Market Segmentation v/s product segmentation:
|
separating the entire market into distinct segments based on shared characteristics or needs.
|
Involves categorizing a business’s product offerings into distinct categories according to predetermined criteria.
|
|
focuses on comprehending and serving various customer segments of the market.
|
focuses on ordering and matching specific client segments with individual items.
|
|
encompasses the entire market and its diverse customer base.
|
focuses on an organization’s product portfolio and how it can be adapted to different audiences.
|
|
Strives to improve product offerings, communication, and advertising strategies for diverse customer segments.
|
Approaches to enhance product development, marketing, and communication for introducing items within the portfolio.
|
|
demographics, psychographics, behavior, customer requirements, location, and geography.
|
Utilize the designs, features, benefits, and specific characteristics of individual items.
|
|
concentrating on various age groups and employing various marketing strategies for a skincare product.
|
Organizing computers based on their intended purpose, which may include gaming PCs, business workstations, and similar categories.
|
|
Broadly outlines approaches for advertising, public relations, and communication across the entire range of products.
|
Directs product development, marketing approaches, and communication for specific items within the portfolio.
|
|
Necessitates flexibility as market dynamics and consumer behaviors undergo long-term changes.
|
Necessitates flexibility as products evolve and market preferences for specific features or benefits change.
|
|
increases in understanding of the market as a whole, customer loyalty, and brand tenacity.
|
“Improves the allocation of resources, the value of products, and the effectiveness of promotions for specific items.” paraphrase this
|
Advantages of Product Segmentation:
- Targeted Marketing: Enables businesses to develop more engaging and individualized showcasing strategies for specific product segments, elevating the significance of specific initiatives.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Organizations can increment consumer loyalty and unwaveringness by offering items that meet the particular prerequisites and inclinations of different market fragments.
- Maximised Resource Distribution: Reduces wastage of resources by concentrating efforts on products with the highest potential for growth within clear segments.
- Competitive Edge: Organization that successfully segment their goods benefit from being able to respond to a variety of market demands and provide solutions that are customized to meet the needs of individual customers.
- Diversification: Facilitates diversification of product portfolios, reducing dependence on a single product or market segment and spreading business risk.
Disadvantages of Product Segmentation:
- Overemphasis on Segments: If you put too much emphasis on segmentation, you run the risk of ignoring larger trends in the market, missing out on opportunities for innovation, or not meeting new needs that aren’t covered by the segments you’ve identified.
- Difficulties in Execution: Effectively executing item division requires coordination across different divisions, and misalignment or absence of cooperation can frustrate the viability of the methodology.
- Consumer Confusion: Too many portioned items or complex division models could confound buyers, making it hard for them to explore and pick items.
- Rapid Market Changes: Markets can change quickly, and a division methodology that was compelling at first could become outdated in the event that it doesn’t adjust to developing purchaser inclinations.
- Risk of Misjudging Segments: Products that do not resonate with customers can result in wasted resources and a loss of market share if segments are not correctly identified or judged.
Conclusion: Product Segmentation
In conclusion, product segmentation emerges as an advanced process that presents organizations in intricate business environments with both advantages and potential challenges. The benefits are evident in the precise targeted marketing it enables, allowing businesses to effectively meet a variety of customer needs. Enhanced customer confidence, more efficient resource allocation, and a competitive edge are significant advantages contributing to long-term success.
FAQs on Product Segmentation:
Q1. What is the importance of product segmentation for businesses?
Businesses should utilize product segmentation because it allows them to tailor their offerings to particular customer groups, enhancing relevance and customer satisfaction. Marketing efficiency boost, resource allocation is optimized, and customer loyalty increases as a result of this strategy.
Q2. Which benchmarks are frequently used to categorize products into various groups?
Demographics (age, income), psychographics (lifestyle, values), behavior (purchase patterns), geographic location, and specific product features or perks are the most usual criteria for product segmentation.
Q3. How challenging is it for businesses to make use of product segmentation?
The need for cross-functional collaboration, the possibility of cannibalization between segmented products, consumer confusion, and the complexity and expense of execution are some of the obstacles. Businesses may also face difficulties in misinterpreting segments and adapting to rapid market shifts.
Q4. How often should companies reevaluate their product segmentation strategies?
Businesses should periodically reevaluate their product segmentation strategies in order to remain in tune with shifting market dynamics and consumer preferences. In order to maintain their effectiveness, businesses can alter and enhance their strategy over time.
Q5. Can product segmentation be utilized by businesses or industries of any size?
Yes, the principles of product segmentation can be applied to a wide range of businesses and industries. In technology, retail, or services, improving overall market performance and competitiveness can be accomplished by comprehending and catering to specific customer segments.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...