PostgreSQL – AVG() Function
Last Updated :
01 Jun, 2020
PostgreSQL provides an AVG() function to calculate the average value of a set. The AVG() function is one of the most frequently used aggregate functions in PostgreSQL. The AVG() function enables users to calculate the average value of a numeric column.
Syntax: AVG(column)
It can be used with both the SELECT and HAVING clause.
Let’s look into some examples now.
Example 1:
We will be using the payment table in the dvdrental sample database for demonstration. In this example we will query to know the average amount that customers paid, using the AVG() function in the amount column as follows:
SELECT
to_char(
AVG (amount),
'99999999999999999D99'
) AS average_amount
FROM
payment;
Output:
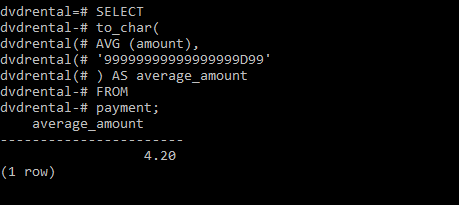
Note: We used the to_char() function to convert the result into a formatted string.
Example 2:
We will be using the payment table in the dvdrental sample database for demonstration. In this example we will query to know the average amount paid by each customer using the command below:
SELECT
customer.customer_id,
first_name,
last_name,
to_char(
AVG (amount),
'99999999999999999D99'
) AS average_amount
FROM
payment
INNER JOIN customer ON customer.customer_id = payment.customer_id
GROUP BY
customer.customer_id
ORDER BY
customer_id;
Output:
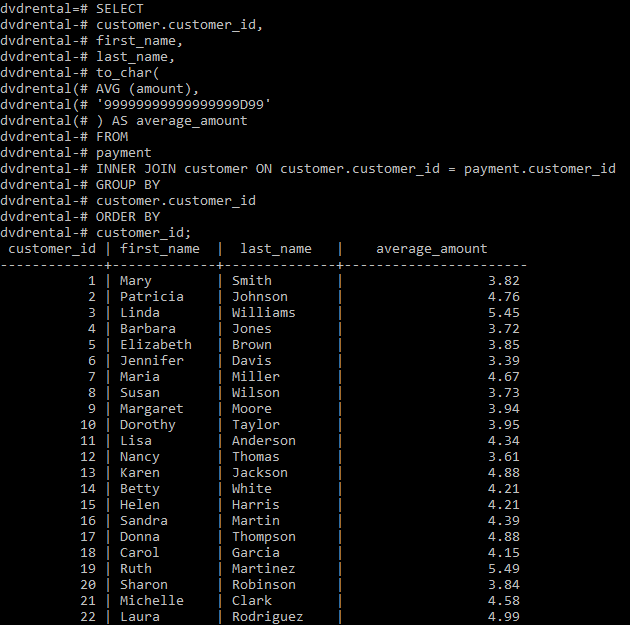
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...