Point Symmetry, or Origin Symmetry, or Central Symmetry is a type of symmetry where an object or shape looks the same when rotated 180° (a half-turn) around a central point.
In this article, we will discuss Point Symmetry in detail including its definition, examples, as well as some real-life examples in nature as well.
What is Symmetry?
Symmetry means when you can split a shape or thing into two parts that look the same. In a symmetrical thing, one side is like a mirror image of the other. The imaginary line you can fold along to make those matching halves is called the line of symmetry.
What is Point Symmetry?
Point symmetry is when any object or anything looks the same after turning it 180° around a central point or we can say, from a certain point when an object is flipped at 180° it gives an equal or identical shape. It’s like a spinning toy that stops looking different no matter how you turn it. The center is the point where it stays unchanged, creating a balanced, matching shape on both sides. To check whether an image creates point symmetry or not, two conditions should be fulfilled:
- Every part of the shape is at the same distance from the center.
- Each part and its matching part point in opposite directions.
Definition of Point Symmetry
Point symmetry, also known as central symmetry, is a geometric property exhibited by certain shapes or figures.
An object is said to have point symmetry if there exists a central point around which the object can be rotated by a certain angle, typically 180°, and still maintain its original appearance.
In simpler terms, if the shape looks unchanged after a half-turn (180-degree rotation) around a specific point, it possesses point symmetry.
How to Identify Point Symmetry?
To identify point symmetry, we can use following steps.
- Identify the Center: Point symmetry occurs when there is a central point around which the object is symmetrical. Locate this central point.
- Check for Symmetry: Examine the object to see if it looks the same when rotated 180° around the central point. If the shape aligns with itself after the rotation, it possesses point symmetry.
- Consider Reflection: Another way to identify point symmetry is by checking if the object is identical on both sides when reflected across the central point.
- Verify in Multiple Directions: Ensure symmetry by checking for consistency in various directions from the central point.
Point Symmetry in Geometric Shapes
In various geometric shapes such as square, rectangle, parallelogram, circle, star, etc., we can observe the point symmetry which is discussed as follows:
Point Symmetry of Square/Rectangle
- Center: The center of point symmetry for a square or rectangle is the intersection point of its diagonals.
- Symmetry Check: When rotated 180° around this central point, the square or rectangle looks the same. Additionally, reflection across the center results in identical shapes on both sides.

Point Symmetry of Parallelogram
- Center: The point symmetry in a parallelogram lies at the intersection of its diagonals.
- Symmetry Check: Similar to a square or rectangle, a parallelogram exhibits point symmetry if rotating it 180° or reflecting it across the central point maintains its original appearance.

Point Symmetry of a Circle
- Center: The center of the circle serves as the point of symmetry.
- Symmetry Check: A circle is inherently symmetric. Rotating it by any degree around the center results in an identical shape.

Point Symmetry of a Star
- Center: For a symmetrical star, the center is often the midpoint of its vertical axis.
- Symmetry Check: The star shows point symmetry when rotated by certain angles around its central point. Reflection across this point also reveals symmetry.

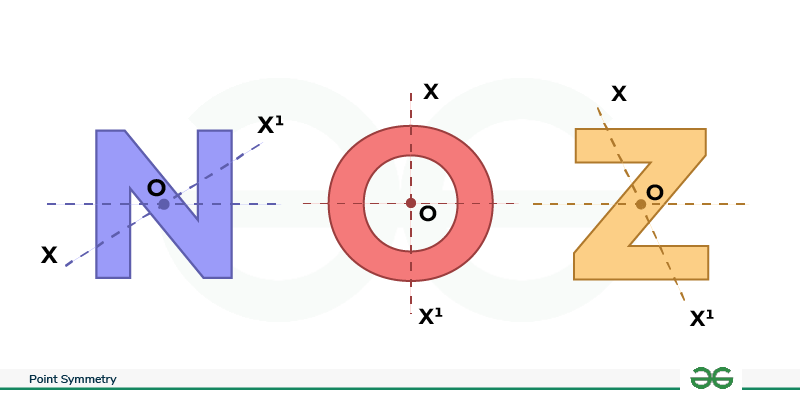
Point Symmetry in Letters
When you have point symmetry in the alphabet, it means that if you draw a line through a certain point, the parts on either side of that point are the same distance from it. In English letters, you can find point symmetry.
Take the letter O, for example. It has a center point, and the parts on opposite sides are the same but facing different ways. Uppercase letters like C, D, H, I, N, O, X, and Z also have point symmetry. If you draw a line from the middle of C, D, H, I, O, or X, both the upper and lower parts will be the same length. So, these letters have both point and line symmetry.
Point Vs Reflection Symmetry
The key differences between point symmetry and reflection symmetry are:
| Occurs when a figure is unchanged by rotating it 180° around a central point, known as the center of symmetry. |
Occurs when a figure remains unchanged when reflected across a line, known as the line of symmetry. |
| Involves rotation around a central point. |
Involves reflection across a line. |
| Center of Symmetry (Point) |
Line of Symmetry |
| Commonly found in circular or radially symmetric figures. |
Commonly found in figures with bilateral symmetry, like rectangles, squares, or letters of the alphabet. |
| Only one central point of symmetry. |
Can have multiple lines of symmetry depending on the figure. |
| The letter “O” has point symmetry because it remains the same when rotated 180° around its center. |
The letter “H” has reflection symmetry because it remains the same when reflected across a vertical line. |
| Rotational |
Reflectional |
Symmetry in Visual Arts
In visual arts, symmetry is a fundamental concept employed to create balance and harmony in compositions. Artists use symmetrical arrangements, where one side mirrors the other, to instill a sense of order and aesthetic appeal.
Symmetry can be found in various art forms, from paintings and sculptures to graphic designs. It serves as a guiding principle for creating visually pleasing and impactful pieces by ensuring a harmonious distribution of elements.
Architectural Designs and Patterns
Architectural designs often incorporate symmetry to achieve a sense of equilibrium and beauty in structures. Symmetrical elements in buildings, such as matching facades or balanced layouts, contribute to a visually cohesive and pleasing architectural aesthetic.
Patterns, whether in tiling, ornamentation, or structural elements, frequently exhibit symmetry to enhance the overall design. This use of symmetry in architecture transcends cultural and historical contexts, representing a timeless approach to creating structures that are not only functional but also visually captivating.
Point Symmetry in Nature
In nature, point symmetry is not as common as other types of symmetry, like bilateral symmetry, but it can still be observed in various forms:
- Starfish
- Flowers
- Crystals
- Snowflakes
Sample Example on Point Symmetry
Example 1: State whether the following statement is true or false: “Every equilateral triangle exhibits point symmetry.”
Solution:
True. Every equilateral triangle exhibits point symmetry. In an equilateral triangle, the point of symmetry is the center of the triangle, where all three medians intersect. This means that if you fold the equilateral triangle along its center, the two resulting halves will perfectly overlap, demonstrating point symmetry.
Example 2: A figure has a point symmetry at the origin. If point B(-2, 5) is part of the figure, find the coordinates of its image point.
Solution:
Point symmetry involves reflecting a point across a central point (in this case, the origin). When a point is symmetrically located with respect to the origin, its coordinates become the negation of the original coordinates.
For point B(-2, 5), the image point (let’s call it B’) can be found by negating the coordinates:
B’ = (-(-2), -(5))
= (2, -5)
Therefore, the image point B’ is (2, -5).
Practice Problems on Point Symmetry
Problem 1: Analyze the following set of points: A(1, 4), B(4, 1), C(-1, -4), and D(-4, -1). Determine if these points form a figure with point symmetry, and if so, identify the point of symmetry.
Problem 2: Identify whether the letter “X” exhibits point symmetry. If yes, describe the point of symmetry; if not, explain why.
Problem 3: Draw a simple figure with point symmetry and describe the coordinates of the point of symmetry.
Problem 4: Given a geometric pattern, analyze whether it displays point symmetry. Provide details on any symmetrical elements.
Point Symmetry: FAQs
1. Define Point Symmetry.
Point symmetry is when a shape has a central point, and every point is the same distance from the central point on both sides.
2. What is Point Symmetry in Real Life?
Some common examples of Point Symmetry in real life are the letter ‘S’, a human face when viewed head-on, or a butterfly’s wings when closed, etc.
3. How do you Draw Point Symmetry?
To draw with point symmetry, rotate every point of an object 180° around a central point. The resulting shape should overlap with the original.
4. What is the Difference between Point Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry?
- Point Symmetry: The shape looks the same after a 180° rotation.
- Rotational Symmetry: The shape can be rotated (less than 360°) about a central point and still look the same. It includes point symmetry as a special case.
5. What is Point Symmetry in Alphabets?
Letters like ‘S’, ‘Z’, ‘N’, and ‘X’ exhibit point symmetry, as they look the same when rotated 180°.
6. What are the 4 Types of Symmetry?
4 Types of Symmetry are:
- Line Symmetry
- Rotational Symmetry
- Point Symmetry
- Translational Symmetry
7. How to Test for Point Symmetry?
To test for point symmetry, you can try these steps:
- Put a Dot: Imagine putting a dot in the center of the shape.
- Check Both Sides: See if both sides of the dot look the same. If they do, the shape has point symmetry.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...