An ombudsman is a neutral and unbiased authority appointed to investigate and address issues or grievances brought forward by individuals against an organization, government agency, or institution. Serving as a mediator, the ombudsman works towards resolving disputes equitably, promoting transparency and accountability. Their primary responsibility is to ensure that individuals’ rights are upheld and administrative procedures are conducted fairly. Ombudsmen can be found in a wide range of fields, including government entities, businesses, schools, and healthcare systems. This crucial role bridges the gap between the public and organizations, providing a confidential platform where individuals can voice their concerns and seek remedies.
Geeky Takeaways:
- An ombudsman is a neutral figure responsible for resolving conflicts and maintaining accountability in various organizations.
- Ombudsmen are independent of their organizations, allowing them to operate without external pressures and providing impartial resolutions.
- Ombudsmen protect individuals’ rights, promote transparency, and maintain confidentiality.
- Ombudsmen also address broader issues within organizations, suggesting changes to prevent future occurrences.
- The ombudsman’s success hinges on their skill in navigating intricate problems, imparting valuable knowledge, and offering practical resolutions, cultivating a climate of fairness and integrity within the organizations they monitor.
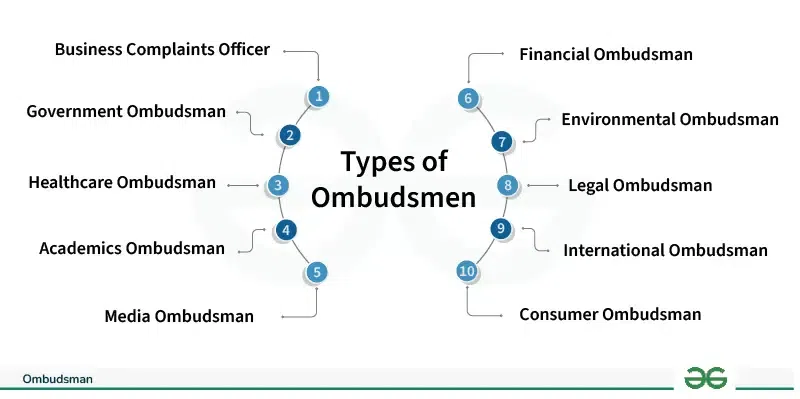
Types of Ombudsmen
There are 10 different types of Ombudsman. These are as follows:
1. Business Complaints Officer: These ombudsmen are specially designated by corporations to handle workplace matters, employee complaints, ethical transgressions, and conflicts within the corporate setting. Their crucial role involves cultivating a positive corporate atmosphere and advocating for just employment practices.
2. Government Ombudsman: Assigned by different levels of government, these ombudsmen are responsible for examining grievances against government institutions and individuals in positions of authority. They play a vital role in upholding responsibility, openness, and equity in public administration, handling concerns such as bureaucratic inadequacy, misconduct, and violations of human rights.
3. Healthcare Ombudsman: Healthcare institutions rely on ombudsmen to handle patient complaints, disputes, and concerns regarding medical treatment. These dedicated individuals are essential in championing patient rights, fostering better communication between healthcare providers and patients, and ensuring the delivery of high-quality healthcare.
4. Academics Ombudsman: Academic ombudsmen are responsible for addressing student and faculty concerns in educational settings. These may include academic disputes, discrepancies in grading, and conflicts within the academic community, all contributing to a fair and nurturing learning environment.
5. Media Ombudsman: Media organizations appoint ombudsmen to address public complaints about journalistic practices. These ombudsmen are responsible for investigating issues about accuracy, fairness, and ethics in reporting. Through their efforts, they promote accountability and uphold the credibility of the media outlet.
6. Financial Ombudsman: In the dynamic world of finance, these specialized ombudsmen thrive by expertly handling grievances lodged by consumers against financial institutions. Their scope encompasses various issues such as fraudulent sales of financial products, disagreements over fees, and other service-related matters; providing a sturdy platform for conflict resolution, outside of tedious legal proceedings.
7. Environmental Ombudsman: With a strong focus on addressing environmental concerns, these ombudsmen take on the task of investigating complaints related to environmental regulations, pollution, and other ecological issues. They strive for the implementation of sustainable practices and diligently ensure compliance with all environmental laws and standards.
8. Legal Ombudsman: In tackling matters within the legal field, legal ombudsmen are responsible for addressing complaints against lawyers and legal service providers. Their role requires them to uphold professional conduct and ethical standards and advocate for fair treatment of clients within the legal system.
9. International Ombudsman: Working on a global scale, these ombudsmen tackle disputes and issues that transcend national boundaries. Whether it’s diplomacy, human rights violations, or conflicts between nations, their ultimate goal is to promote peace and justice on an international level.
10. Consumer Ombudsman: Advocating for consumer rights, these ombudsmen take charge of grievances filed against businesses for issues such as defective products, deceptive marketing, and unjust business practices. They play a crucial role in safeguarding consumers and upholding ethical business practices.
How an Ombudsman Works?
1. Acceptance of Concerns: The ombudsman provides a safe and open space for individuals to voice their concerns, complaints, and disputes in various ways, such as in person, through email, or other designated channels.
2. Private Consultations: Through confidential consultations, the ombudsman gains a thorough understanding of the individuals’ concerns, ensuring that all parties involved maintain confidentiality while fully exploring the issues at hand.
3. Practical Judgment: The ombudsman carefully examines all facts, perspectives, and pertinent information surrounding the concerns through an unbiased analysis. This is essential in comprehending the intricacies of the issues at hand.
4. Unofficial Facilitation or Mediation: The ombudsman may utilize informal mediation or facilitation methods to aid parties in finding mutually beneficial resolutions when appropriate. This encourages teamwork and can effectively resolve conflicts without resorting to formal interventions.
5. Identification of Systemic Issues: Ombudsmen possess a unique ability to delve deeper into individual cases and unearth patterns and systemic issues within the organization. Through thorough examination and analysis of complaint trends, they bring to light underlying problems that warrant the attention of the organization as a whole.
6. Suggestions for Resolving: Drawing upon their observations and evaluations, ombudsmen offer strategic recommendations for addressing and resolving issues. Their proposals may encompass amendments to policies, procedures, or practices, all designed to tackle the root causes of concerns and prevent future occurrences.
7. Remarks for the Management: To uphold confidentiality, ombudsmen can share summarized feedback with leaders in an organization. This valuable feedback sheds light on common issues and patterns, enabling management to make well-informed decisions for the betterment of the organization.
8. Outreach and Education: Ombudsmen proactively work towards educating others about the role they play and the services they provide. This proactive strategy aims to prevent conflicts by familiarizing individuals with the resources available for addressing any concerns they may have.
9. Record-keeping: The ombudsmen meticulously keep records of all cases, ensuring precise documentation of concerns, resolutions, and recommendations. These records are a crucial tool for analyzing, reporting, and organizational development.
10. Reports for the Year: In addition, the ombudsmen may deliver yearly reports summarizing the various issues addressed, noteworthy patterns observed, and recommended solutions. These reports greatly contribute to the organization’s growth, openness, and responsibility.
Also refer to: Ombudsman: Meaning, Responsibilities and Benefits
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...