Linux setfacl command with Example
Last Updated :
04 Nov, 2023
In Linux distribution, setfacl stands for Set File Access Control List. It is a command utility tool for setting access control lists in files and directories. setfacl is a powerful tool for managing file permission based on respective Users and Groups rather than general file permission.
What is an Access Control List?
Access Control List is a set of rules implemented on the Files, Directories, Networking devices, etc. The permission given to the Users and Groups is based on their roles to perform certain actions or to execute certain tasks. The ACL is controlled and managed by the System Administrator.
Advantages of setfacl
- It allows the administrator to define specific permission for users and groups on specific files and directories.
- It has more flexibility than general file permission as we can assign multiple permissions at the same time.
- It helps to maintain specific permission without affecting others.
- It enhances the security level so that only authorized persons can access sensitive files and directories.
- It can modify or change the permission without interrupting the ongoing activities.
How to manage setfacl command
For implementing or managing the ACL using setfacl command, we need to know some basics of setfacl before defining the permissions.
- The `–set` and ‘–set-file‘ are the options used to set the ACL of files and directories.
- The ‘-m (–modify)‘ and ‘-M (–modify-file)‘ are the options used to modify the ACL of the files and directories.
- The ‘-x (–remove)’ option is used to remove the ACL of files and directories.
Options for setfacl
|
For modifying the ACL.
|
|
For removing the permission from the ACL.
|
|
For removing all permission from the ACL.
|
|
Apply default permissions to newly created files and folders along the route.
|
|
Recursively apply modifications to all files and directories in the given path.
|
|
Remove a file or directory’s default entry from the ACL.
|
|
Recalculating the effective rights mask using ACL entries is not permitted.
|
|
For specifying the effective right mask for modifying ACL
|
|
For restoring ACL from a specific file
|
|
For applying the permission to specific files or directories.
|
Syntax for modifying the ACL
setfacl -option file_owner:file_permission filename
Here,
setfacl: setfacl is a Linux utility for setting up the ACL entries in files and directories
-option: There are multiple options available for configuring the ACL like, ‘-m’ for modifying, ‘-x’ for removing, and more.
file_owner: There are three types of file-owner:
|
Specify the name of the User/Owner for configuring the ACL
|
|
Specify the name of the Group for configuring the ACL
|
|
Specify the name of Other for configuring the ACL
|
file_permission: There are three types of file-permission-
|
For read, it will allow the user to access the file.
|
|
For writing, it will allow the user to make modification or changes in the file.
|
|
For execution, it will allow the user to execute or run the file.
|
filename: Specify the filename or directory_name on which the ACL can be configured.
Examples:
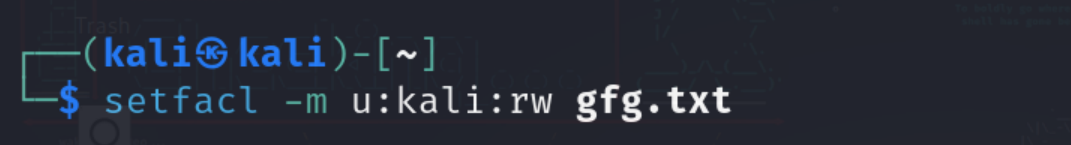
Step 1: Set filepermission to users on a specific file
It is used to configure the permission on one file or more than one file based on user type(user, group, other). we can assign multiple users for the same file.
setfacl -m u:kali:rw gfg.txt
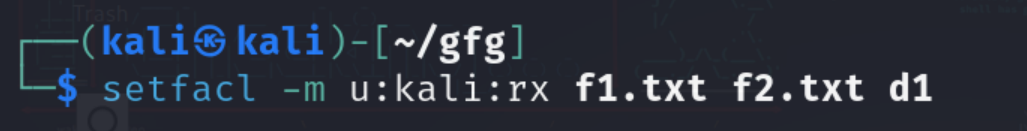
Step 2: set the permission to user for multiple files and directories
As we have the advantage of setfacl, we can assign permission on multiple files and directories at the same time.
setfacl -m u:kali:rx f1.txt f2.txt d1
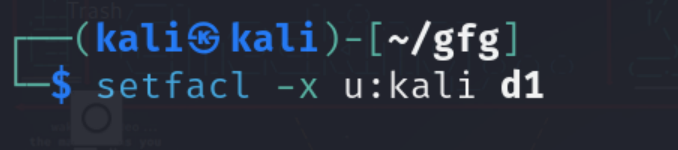
Step 3: Deny all permission on a Wespecific directory
We can remove the ACL permission using the (-x) option while specifying the user type and file(s) or directory(s) name.
setfacl -x u:kali d1
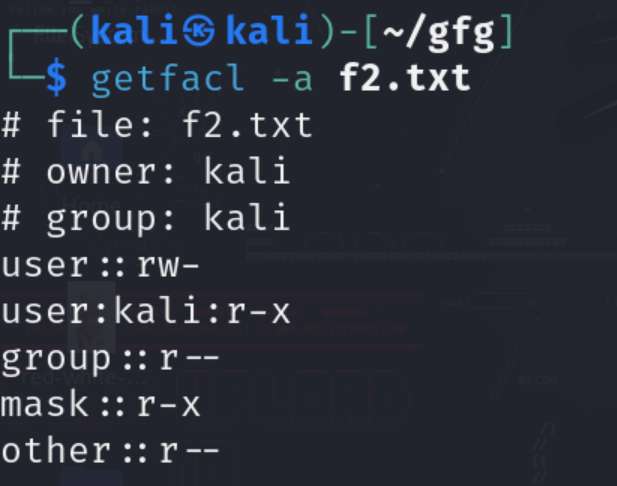
Step 4: Display the file access control list
It is used to display the details of ACL on a specific file or directory. It contains information like file_name, owner and group name, file permission, and umask.
getfacl -a f2.txt
Step 5: Display the default access control list
It is used to display basic information like file_name, and owner/group name.
getfacl -d f2.txt
.png)
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1. What does the Linux command setfacl?a How is it different, from file permissions?
Setfacl is a command in Linux that enables users to set Access Control Lists (ACLs) for files and directories. Unlike file permissions such as read, write and execute which are restricted to the owner, group and others ACLs offer a detailed level of control. They allow users to specify permissions, for users and groups.
Q2. How can I check the existing ACLs of a file or directory using getfacl?
To check the ACLs of a file or directory using getfacl simply use the command followed by the path of the file or directory . Here’s an example:
getfacl filename
Q3. Is it possible to establish default access control lists (ACLs) in such a way that all created files and directories, within a directory automatically inherit specific permissions?
Certainly! To establish default ACLs on a directory you can utilize the (-d ) option along, with setfacl. This guarantees that any fresh files or directories generated within that directory will inherit the designated ACLs. Here’s an example:
setfacl -d -m u:username:permission filename
Q4. If both traditional Unix permissions and ACLs are applied to a file or directory what will be the outcome?
If both Unix permissions and ACLs are set on a file or directory, the most restrictive permission takes precedence. This means that if the Unix permissions allow read access but the ACL denies it, the user will be denied read access. It is important to manage permissions carefully to avoid conflicts and ensure the desired level of security.
Q5. How can I recursively apply ACLs to a directory?
We use recursively ACL to assign the permission on files and subdirectories within the directory. We can use the -R option with the setfacl command. For example, to set ACLs on a directory and apply them to all its contents:
setfacl -R -m u:username:permission directoryname
Conclusion
As we have discussed in this topic, setfacl is a tool used to set an Access Control List(ACL) on Files and Directories. It is a more powerful tool for configuring permission than general file permission. With the help of setfacl we can configure multiple permissions simultaneously in terms of users, groups and others.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...