Linear Scheduling Method in Operating System
Last Updated :
22 Sep, 2020
Linear Scheduling Method is graphical technique in which horizontal axis is used to represent length of linear project, and vertical axis represents duration of project’s activities. It is also known as distance-time scheduling. Every activity is mapped sequentially on graph, depending on sequence of activities in project section. The starting time and location of the activity are showcased as starting point of activity, and end time and location of activity are showcased as endpoint in linear schedule graph.
In Operating Systems, Linear Scheduling Method is most commonly used to schedule resources for repetitive activities in which tasks are sequentially scheduled in queue (same as in LSM implementation in highway, rail, pipeline, and other construction projects).
It schedules activities to ensure :
- Maximum resource utilization.
- Minimum process interruptions.
- Increase in effect of learning curve phenomenon.
Elements of Linear Scheduling Method :
- Parameters representing start time and end time (Axis arguments).
- Place of activity (location).
- Progress measurement (distance in case of transportation projects, floors in case of buildings, etc).
Implementations of Linear Scheduling Method :
- Acts as scheduling algorithm in Operating Systems.
- Mostly used in continuous activities like highway construction, railroads, airport runway construction, pipelines, etc.
- Buildings and other infrastructure constructions.
- Repetitive building units like infrastructure maintenance.
Implementation of Linear Scheduling Method in Operating Systems :
Consider two activities, Activity A and Activity B, both require group of processes to be executed.
- Activity A : Initiates as soon as the system starts Requires access to 8 locations and can be completed in 5 seconds.
- Activity B : Initiates at 3rd second Requires access to 6 locations and can be completed in 2 seconds.
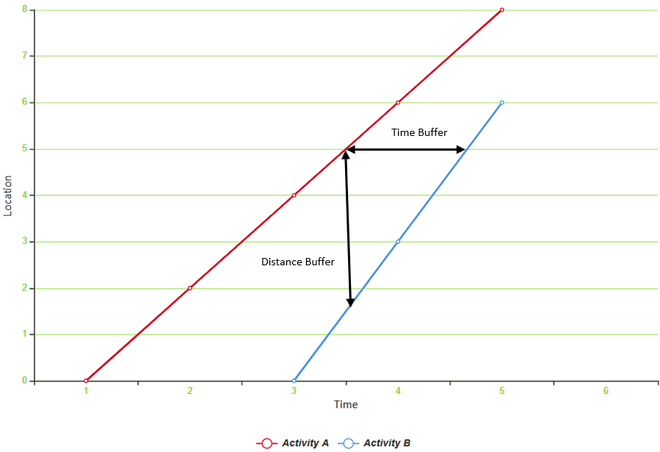 Time-Distance graph to illustrate implementation of LSM in Operating Systems
Time-Distance graph to illustrate implementation of LSM in Operating Systems
Both activities are initiated from location 0 at different intervals, both access different memory locations at particular intervals in-order to execute their processes. Hence, after the successful execution of processes (sub-activities) of both process, both activities are terminated.
Buffer :
When activities progress continuously in chain, some spacing between activities is required. This spacing serves as buffer and can be distance or time interval between activities.
Advantages of Linear Scheduling Method :
- It keeps resources continuously at work.
- Provides further information on planned method of operations.
- Offers advantages due to network approach in certain of activities.
Disadvantages of Linear Scheduling Method :
- Activities do not often progress sequentially.
- This approach often causes problems for construction managers.
- This method is not referred to as optimized for Operating Systems.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...