Java Program to Split an Array from Specified Position
Last Updated :
02 Dec, 2022
Given an array of size N, our job is to split the array at a specific position specified by the user. Will also discuss the boundary cases.
Consider the following example.
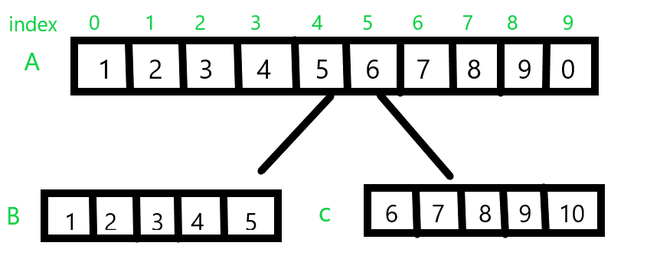
From the above example let A be the original array we want to split. Let N be the length of the array A (N = 10) and let pos be the position we want to split. In the above example pos = 5. All the elements before this position i.e; from index 0 – 4 will be split into one array while elements from index 5 – 10 are split into the later part, labeled as B and C respectively. But if the position is 0 or greater than N then it’s not able to split the array and the invalid position message is displayed.
Examples:
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
pos = 5
Output: B[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
C[] = { 6,7,8,9,0}
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
pos = -1
Output: Invalid position
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
pos = 20
Output: Invalid position
Method 1: In the first method, we will be using two for loops. This approach is quite a straight forward method.
- Step 1: first we accept the value of pos from the user
- Step 2: we declare two arrays B and C having size pos and N – pos respectively.
- Step 3: Then we have two loops the first loop runs from 0 – pos initializing array B while the second loop runs from 0 to N – pos initializing array C.
We have also added a helper method pprint() which accepts an array and prints it. We also have an if statement checking for valid pos value.
Example:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class SplittingArray1 {
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
int n = a.length;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
b[i] = a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - pos; i++) {
c[i] = a[i + pos];
}
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}
|
Output
Enter position to split.
Invalid position.
Method 2: In this method instead of using two for loops we try to implement the same program using just one.
- Step 1 and Step 2 are similar to method 1
- Step 3: we run a for loop from 0 to N – 1
if index < pos
we initialize array B
else if pos >index
we initialize array C
Example:
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SplittingArray2 {
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
int n = a.length;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < pos)
b[i] = a[i];
else
c[i - pos] = a[i];
}
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}
|
Output
Enter position to split.
Invalid position.
Method 3:
This is the shortest method. In this method, we use the in-built Arrays.copyOfRange() method.
public static short[] copyOfRange(short[] original, int from, int to)
original − This is the array from which a range is to be copied.
from − This is the initial index of the range to be copied, inclusive.
to − This is the final index of the range to be copied, exclusive.
Example:
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SplittingArray3 {
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
int n = a.length;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, pos);
c = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, pos, n);
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}
|
Output
Enter position to split.
Invalid position.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...