Implementation of Doubly Linked List in JavaScript
Last Updated :
11 Sep, 2023
This article will demonstrate the Implementation of Doubly Linked List In JavaScript.
A doubly linked list (DLL) is a special type of linked list in which each node contains a pointer to the previous node as well as the next node of the linked list.
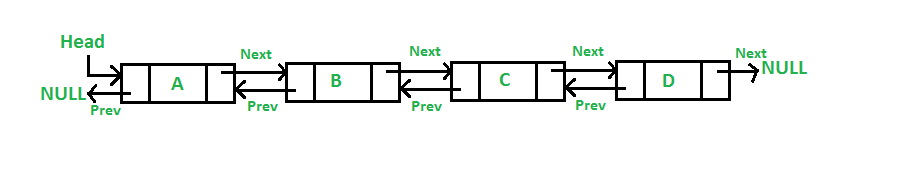
Doubly Linked List in JavaScript
To create we have to create the following classes:
- Node Class: To implement and create elements and link other elements.
- Doubly Linked List Class: To store and access all nodes of the list.
Doubly LinkedList Node is constructed of the following items
- A class named node
- A class constructor, and
- Data items/variables
- data: to contain respective node value
- next: to link the next node with the default value as null.
- prev: to link the previous node with the default value as null.
Example:
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
|
Doubly Linked List is constructed of the following items
- Class Named DoublyLinkedList
- A constructor to create the DLL
- Data items/variables:
- head: to store the starting node
- tail: to store the ending node
Example:
Javascript
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
}
|
Basic Operations in Doubly Linked Lists:
Method to Check if the List is Empty:
- Check if the head is null or not and return result
Javascript
isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) return true;
return false;
}
|
Method to Insert Element:
- Create a new node with value as argument
- Check if the head is null insert at head
- Else insert the new node at the tail and shift tail pointer
Javascript
addItem(val) {
let temp = new Node(val);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = temp;
this.tail = temp;
}
else {
temp.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = temp;
this.tail = this.tail.next;
}
}
|
To traverse and display the list:
- Check is the list is not null
- Use a current poiter to treaverse the list and display value using console.log()
Javascript
display() {
if (!this.isEmpty()) {
let curr = this.head;
while (curr !== null) {
console.log(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
}
}
|
Implementation of Doubly Linked List
Example: This example demonstrate the basic implementation of a link list.
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) return true;
return false;
}
addItem(val) {
let temp = new Node(val);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = temp;
this.tail = temp;
}
else {
this.tail.next = temp;
this.tail = this.tail.next;
}
}
display() {
if (!this.isEmpty()) {
let curr = this.head;
while (curr !== null) {
console.log(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
}
}
}
const dll = new DoublyLinkedList();
dll.addItem(25);
dll.addItem(27);
dll.addItem(17);
dll.addItem(29);
dll.display();
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...