How to Implement Stack in Java Using Array and Generics?
Last Updated :
14 Feb, 2023
Stack is a linear Data Structure that is based on the LIFO concept (last in first out). Instead of only an Integer Stack, Stack can be of String, Character, or even Float type. There are 4 primary operations in the stack as follows:
- push() Method adds element x to the stack.
- pop() Method removes the last element of the stack.
- top() Method returns the last element of the stack.
- empty() Method returns whether the stack is empty or not.
Note: Time Complexity is of order 1 for all operations of the stack
Illustration:
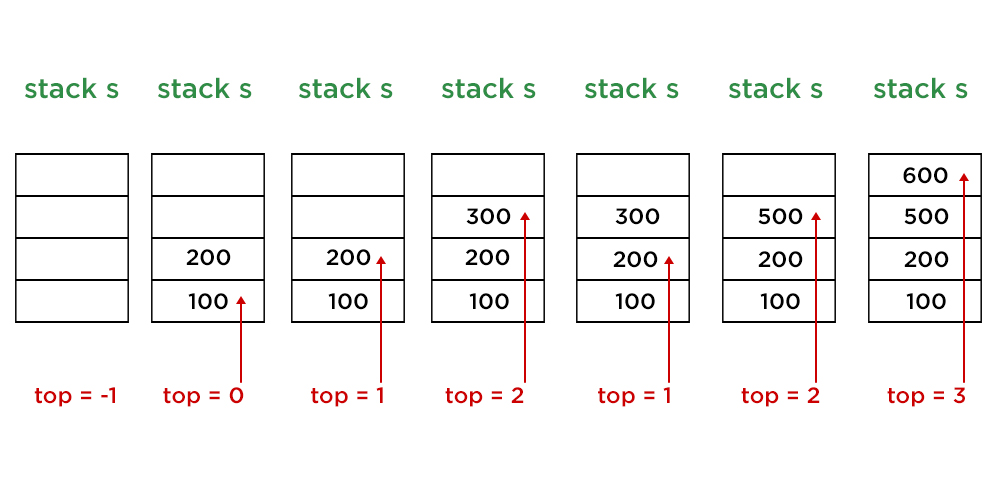
Stack 1
let s = empty stack of Integer type with size 4
Stack 2
push (100) : top = top + 1 and s[top] = 100
Stack 3
push (200) : top = top + 1 and s[top] = 200
Stack 4
push (300) : top = top + 1 and s[top] = 300
Stack 5
pop ( ) : top = top - 1
Stack 6
push (500) : top = top + 1 and s[top] = 500
Stack 7
push (600) : top = top + 1 and s[top] = 600
Note:
push (700) : top +1 == size of stack : Stack Overflow !
// Since top = 3 and size of stack = 4, no more elements can be pushed
Implementation:
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class stack<T> {
ArrayList<T> A;
int top = -1;
int size;
stack(int size)
{
this.size = size;
this.A = new ArrayList<T>(size);
}
void push(T X)
{
if (top + 1 == size) {
System.out.println("Stack Overflow");
}
else {
top = top + 1;
if (A.size() > top)
A.set(top, X);
else
A.add(X);
}
}
T top()
{
if (top == -1) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return null;
}
else
return A.get(top);
}
void pop()
{
if (top == -1) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
}
else
top--;
}
boolean empty() { return top == -1; }
public String toString()
{
String Ans = "";
for (int i = 0; i < top; i++) {
Ans += String.valueOf(A.get(i)) + "->";
}
Ans += String.valueOf(A.get(top));
return Ans;
}
}
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
stack<Integer> s1 = new stack<>(3);
s1.push(10);
s1.push(20);
s1.push(30);
System.out.println(
"s1 after pushing 10, 20 and 30 :\n" + s1);
s1.pop();
System.out.println("s1 after pop :\n" + s1);
stack<String> s2 = new stack<>(3);
s2.push("hello");
s2.push("world");
s2.push("java");
System.out.println(
"\ns2 after pushing 3 elements :\n" + s2);
System.out.println(
"s2 after pushing 4th element :");
s2.push("GFG");
stack<Float> s3 = new stack<>(2);
s3.push(100.0f);
s3.push(200.0f);
System.out.println(
"\ns3 after pushing 2 elements :\n" + s3);
System.out.println("top element of s3:\n"
+ s3.top());
}
}
|
Output
s1 after pushing 10, 20 and 30 :
10->20->30
s1 after pop :
10->20
s2 after pushing 3 elements :
hello->world->java
s2 after pushing 4th element :
Stack Overflow
s3 after pushing 2 elements :
100.0->200.0
top element of s3:
200.0
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space : O(n)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...