How to dynamically allocate a 3D array in C++
Last Updated :
24 Mar, 2021
Prerequisite: Array Basics
In C/C++, multidimensional arrays in simple words as an array of arrays. Data in multidimensional arrays are stored in tabular form (in row major order). Below is the general form of declaring N-dimensional arrays:
Syntax of a Multidimensional Array:
data_type array_name[size1][size2]….[sizeN];
data_type: Type of data to be stored in the array.
Here data_type is valid C/C++ data type
array_name: Name of the array
size1, size2, …, sizeN: Sizes of the dimensions
3-D arrays are an array of Double dimensional arrays:
Syntax of a 3D array:
data_type array_name[x][y][z];
data_type: Type of data to be stored. Valid C/C++ data type.
For more details on multidimensional and, 3D arrays, please refer to the Multidimensional Arrays in C++ article.
Problem: Given a 3D array, the task is to dynamically allocate memory for a 3D array using new in C++.
Solution: In the following methods, the approach used is to make two 2-D arrays and each 2-D array is having 3 rows and 4 columns with the following values.
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
X = No of 2D arrays.
Y = No of rows of each 2D array.
Z = No of columns of each 2D array.
Method 1: using single pointer – In this method, a memory block of size x*y*z is allocated and then the memory blocks are accessed using pointer arithmetic. Below is the program for the same:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 2, y = 3, z = 4;
int count = 0;
int* a = new int[x * y * z];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
*(a + i * y * z + j * z + k) = ++count;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
cout << *(a + i * y * z + j * z + k) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
delete[] a;
return 0;
}
|
Output:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
Method 2: using triple pointer – Below is the diagram to illustrate the concept:
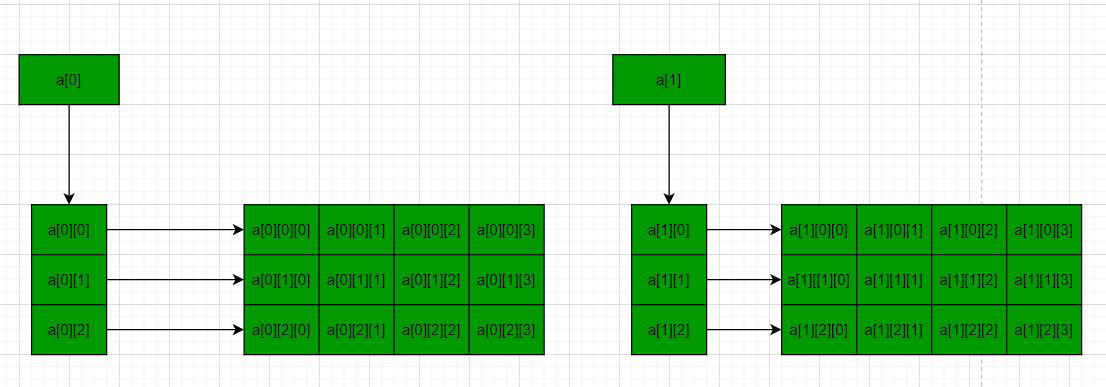
Below is the program for the same:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 2, y = 3, z = 4;
int count = 0;
int*** a = new int**[x];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
a[i] = new int*[y];
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
a[i][j] = new int[z];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
a[i][j][k] = ++count;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
cout << a[i][j][k] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
delete[] a[i][j];
}
delete[] a[i];
}
delete[] a;
return 0;
}
|
Output:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...