How does Query.prototype.cursor() work in Mongoose?
Last Updated :
17 Mar, 2021
The Query.prototype.cursor() function returns a wrapper around a MongoDB driver cursor. And this function triggers the pre find hooks, not the post find hooks.
Syntax:
Query.prototype.cursor()
Parameters: This function has one optional parameter i.e. transform which is an optional function which accepts a mongoose document.
Return Value: This function returns QueryCursor Object.
Installing mongoose :
npm install mongoose
After installing the mongoose module, you can check your mongoose version in command prompt using the command.
npm mongoose --version
Now, create a folder and add a file for example, index.js as shown below.
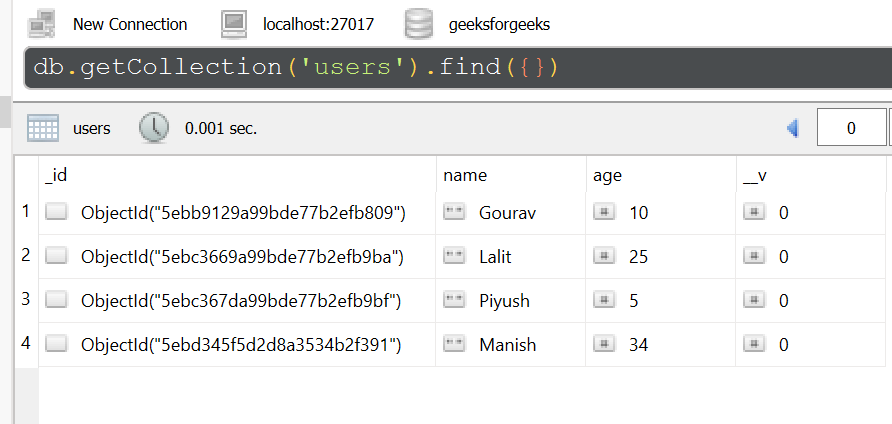
Database: The sample database used here is shown below:
Example 1:
index.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
useNewUrlParser: true,
useCreateIndex: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
});
const User = mongoose.model('User', {
name: { type: String },
age: { type: Number }
});
var cursor = User.find({}).cursor();
cursor.next(function(error, doc) {
console.log(doc);
});
|
Steps to run the program:
The project structure will look like this:
Run index.js file using below command:
node index.js
Output:
{ _id: 5ebb9129a99bde77b2efb809, name: ‘Gourav’, age: 10, __v: 0 }
Example 2:
index.js
const express = require('express');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const app = express()
useNewUrlParser: true,
useCreateIndex: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
});
const User = mongoose.model('User', {
name: { type: String },
age: { type: Number }
});
var cursor = User.find({}).cursor();
cursor.next(function(error, doc) {
console.log(doc);
});
cursor.next(function(error, doc) {
console.log(doc);
});
cursor.next(function(error, doc) {
console.log(doc);
});
app.listen(3000, function(error ) {
if(error) console.log(error)
console.log("Server listening on PORT 3000")
});
|
Steps to run the program:
The project structure will look like this:

Run index.js file using below command:
node index.js
Output:
Server listening on PORT 3000
{ _id: 5ebb9129a99bde77b2efb809, name: ‘Gourav’, age: 10, __v: 0 }
{ _id: 5ebc3669a99bde77b2efb9ba, name: ‘Lalit’, age: 25, __v: 0 }
{ _id: 5ebc367da99bde77b2efb9bf, name: ‘Piyush’, age: 5, __v: 0 }
Reference:
https://mongoosejs.com/docs/api/query.html#query_Query-cursor
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...