Generate Binary Strings of length N using Branch and Bound
Last Updated :
01 Mar, 2023
The task is to generate a binary string of length N using branch and bound technique Examples:
Input: N = 3 Output: 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 Explanation: Numbers with 3 binary digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 Input: N = 2 Output: 00 01 10 11
Approach: Generate Combinations using Branch and Bound :
- It starts with an empty solution vector.
- While Queue is not empty remove partial vector from queue.
- If it is a final vector print the combination else,
- For the next component of partial vector create k child vectors by fixing all possible states for the next component insert vectors into the queue.
Below is the implementation of the above approach
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int *soln;
int level;
vector<Node *> child;
Node *parent;
Node(Node *parent, int level, int N)
{
this->parent = parent;
this->level = level;
this->soln = new int[N];
}
};
void generate(Node *n, int &N, queue<Node *> &Q)
{
if (n->level == N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
cout << n->soln[i];
cout << endl;
}
else
{
int l = n->level;
for (int i = 0; i <= 1; i++)
{
Node *x = new Node(n, l + 1, N);
for (int k = 0; k < l; k++)
x->soln[k] = n->soln[k];
x->soln[l] = i;
n->child.push_back(x);
Q.push(x);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int N = 3;
Node *root;
root = new Node(NULL, 0, N);
queue<Node *> Q;
Q.push(root);
while (!Q.empty())
{
Node *E = Q.front();
Q.pop();
generate(E, N, Q);
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int soln[];
int level;
ArrayList<Node> child;
Node parent;
Node(Node parent, int level, int N)
{
this.parent = parent;
this.level = level;
this.soln = new int[N];
}
}
class GFG {
static int N;
public static Queue<Node> Q;
public static void generate(Node n)
{
if (n.level == N) {
for (int i = 0; i <= N - 1; i++) {
System.out.print(n.soln[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
else {
n.child = new ArrayList<Node>();
int l = n.level;
for (int i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
Node x = new Node(n, l + 1, N);
for (int k = 0; k < l; k++) {
x.soln[k] = n.soln[k];
}
x.soln[l] = i;
n.child.add(x);
Q.add(x);
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
N = 3;
Node root = new Node(null, 0, N);
Q = new LinkedList<Node>();
Q.add(root);
while (Q.size() != 0) {
Node E = Q.poll();
generate(E);
}
}
}
|
Python3
from queue import Queue
class Node:
def __init__(self, parent, level, N):
self.parent = parent
self.level = level
self.soln = [0]*N
self.child = []
Q = Queue()
def generate(n):
if n.level == N:
print(''.join(str(x) for x in n.soln))
else:
n.child = []
l = n.level
for i in range(2):
x = Node(n, l + 1, N)
x.soln[:l] = n.soln[:l]
x.soln[l] = i
n.child.append(x)
Q.put(x)
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 3
root = Node(None, 0, N)
Q.put(root)
while not Q.empty():
E = Q.get()
generate(E)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node
{
public int []soln;
public int level;
public List<Node> child;
public Node parent;
public Node(Node parent,
int level, int N)
{
this.parent = parent;
this.level = level;
this.soln = new int[N];
}
}
class GFG
{
static int N;
public static Queue<Node> Q;
public static void generate(Node n)
{
if (n.level == N)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= N - 1; i++)
{
Console.Write(n.soln[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
n.child = new List<Node>();
int l = n.level;
for (int i = 0; i <= 1; i++)
{
Node x = new Node(n, l + 1, N);
for (int k = 0; k < l; k++)
{
x.soln[k] = n.soln[k];
}
x.soln[l] = i;
n.child.Add(x);
Q.Enqueue(x);
}
}
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
N = 3;
Node root = new Node(null, 0, N);
Q = new Queue<Node>();
Q.Enqueue(root);
while (Q.Count != 0)
{
Node E = Q.Dequeue();
generate(E);
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(parent, level, N) {
this.parent = parent;
this.level = level;
this.soln = new Array(N).fill(0);
this.child = [];
}
}
const Q = [];
function generate(n, N) {
if (n.level === N) {
console.log(n.soln.join(""));
} else {
n.child = [];
const l = n.level;
for (let i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
const x = new Node(n, l + 1, N);
x.soln = n.soln.slice();
x.soln[l] = i;
n.child.push(x);
Q.push(x);
}
}
}
(() => {
const N = 3;
const root = new Node(null, 0, N);
Q.push(root);
while (Q.length > 0) {
const E = Q.shift();
generate(E, N);
}
})();
|
Output:000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
Time Complexity: 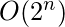
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...