Find last remaining Array element by multiplying boundary elements based on given rules
Last Updated :
24 Mar, 2023
Given an array arr[], the task is to find the only remaining element in the array after applying the below operation till there is only one element left in the array. In an operation, multiply the boundary elements of this array and if the size of the array is:
- Even: Insert the product in the middle of the array and remove the boundary elements
- Odd: Subtract the middle element from the product and replace the middle element with the absolute difference and remove the boundary elements.
Examples:
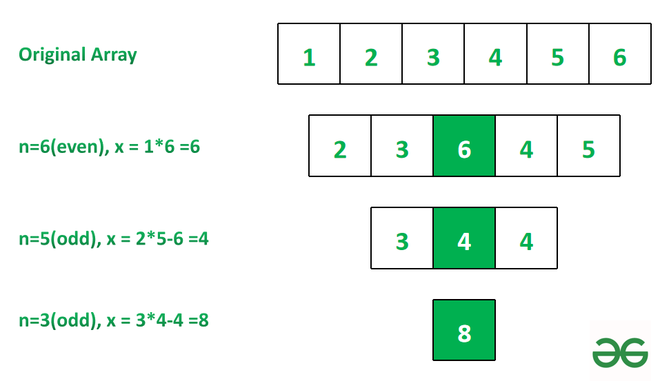
Input: arr[] = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
Output: 8
Explanation: See the image below for explanation.
Input: arr[] = [ 3, 5, 1, 8, 9]
Output: 14
Approach: The solution is based on greedy approach. Delete the elements from the ends of the array and insert the data in the middle of the array. Now follow the below steps to solve this problem:
- Run a while loop, till the size of the array arr[] is greater than 1. In each iteration of this loop:
- Take the product of the first and the last elements and then pop them.
- If the size of the array is even, then insert the product in the middle of the array arr[].
- If it is odd then subtract the middle element from the product and replace it with the middle element.
- After the loop ends, print the only remaining element in the array.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void PSarray(vector<int> A)
{
while (A.size() != 1) {
if (A.size() % 2 == 0) {
int x = A[0] * A[A.size() - 1];
A.erase(A.begin());
A.pop_back();
int n = A.size();
A.insert(A.begin() + n / 2, x);
}
else {
int x = A[0] * A[A.size() - 1];
A.erase(A.begin());
A.pop_back();
int n = A.size();
A[n / 2] = x - A[n / 2];
}
}
cout << A[0] << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
PSarray(arr);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
class GFG
{
static void PSarray(ArrayList<Integer> A)
{
while (A.size() != 1)
{
if (A.size() % 2 == 0){
int x = A.get(0)*A.get(A.size()-1);
A.remove(0);
A.remove(A.size() - 1);
int n = A.size();
A.add(n/2, x);
}
else {
int x = A.get(0)*A.get(A.size() - 1);
A.remove(0);
A.remove(A.size() - 1);
int n = A.size();
A.set(n / 2, x - A.get(n / 2));
}
}
System.out.println(A);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer []arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
ArrayList<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(arr));
PSarray(A);
}
}
|
Python3
def PSarray(A):
while len(A) != 1:
if len(A) % 2 == 0:
x = A.pop(0)*A.pop()
n = len(A)
A.insert(n//2, x)
else:
x = A.pop(0)*A.pop()
n = len(A)
A[n//2] = x-A[n//2]
print(A[0])
if __name__ == "__main__":
A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
PSarray(A)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static void PSarray(List<int> A)
{
while (A.Count != 1)
{
if (A.Count % 2 == 0){
int x = A[0]*A[A.Count-1];
A.RemoveAt(0);
A.RemoveAt(A.Count - 1);
int n = A.Count;
A.Insert(n/2,x);
}
else {
int x = A[0]*A[A.Count - 1];
A.RemoveAt(0);
A.RemoveAt(A.Count - 1);
int n = A.Count;
A[n / 2] = x - A[n / 2];
}
}
A.ForEach(x=>Console.Write(x));
}
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
List<int> A = new List<int>(arr);
PSarray(A);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function PSarray(A)
{
while (A.length != 1)
{
if (A.length % 2 == 0)
{
let x = A.shift() * A.pop()
let n = A.length
let p1 = A.slice(0, Math.floor(A.length / 2))
p1.push(x)
let p2 = A.slice(Math.floor(A.length / 2))
A = p1.concat(p2)
}
else
{
let x = A.shift() * A.pop()
let n = A.length
A[(Math.floor(n / 2))] = x - A[(Math.floor(n / 2))]
}
}
document.write(A[0])
}
let A = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
PSarray(A)
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...