Today we are living in a heroic age of extreme development. The demand for advanced software drives software engineers to explore new methods for software development. However, new technologies follow the same old methods but in a modern way. Have you ever wondered how any software is created and what processes developers follow to create new software?
Software development is becoming important for almost every organization. The practice of software development has advanced since its beginning nearly half a century ago.

Evolution of Software Development Life Cycle Methodologies
Evolution of SDLC Methodologies
The development of information systems began from 1940 to 1960. The rise of software crises led to the development of organized and systematic software engineering approaches. Certainly, the software industry is too dynamic and requires constant updating. Therefore, many methods of software development have been proposed to improve the efficiency and improvement of software. Currently, the field of software engineering is using life cycle models for software development.
These models include the Waterfall Model, Agile Model, etc. Among all the life cycle models, Agile is widely used and the most popular and reliable:
Waterfall Model (1970s):
- The Waterfall model was the earliest SDLC methodology, following a linear and sequential approach.
- Each phase (requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment) must be completed before moving to the next.
Iterative Models (1980s):
- Iterative models allowed for cycles of development, enabling partial implementation and feedback before proceeding.
- Prototyping and incremental development emerged as variations.
Agile Manifesto (2001):
- The Agile Manifesto emphasized collaboration, customer feedback, and iterative development.
- Agile methodologies like Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP) gained popularity.
Scrum Framework (Early 2000s):
- Scrum, an Agile framework, introduced time-boxed iterations (sprints), daily stand-ups, and roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner.
Lean Software Development (2003):
- Lean principles, derived from manufacturing, were applied to software development, focusing on minimizing waste and maximizing customer value.
DevOps (2009):
- DevOps emerged as a response to the need for collaboration between development and operations teams.
- It emphasizes automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery for faster and more reliable releases.
Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) (2011):
- SAFe was introduced to address the challenges of scaling Agile practices to large enterprises.
- It provides a framework for implementing Agile at scale, incorporating Lean and Agile principles.
DevSecOps (2015):
- DevSecOps extends DevOps by integrating security measures into the entire software development lifecycle.
- Security considerations become an integral part of development practices.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) (2010s):
- CI/CD practices automate building, testing, and deployment processes for quicker and more reliable software delivery.
Hybrid Approaches (Ongoing):
- Many organizations adopt hybrid approaches, combining elements from various methodologies to create customized SDLC processes.
- Flexibility and adaptability remain key considerations.
Low-Code/No-Code Platforms (2010s-2020s):
- Low-code/no-code platforms enable users with varying technical expertise to participate in software development, accelerating development timelines.
Software Development Methods:
Software development methodology is a framework used to plan, structure, and process the development of information systems. In the field of software engineering the following methods are used for software development.
- Software development life cycle.
- Crystal methods.
- Dynamic System Development Model.
- Extreme Programming.
- Facility driven development.
- Joint application development.
- Rapid Application Development.
- Lean development.
- Rational Unified Process.
The software development life cycle is a theoretical approach to project management. It is a series of steps that provide a general understanding of the process of software development. Furthermore, the SDLC process consists of different key steps, each of which performs a different function. Software development life cycle improves the development process and quality of software.
SDLC includes the following steps:
- Requirement analysis
- Design
- Execution
- Testing
- Launch and Maintenance
For software development, SDLC models are used which include:
- Waterfall model
- V-shaped model
- Evolutionary prototype model
- Spiral model
- Iterative and incremental method
- Agile development
1. Waterfall Model
This is a traditional approach to project management. The waterfall model is a linear sequential flow. In the waterfall model, motion flows in a linear manner from higher levels to lower levels, just like waterfall flow. As discussed earlier, the waterfall model consists of several stages of a software application. The gradual downward flow is completed and various stages begin one after the other. Also, the stages never overlap because the output of one stage serves as the input of the next stage. This is the most primitive approach which is the core of software development.
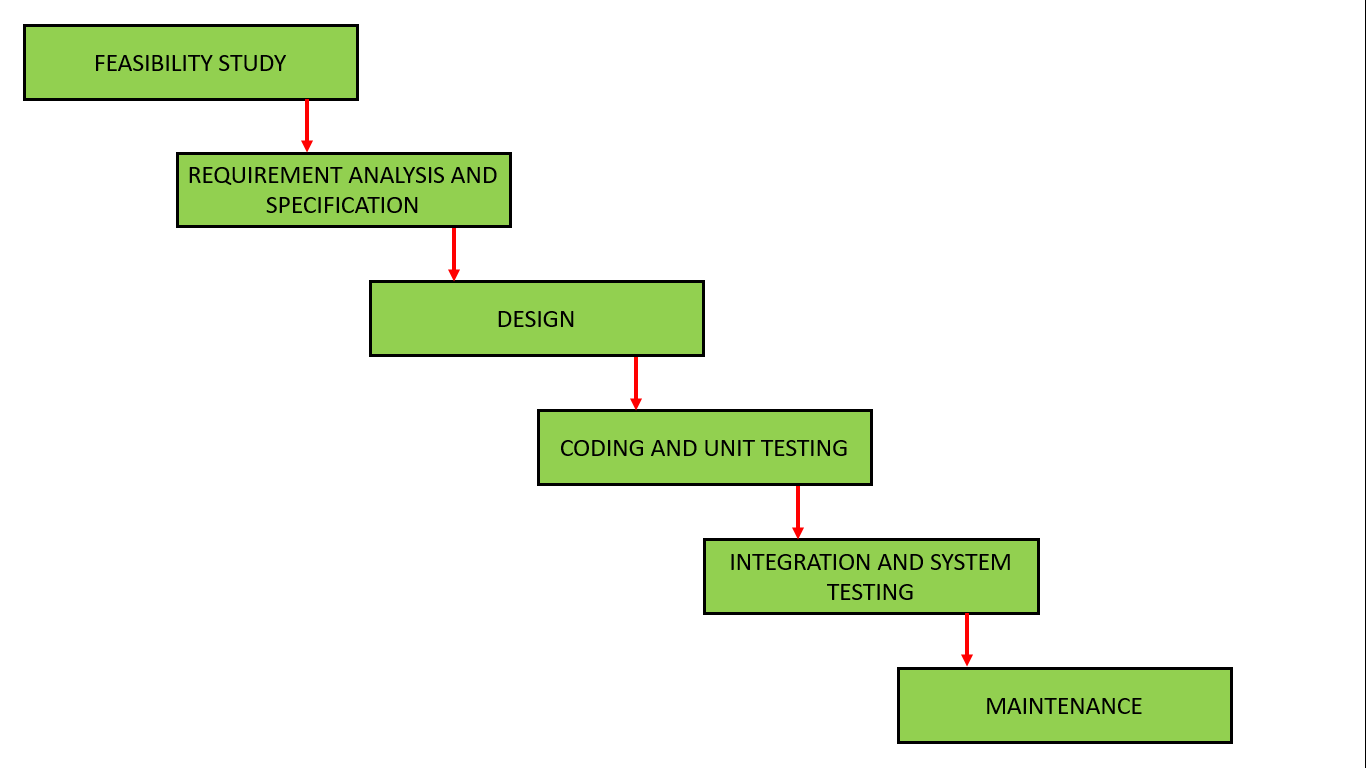
Waterfall Model
The waterfall model is beneficial for some projects, although it also has some disadvantages.
Advantages of waterfall model are as follows:
- easy to explain to customer
- structural approach
- well-defined stages
- schedule project
Disadvantages of waterfall model:
- Difficult to return to the previous era.
- less flexible
- Does not allow changes to previous step
- Expensive and takes more time
Thus, the waterfall model is ideal for projects that do not focus on changing requirements.
2. V-shaped Model:
The V-shaped model is an extension of the waterfall approach. Like the waterfall model, the V-shaped model does not flow in a linear manner, rather the process moves in a V shape. The steps of the process curve upwards after the implementation and coding phase. Initial testing planning is the major difference between waterfall and V-shaped models.

V-Model
Advantages of the V-shaped model are as follows:
- Simple and easy to use
- Specific deliverables at each stage
- Chances of success are higher than waterfall model
Disadvantages of the V-shaped model:
- not flexible
- Difficult and expensive adjustment range
- No initial prototype is created before the implementation phase
- does not offer any clear solutions to problems
Therefore, projects with clearly defined and known software requirements use this model. Another condition that imposes this model is that the software development technologies and tools must be well known.
3. Evolutionary Prototype Model:
Prototyping models refers to creating prototypes for software applications. This model creates dummy prototypes by developing incomplete versions of software programs. Certainly, prototyping is a common process in software development. Thus, this process visualizes the components of the software. It also limits the time it takes for problems to occur, reducing recurrences.
The prototype is of the following types:
- Throwaway Prototyping: These are eventually removed and do not become part of the final software.
- Evolutionary Prototype: These develop into final systems. Iterative incorporation of user’s feedback helps this process.
- Incremental Prototyping: The final product is created after creating several different prototypes. These separate prototypes eventually merge to create an overall design.
- Excessive Prototyping: It divides web development into three phases. The first step is an HTML-based static prototype. In the second step, the simulated services layer programs the screen and makes it fully functional. The third phase is of implementation.
The benefits of the prototype model are as follows:
- Time and cost are reduced
- Appreciates user participation
The disadvantages are as follows:
- Inadequate analysis
- Excessive prototype development time
In conclusion, the prototyping model is good for projects that involve user participation.

Evolutionary Prototype Model
4. Spiral Model:
Spiral model is a combination of prototyping and waterfall model. This model is ideal for large complex projects. Furthermore, it follows the same steps as the waterfall model. However, it is separate from planning, risk assessment and prototype construction and simulation.
The benefits of the spiral model include realistic projections and risk management. Whereas, the disadvantage of this model is that it requires special skills to evaluate the risks. Furthermore, it is highly customized which limits reusability.
Therefore, projects that have large applications and systems use the spiral model.
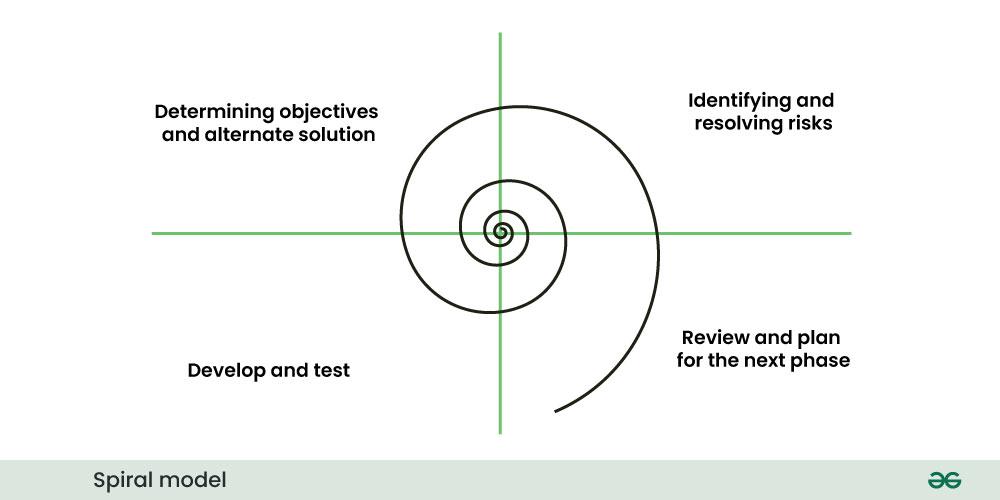
Spiral Model
5. Iterative and Incremental Models:
This model overcomes the limitations of the waterfall model. This starts with initial planning and ends with deployment. Cyclical interactions occur in all phases. Furthermore, this model has repetitive cycles that make the development of each cycle easier. Additionally, this model includes a mini waterfall or V-shaped model.
The advantage of the iterative model is that it can detect project problems at an early stage. Also, it focuses more on customer value and can accommodate some change requests. However, there are some disadvantages, including heavy documentation. It also requires more customer involvement than the linear approach.
Therefore, projects with separate components or segments use this model as a shrink-wrap application.

Iterative Model
The Incremental Model is an iterative software development process where the product is designed, implemented, and tested incrementally (a little more is added each time) until the product is finished. Each iteration represents a small part of the overall system and includes both new features and enhancements to existing ones.

Incremental Model
6. Agile Model:
In the Agile model, requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between cross-functional teams. The Agile model is based on iterative and incremental approach. In addition, there are many Agile methodologies including Crystal Method, Dynamic System Development Model, and Scrum, etc. However, most Agile methods reduce risk by developing software in iterations. So each iteration is like a small-scale software design in itself. It also includes all the work needed to provide small-increments of new functionality. For example, planning, requirements analysis, design, coding, testing, and documentation. Whereas iteration may not add substantial functionality to the license that distributes the product. Thus, the goal of an Agile software project is to be able to deliver new software at the end of each iteration. At the end of each iteration, the team re-examines the project priorities.
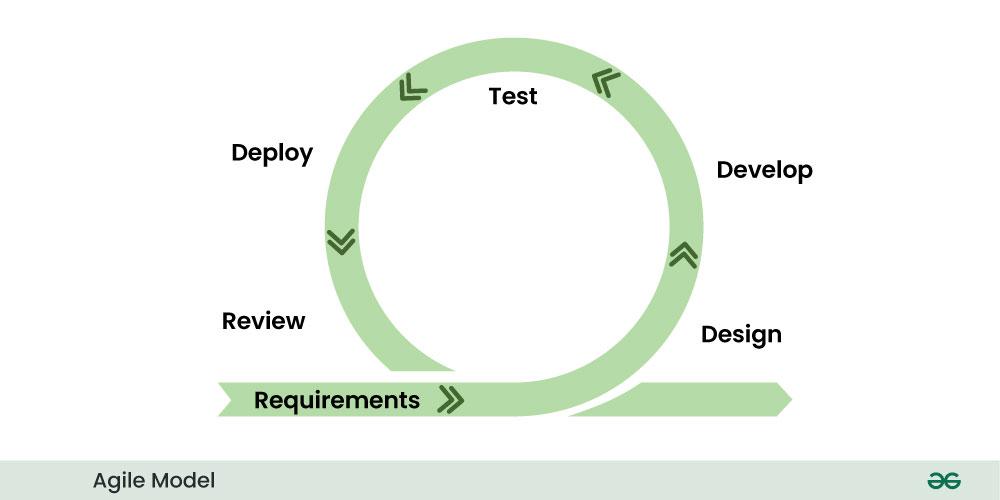
Agile Model
Agile can be used in any type of project. The benefits of Agile include customer involvement, shorter development time, and higher quality end results, etc. However, the disadvantages of Agile are last-stage documentation, scalability, low usability, etc.
Agile methodology also highlights working software as the primary measure of progress. Furthermore, Agile methods produce much less written documentation than other methods.
The Latest Trends in Software Development Life Cycle Methodologies:
Every firm now needs software development, thus choosing the appropriate software development life cycle (SDLC) approach is very crucial. Planning thoroughly is essential before deciding on the best SDLC strategy for your next project. Each offers advantages and disadvantages that businesses must consider.
However, these approaches also evolve with time.
As people find and create more tools to aid them in various activities, trends start to form. It’s crucial that you understand the effects of these trends so that, regardless of the SDLC you select for your project, you may succeed.
Conclusion:
The evolution of software development life cycle (SDLC) techniques is indicative of an ongoing search for methodologies that improve software development processes’ overall efficiency, responsiveness to change, and collaboration. The adoption of Agile and iterative methodologies, in conjunction with the integration of DevOps and security protocols, denotes a dedication to producing software that meets high standards in a dynamic and competitive environment. Future developments in organizational structures, customer-centric development, and technological breakthroughs will probably all continue to impact SDLC methodology evolution.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...