Dominant Set of a Graph
Last Updated :
26 Oct, 2023
In graph theory, a dominating set for a graph G = (V, E) is a subset D of V such that every vertex not in D is adjacent to at least one member of D. The domination number is the number of vertices in a smallest dominating set for G.
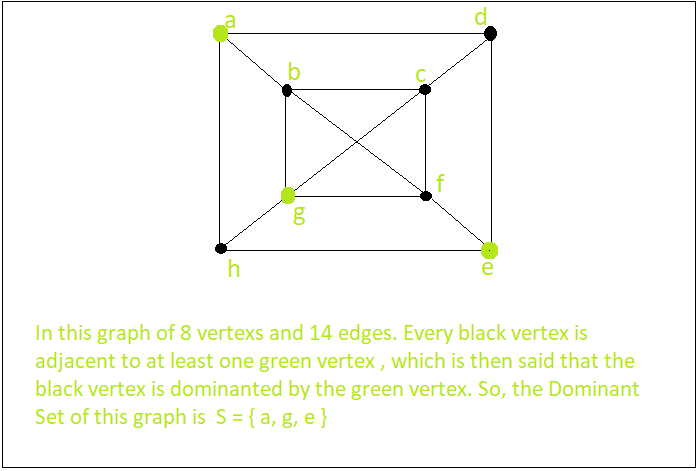
Examples:
Input : A graph with 4 vertex and 4 edges
Output : The Dominant Set S= { a, b } or { a, d } or { a, c } and more.
Input : A graph with 6 vertex and 7 edges
Output : The Dominant Set S= { a, d, f } or { e, c } and more.
It is believed that there may be no efficient algorithm that finds a smallest dominating set for all graphs, but there are efficient approximation algorithms.
Algorithm :
- First we have to initialize a set ‘S’ as empty
- Take any edge ‘e’ of the graph connecting the vertices ( say A and B )
- Add one vertex between A and B ( let say A ) to our set S
- Delete all the edges in the graph connected to A
- Go back to step 2 and repeat, if some edge is still left in the graph
- The final set S is a Dominant Set of the graph
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int> > g;
bool box[100000];
vector<int> Dominant(int ver, int edge)
{
vector<int> S;
for (int i = 0; i < ver; i++) {
if (!box[i]) {
S.push_back(i);
box[i] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)g[i].size(); j++) {
if (!box[g[i][j]]) {
box[g[i][j]] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
return S;
}
int main()
{
int ver, edge, x, y;
ver = 5;
edge = 6;
g.resize(ver);
memset(box, 0, sizeof(box));
g[0].push_back(1);
g[1].push_back(0);
g[1].push_back(2);
g[2].push_back(1);
g[2].push_back(3);
g[3].push_back(2);
g[0].push_back(3);
g[3].push_back(0);
g[3].push_back(4);
g[4].push_back(3);
g[2].push_back(4);
g[4].push_back(2);
vector<int> S = Dominant(ver, edge);
cout << "The Dominant Set is : { ";
for (int i = 0; i < (int)S.size(); i++)
cout << S[i] + 1 << " ";
cout << "}";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static Vector<Integer> []g;
static boolean []box = new boolean[100000];
static Vector<Integer> Dominant(int ver, int edge)
{
Vector<Integer> S = new Vector<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < ver; i++)
{
if (!box[i])
{
S.add(i);
box[i] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)g[i].size(); j++)
{
if (!box[g[i].get(j)])
{
box[g[i].get(j)] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
return S;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ver, edge, x, y;
ver = 5;
edge = 6;
g = new Vector[ver];
for (int i = 0; i < ver; i++)
g[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
g[0].add(1);
g[1].add(0);
g[1].add(2);
g[2].add(1);
g[2].add(3);
g[3].add(2);
g[0].add(3);
g[3].add(0);
g[3].add(4);
g[4].add(3);
g[2].add(4);
g[4].add(2);
Vector<Integer> S = Dominant(ver, edge);
System.out.print("The Dominant Set is : { ");
for (int i = 0; i < (int)S.size(); i++)
System.out.print(S.get(i) + 1 + " ");
System.out.print("}");
}
}
|
Python3
from typing import List
g = []
box = []
def Dominant(ver: int, edge: int) -> List[int]:
S = []
for i in range(ver):
if not box[i]:
S.append(i)
box[i] = True
for j in range(len(g[i])):
if not box[g[i][j]]:
box[g[i][j]] = True
break
return S
if __name__ == '__main__':
ver = 5
edge = 6
for i in range(ver):
g.append([])
box = [False for i in range(ver)]
g[0].append(1)
g[1].append(0)
g[1].append(2)
g[2].append(1)
g[2].append(3)
g[3].append(2)
g[0].append(3)
g[3].append(0)
g[3].append(4)
g[4].append(3)
g[2].append(4)
g[4].append(2)
S = Dominant(ver, edge)
print("The Dominant Set is : {{ {} }}".format(" ".join(str(x+1) for x in S)))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static List<int> []g;
static bool []box = new bool[100000];
static List<int> Dominant(int ver, int edge)
{
List<int> S = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < ver; i++)
{
if (!box[i])
{
S.Add(i);
box[i] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)g[i].Count; j++)
{
if (!box[g[i][j]])
{
box[g[i][j]] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
return S;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int ver, edge;
ver = 5;
edge = 6;
g = new List<int>[ver];
for (int i = 0; i < ver; i++)
g[i] = new List<int>();
g[0].Add(1);
g[1].Add(0);
g[1].Add(2);
g[2].Add(1);
g[2].Add(3);
g[3].Add(2);
g[0].Add(3);
g[3].Add(0);
g[3].Add(4);
g[4].Add(3);
g[2].Add(4);
g[4].Add(2);
List<int> S = Dominant(ver, edge);
Console.Write("The Dominant Set is : { ");
for (int i = 0; i < (int)S.Count; i++)
Console.Write(S[i] + 1 + " ");
Console.Write("}");
}
}
|
Javascript
function findDominantSet(ver, edge, g) {
let S = [];
let box = new Array(ver).fill(false);
for (let i = 0; i < ver; i++) {
if (!box[i]) {
S.push(i);
box[i] = true;
for (let j = 0; j < g[i].length; j++) {
if (!box[g[i][j]]) {
box[g[i][j]] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
return S;
}
function main() {
const ver = 5;
const edge = 6;
const g = new Array(ver);
for (let i = 0; i < ver; i++) {
g[i] = [];
}
const box = new Array(100000).fill(false);
g[0].push(1);
g[1].push(0);
g[1].push(2);
g[2].push(1);
g[2].push(3);
g[3].push(2);
g[0].push(3);
g[3].push(0);
g[3].push(4);
g[4].push(3);
g[2].push(4);
g[4].push(2);
const S = findDominantSet(ver, edge, g);
console.log("The Dominant Set is : { " + S.map(val => val + 1).join(" ") + " }");
}
main();
|
Output
The Dominant Set is : { 1 3 5 }
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...