Concepts of Revenue| Total Revenue, Average Revenue and Marginal Revenue
Last Updated :
10 Aug, 2023
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the amount received by an organisation from the sale of a given quantity of a commodity in the market. Simply put, is the amount of money received by a producer for the sale proceeds. For example, if a firm gets ₹20,000 by selling 100 tables, then ₹20,000 will be the revenue of the firm.
Revenue is an essential concept in the analysis of an economy. Sales level has a direct impact on revenue. It means that if sales increase, then revenue will also increase. Revenue is not the same as Profit. Revenue is the sale proceeds; however, Profit is the excess of revenue over costs.
Profit = Revenue – Costs
There are three important terms in Revenue; viz., Total Revenue, Average Revenue, and Marginal Revenue.
What is Total Revenue?
The total receipts from the sale of a given quantity of a commodity are known as Total Revenue. In simple terms, Total Revenue is the total income of a firm and is determined by multiplying the quantity of the commodity sold by its price. The formula for Total Revenue is,
Total Revenue = Quantity x Price
For example, if a firm sells 100 tables for ₹200 each, then the Total Revenue of the firm will be 100 x 200 = ₹20,000.
What is Average Revenue?
The revenue per unit of the output sold of a commodity is known as Average Revenue. It is determined by dividing the Total Revenue by the number of units sold of a commodity. The formula for Average Revenue is,
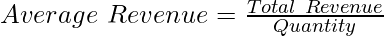
For example, if the Total Revenue of a firm is ₹20,000 by selling 100 tables, then the Average Revenue will be, 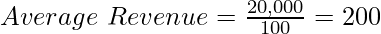
Average Revenue (AR) and Price are the same
As we know, Average Revenue is the per unit sales receipt of a commodity and price is always per unit. Now, as the sellers receive revenue based on the price of the commodity, Price and Average Revenue are one and the same thing.
Explanation:
TR = Quantity x Price ……………………. (1)
 …………………….. (2)
…………………….. (2)
Now, by putting the value of (1) in (2), we get
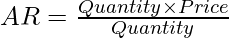
AR = Price
What is Marginal Revenue?
The additional revenue generated by selling an additional unit of output is known as Marginal Revenue. In simple terms, it is the change in Total Revenue from the sale of one more unit of a commodity. The formula for Marginal Revenue is,
MRn = TRn – TRn-1
Where,
MRn = Marginal Revenue of the nth unit
TRn = Total Revenue from n units
TRn-1 = Total Revenue from n-1 units
n = Number of units sold
For example, if the total revenue generated from the sale of 100 tables is ₹20,000 and from the sale of 101 tables is ₹20,500; then the Marginal Revenue of the 101st table will be,
MRn = TRn – TRn-1
MR101 = 20,500 – 20,000 = ₹500
One more way to calculate MR
As we already know, Marginal Revenue is the change in TR when one more unit of the output is sold. However, when the change in units of output sold is more than one, then the previous formula can be difficult to use. In those cases, MR can be determined by using the following formula:
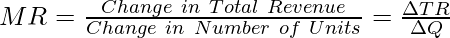
For example, if the TR from the sale of 100 tables is ₹20,000 and 110 tables is ₹24,500; then the Marginal Revenue will be,
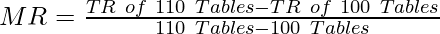
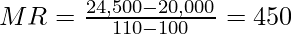
Slope of Total Revenue Curve is represented by Marginal Revenue. It is because 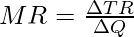
TR is the summation of MR
Another way to calculate TR is by adding the Marginal Revenues of all the units sold. In simple terms, another formula for determining TR is,
TRn = MR1 + MR2 + MR3 + ……………….+MRn
OR
TR = ∑MR
Illustration 1:
From the following table, determine TR, AR, and MR:
Solution:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...