Living Things: Characteristics and Examples
Last Updated :
24 Jul, 2023
Living Things-Characterstics and Examples: Living things are actually just creatures that interact with their surroundings in order to survive. The only things around us that are alive and breathing are living beings. Living things consume food, develop, reproduce, and eventually perish. A living entity is defined as having a predictable life cycle. ‘Living Things’ is an important topic for the exam. We are learning about Living Things – Characteristics, Classification, What Living Things are made of, and Basic Needs of Living Things. Some frequently asked questions help to understand Living Things better.
What are Living Things?
A living thing refers to any organism or life form that has or exhibits the qualities of life or being alive. Living things include many types of organisms, from plants, animals, fungi, and algae that are easily recognized in nature, to a variety of tiny creatures known as protozoa, bacteria, and archaea that cannot be seen under the microscope alone are visible. Living things are found in all types of habitats on Earth: on land, in lakes, rivers, and oceans. Although all of these organisms are very different, they all have two things in common: they all descend from an ancient ancestor and they are all alive.
The earliest life forms we know of are microscopic organisms (microbes) that left traces of their presence in rocks about 3.7 billion years ago. The signals consisted of a type of carbon molecule produced by living things. Evidence of microbes is also preserved in the hard structures they created called stromatolites, which are 3.5 billion years old. Stromatolites form sticky mats of microbes that entrap and bind sediment in layers. Minerals are deposited in the layers, forming permanent structures even as the microbes die. Scientists are studying the now-rare living stromatolite coral reefs to better understand early life on Earth.
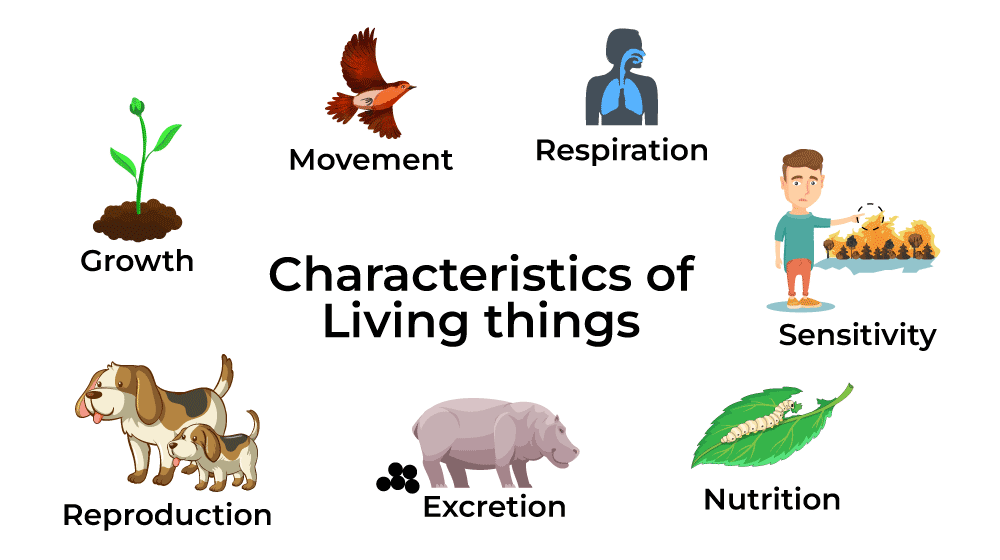
Characteristics of Living Things
To be categorized as a living thing, an organism possesses these below-mentioned characteristics or processes, necessary for life:
- Movement: Living things have the ability to move in one direction or another without outside help. Movement can be the flow of matter within an organism or the external movement of an organism or a part of an organism.
- Sensitivity: Living things react to the conditions around them. For example, green plants grow toward the sunlight, some microorganisms shrink into globules when touched, and people blink when light shines in their eyes.
- Respiration: All living organisms are able to release the energy stored in food molecules through a chemical process known as cellular respiration. During aerobic respiration, oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is released. In unicellular organisms, these gases are exchanged with the environment through the cell membrane of the organism. In multicellular organisms, gas exchange with the environment is somewhat more complex and usually takes place via organs specially adapted for this purpose.
- Nutrition: Living things need energy to survive. Energy comes from nutrients or food. Green plants, algae, and some archaea and bacteria can make food from water and carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. Legumes can produce protein by absorbing nitrogen provided by bacteria that live in the plant’s root nodules. Animals, fungi, protozoa, and many archaea and bacteria require food from an external source.
- Growth: Living things grow by creating new parts and materials and changing old ones. It happens when a seed becomes a plant or a chick becomes a hen. As humans grow, they add new structures, such as teeth, and change the proportions of others.
- Reproduction: By the process of reproduction living things create new organisms. This is the same even for the simplest microbes, which can multiply by simply dividing into two. Each new part is able to move, feed, grow, and perform other vital functions. This type of reproduction is called asexual reproduction because it does not require a mating partner. Asexual reproduction is more common in lower organisms such as bacteria and some species of protozoa and fungi. On the other hand, higher organisms like mammals, and birds require partners for mating which is called sexual reproduction.
- Excretion: The process by which living things remove waste products from the body is called excretion. Excretion in living organisms can be done with the help of skin, Lungs, and Kidneys.
Classification of Living Things
Living things are classified into a series of hierarchical categories: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. An important way for scientists to show how living things are related to each other is by classifying living things into these categories. They classify living things into one of the following six kingdoms.
- Bacteria: These are unicellular microorganisms that do not have a nuclear membrane.
- Protists: These are unicellular organisms, usually much larger than bacteria. They can be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
- Archaea: They are prokaryotic forms of life sharing some features with bacteria and other features with eukarya. Archaea comprise only single-celled organisms and are devoid of nuclei.
- Fungi: They are multicellular and dependent on the decomposition of organic matter because they cannot produce their own food.
- Plants: They are multicellular and autotrophic. They use photosynthesis to produce food from sunlight.
- Animals: Animals are multicellular. They are heterotrophs and depend on food from other organisms.
What is Living Things are made of?
Cells are made of molecules. All living things contain four major carbon-based molecules:
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are used inside cells mainly for quick energy, but also can be used in structure and cell signaling.
- Proteins: Proteins are the building blocks of cells and carry out many important functions from transport to catalyzing chemical reactions to structure.
- Lipids: Lipids are used for long-term energy storage.
- Nucleic acids: Nucleic acids contain the genetic information of the cell and include molecules like DNA and RNA. In addition to these four molecules, cells are also made of inorganic ions such as sodium or potassium and water.
Basic Needs of Living Things
All living beings have certain basic needs:
- Water: The most basic need of all living things is water. Life could not exist without this important resource. Water is required for many chemical reactions in cells. It also helps transport nutrients and eliminate waste.
- Nutrients: All organisms require nutrients for energy, growth, and repair. Every organism has its own way of absorbing nutrients. Some organisms, such as animals and protozoa, get their nutrients from food. Plants and algae produce their own food through photosynthesis. Fungi gain nutrients by breaking down and absorbing decaying organic matter.
- Air and Light: Air and light are also basic needs of certain organisms. Air is a basic need of most living things, although some species of microorganisms cannot tolerate oxygen. For plants and other organisms that carry out photosynthesis, light is an essential requirement for life.
- Habitat: Space is another basic requirement; Organisms such as plants and fungi that are anchored in the substrate need space to grow and develop. Animals and other motile organisms need a place to live and a territory where they can find food and mates.
FAQs on Living Things
Q: What living things are made of?
Answer:
All living things contain four major carbon-based molecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic acids.
Q: What are the types of living things?
Answer:
Living things are classified into one of the following six kingdoms: Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromists, Fungi, Plants, Animals.
Q: What are the life processes carried out by living things?
Answer:
Life processes carried out by living things are Respiration, Movement, Growth, Sensitivity, Nutrition, Reproduction, and Excretion.
Q: What are the basic needs of living things?
Answer:
All living beings have certain basic needs: Water, Nutrients, Air, Light, and Habitat.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...