Break-even Analysis: Importance, Uses, Components and Calculation
Last Updated :
11 Aug, 2023
What is Break-even Analysis?
Break-even Analysis is an economic concept that is used to determine the number of units that needs to be sold by the company to cover the costs and gain no profits. It is the level of units that a company should at least reach in order to survive in the market. Break-even is a level where a company neither earns any profits nor suffers any losses. Basically, the break-even point tells us the units to be sold in order to cover costs.
Key Takeaways from Break-even Analysis:
- Break-even Analysis is a concept used to determine the point where there are no profits and no losses.
- Break-even is a point where the company covers all of its costs.
- Lower fixed costs lead to a lower break-even point and higher fixed costs lead to higher break-even point.
Importance of Break-even Analysis
Break-even Analysis is essential because of the following reasons:
1. Set the number of units to be sold: With the help of break-even analysis, a manager can set a target for the number of units to be sold in order to cover the costs. Variable costs, fixed costs, and the selling price are generally used in the calculation of the break-even point.
2. Pricing Strategy: Break-even Analysis tells the company about the selling price; i.e., What selling price can be charged per unit in order to cover the expenses. Also, if the selling price of a commodity is increased, then the number of units of that product to be sold to achieve the break-even point will be reduced. Similarly, if the selling price of a commodity is reduced, then the company will have to sell extra to achieve the break-even point.
3. Setting Targets: The target being set under break-even analysis acts as the goal of the sales team so that they can plan on how and when to sell the units in order to reach the target.
4. Monitors and Controls Costs: Break-even Analysis helps in monitoring the costs occurring in the production process and then control them by cutting down the useless expenses.
5. Manages the Margin of Safety: During financial breakdown, a company’s sales tend to fall. Under those circumstances, break-even analysis helps in deciding the least number of sales that the company needs to make profits. Besides, with the help of margin of safety reports, the management of a company can easily execute high business decisions.
Components of Break-even Analysis
The three components of Break-even Analysis are as follows:
1. Fixed Costs: These are the costs that the company has to bear even when there is no production of units. Fixed costs remain constant and do not change with the level of production. Fixed Costs are also known as Overhead Costs. For example, Rent or mortgage, equipment costs, salaries, taxes, insurance premiums, etc.
2. Variable Costs: Variable Costs are the costs that change with the change in output. Variable Costs rise as the production rises and falls when production falls. These costs include packaging costs, wages, cost of raw materials, etc.
3. Selling Price: Selling price is the amount that the seller/company charges the customers in exchange for their product or services. The selling price is determined on the basis of raw materials used for production, wages, fixed expenses, etc.
Uses of Break-even Analysis
Following are some of the uses of Break-even Analysis:
1. Change in Business Model: When a company is changing business models like shifting from wholesale business to retail business or shifting from retail business to wholesale business, break-even analysis will help the business in deciding the selling price of the product.
2. Expansion of Business: If a company is deciding to expand its business or launch a new product, the company will do the break-even analysis first to decide on the selling price of the product.
3. Lowering Prices: Sometimes, businesses need to lower down the price of their product so that they can increase their sale and beat the competitors. So, when lowering pricing, businesses need to figure out how many more units they need to sell to offset or make up a price decrease.
Calculation of Break-even Point
The break-even point is calculated using the selling price per unit, variable costs, and fixed costs.
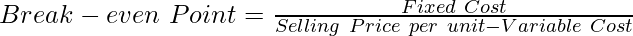
Example:
Particulars
| Amount (in ₹)
|
|---|
Fixed Expense
| 2,00,000
|
Variable Expenses
| 4/unit
|
Selling Price
| 24
|
Solution:
Here, Fixed Cost = ₹2,00,000; Variable Expense = ₹4 per unit; and Selling Price = ₹24
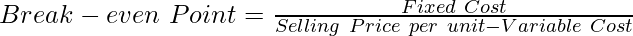
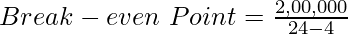
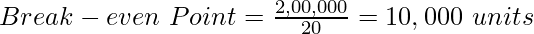
Break-even Point = 10,000 units
It means that the company would need to sell 10,000 units of the product to attain break-even.
Graphical Presentation of Break-even point
In the above graph, X-axis shows units being sold and Y-axis shows the revenue made. The cost line shows the total cost that occurs during the production process, the fixed cost line shows the occurrence of fixed costs, and the revenue line shows the total sales being made. The intersection of the revenue curve and cost curve determines the break-even point; i.e., point E.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...