Virtual base class in C++
Last Updated :
06 Sep, 2023
Virtual base classes are used in virtual inheritance in a way of preventing multiple “instances” of a given class appearing in an inheritance hierarchy when using multiple inheritances.
Need for Virtual Base Classes: Consider the situation where we have one class A . This class A is inherited by two other classes B and C. Both these class are inherited into another in a new class D as shown in figure below.
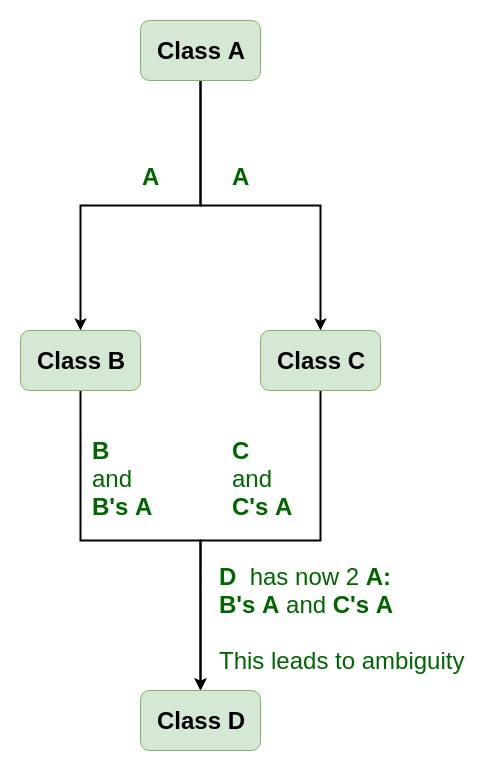
As we can see from the figure that data members/function of class A are inherited twice to class D. One through class B and second through class C. When any data / function member of class A is accessed by an object of class D, ambiguity arises as to which data/function member would be called? One inherited through B or the other inherited through C. This confuses compiler and it displays error.
Example: To show the need of Virtual Base Class in C++
CPP14
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
void show()
{
cout << "Hello form A \n";
}
};
class B : public A {
};
class C : public A {
};
class D : public B, public C {
};
int main()
{
D object;
object.show();
}
|
Compile Errors:
prog.cpp: In function 'int main()':
prog.cpp:29:9: error: request for member 'show' is ambiguous
object.show();
^
prog.cpp:8:8: note: candidates are: void A::show()
void show()
^
prog.cpp:8:8: note: void A::show()
How to resolve this issue?
To resolve this ambiguity when class A is inherited in both class B and class C, it is declared as virtual base class by placing a keyword virtual as :
Syntax for Virtual Base Classes:
Syntax 1:
class B : virtual public A
{
};
Syntax 2:
class C : public virtual A
{
};
Note:
virtual can be written before or after the public. Now only one copy of data/function member will be copied to class C and class B and class A becomes the virtual base class. Virtual base classes offer a way to save space and avoid ambiguities in class hierarchies that use multiple inheritances. When a base class is specified as a virtual base, it can act as an indirect base more than once without duplication of its data members. A single copy of its data members is shared by all the base classes that use virtual base.
Example 1
CPP14
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
int a;
A()
{
a = 10;
}
};
class B : public virtual A {
};
class C : public virtual A {
};
class D : public B, public C {
};
int main()
{
D object;
cout << "a = " << object.a << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Explanation :
The class A has just one data member a which is public. This class is virtually inherited in class B and class C. Now class B and class C use the virtual base class A and no duplication of data member a is done; Classes B and C share a single copy of the members in the virtual base class A.
Example 2:
CPP14
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
void show()
{
cout << "Hello from A \n";
}
};
class B : public virtual A {
};
class C : public virtual A {
};
class D : public B, public C {
};
int main()
{
D object;
object.show();
}
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...