Remarketing, often known as retargeting, is one of the most popular and widely used digital marketing strategies. Regardless of whether they completed a certain activity or not, it entails showing advertisements to visitors who have already visited a website or a particular page. This tactic builds on the interest that these people have previously expressed and presents an opportunity to re-engage and maybe convert them. Frequently referred to as “re”-marketing, it offers a second chance to convert, upsell, or keep clients by using focused internet advertisements or campaigns. Remarketing is a vital tool in every marketer’s toolbox since it can be used through a variety of ad networks, including Outbrain, Google Ads, and Facebook Ads.
Geeky Takeaways:
- Remarketing, often known as retargeting, focuses on visitors who have interacted with a website or piece of content in the past but have not yet performed the required action.
- It entails providing these consumers with pertinent advertisements across a range of internet channels, prompting them to revisit their original interests and urging more engagement.
- The objectives of this strategic approach are to maximize marketing campaign ROI, raise brand recognition, and increase conversion rates.
1. Stay Engaged with Your Target Audience: Retargeting is a crucial digital marketing tactic used to combat the large percentage of website visitors who depart without making a purchase. Remarketing seeks to re-engage these users and direct them back to the website by monitoring user activity and presenting customized advertising across online platforms.
2. Increase Brand Awareness: Notably, 43% of businesses use remarketing techniques to increase online brand identification and exposure. By using remarketing strategies, companies may efficiently raise brand recognition in the early phases of the customer journey and establish themselves as respected authorities in their respective fields.
3. Increasing Brand Recognition and Memory: Remarketing aims to enhance awareness of the brand and memory among prospective consumers by constantly exposing them to targeted advertisements. Constant exposure increases brand recognition and trust, increasing the probability that consumers will choose the brand when making decisions.
4. Improving Customer Retention: Remarketing reminds current consumers of other goods and services that they may find interesting, which helps companies develop connections with them. Businesses may promote repeated transactions and long-term client loyalty by remaining in contact and making pertinent offers for them.
5. Enhancing Marketing Returns: Businesses may attain greater conversion rates and ROI in comparison to traditional marketing strategies by focusing on people who have already interacted with their content or website. Because they attract individuals who are more likely to convert, remarketing efforts are usually more economical and effective.
6. Modifying the Customer Experience: With the help of remarketing, companies may show customers relevant and personalized commercials based on their prior interactions and activities. This customized strategy boosts client happiness and retention rates by improving entire customer experience and engagement.
1. Visitor Interaction: A website’s user interface allows visitors to engage with various types of information, explore product pages, add products to a cart for purchase, subscribe to newsletters, and submit contact forms. These behaviors show the user’s interest, their inclination to buy from, and desire for more interaction with the brand and website. Marketers use these exchanges to target their remarketing initiatives, bring interested customers back into the fold, and increase conversions. Gaining knowledge from visitor behavior may help enhance marketing tactics and improve user’s experience.
2. Placement of Tracking Pixels: A tracking pixel, also known as a cookie, is installed on the user’s browser when they interact with the website. This pixel gathers data relating to the user’s activities, such as the pages they viewed, the length of time they spent on each page, and whether they took any requested actions.
3. Audience Segmentation: Website users are divided by segmentation of audience based upon their demographics, preferences, and activity. Marketers apply data analysis to personalize tactics, such as providing product-specific advertising and offering recovery incentives to cart abandoners. This strategy maximizes remarketing efficiency by aligning messages to user interests, that enhances engagement and conversions. All things considered, segmentation improves communication and maximizes marketing impact.
4. Ad Display: Targeting marketing via audience segmentation data, developing eye-catching commercials, choosing suitable distribution channels, taking part in ad space auctions, distributing ads to particular audiences, and tracking performance indicators are all part of ad display. Through relevant and captivating advertisements, marketers may effectively reach their target audience across numerous web channels, increasing traffic and accomplishing marketing goals.
5. Re-Engagement: In remarketing, re-engagement is the method of reminding people of their prior encounters with a company through well positioned advertisements on various internet platforms. The purpose of these reminders is to spur users’ attention once again and encourage them to take action, such as completing a form or making a purchase. Remarketing builds relationships and encourages brand loyalty by sending consumers tailored messages that are relevant to their previous interactions.
6. Conversion Tracking: Utilizing a variety of techniques and technologies, conversion tracking in remarketing entails keeping an eye on user behaviors including clicks and conversions. Conversions are defined by marketers as certain acts, such as finishing a transaction or subscribing to a newsletter. Marketers may learn more about the efficacy of a campaign by examining important performance metrics like conversion rates and return on advertising expenditure.
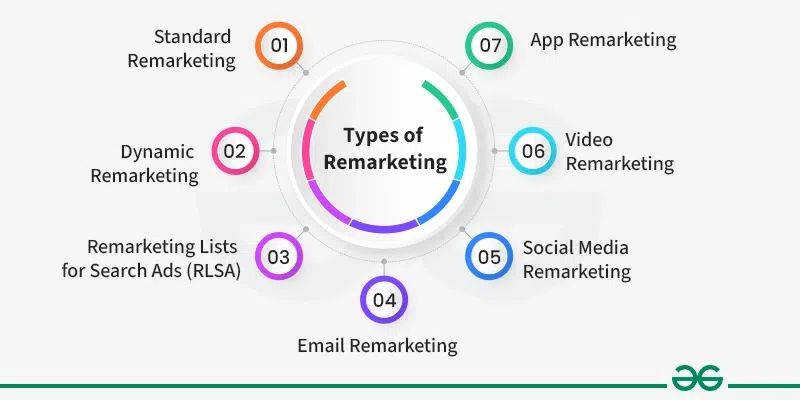
1. Standard Remarketing: By showing advertisements as users explore other websites and applications on the Display Network, standard remarketing targets those who have already visited an online portal or app. Remarketing cookies are downloaded and placed on users’ browsers, an audience list is compiled based on their activities, and then users are shown with relevant advertisements. In order to maximize results and attract consumers to return to the website and finish desired actions, marketers might alter campaigns and bidding strategies. This strategy effectively boosts conversions and assures continuous brand exposure.
2. Dynamic Remarketing: Users’ interactions with websites are used by dynamic remarketing to customize advertising for them. Through an analysis of user activity, such as goods seen, it creates customized adverts that are shown to consumers while they explore. By reminding customers of things they’ve expressed interest in, this tactic increases conversions and user engagement.
3. Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA): Remarketing Lists for Search adverts, or RLSA, adjusts prices and search advertisements for visitors who have already visited a website. Based on the user’s previous engagements, advertisers can modify landing pages, bids, and ad wording. Using individuals who have already interacted with the website as its target improves ad relevancy and raises conversion rates. By focusing their search advertising on a more targeted demographic, advertisers may increase return on investment and boost conversion rates.
4. Email Remarketing: Email remarketing sends customized emails to consumers who have abandoned their shopping carts, urging them to come back and finish their transaction. The objective is to stimulate curiosity and encourage response by means of customized communication and rewards such as coupons. Email remarketing assists companies in regaining lost sales and increasing income by sending prospective clients back to the website through nurturing.
5. Social Media Remarketing: With social media remarketing, individuals who have previously interacted with a website or app on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter are targeted and shown customized advertisements based on their past behavior. Advertisers may effectively re-engage consumers and drive conversions via customized advertisements based on data collected via product views and website visits. Using appropriate data, this strategy directs consumers through the customer journey and raises brand awareness.
6. Video Remarketing: By delivering customized advertisements, video remarketing targets people who have interacted with a the company’s video or YouTube channel. These advertisements aim to persuade viewers to do something, like go to the website or buy something. Video Remarketing efficiently increases brand visibility and promotes conversions by reconnecting with with interested viewers.
7. App Remarketing: App Remarketing targets users who’ve installed a mobile app but aren’t active, encouraging them to reopen the app or take specific actions. By sending personalized messages and incentives, it reignites interest and boosts app engagement, retention, and revenue potential.
1. Increased Conversions: Remarketing tries to get visitors who have interacted with your brand in earlier times back to your website to fulfill desired activities. Remarketing raises the possibility of conversions by displaying customized messaging and targeted adverts that keep your brand in front of consumers’ minds.
2. Improved ROI: Because they engage a specific audience, remarketing efforts surpass traditional advertising in terms of return on investment and generate greater conversion rates. Remarketing minimizes acquisition costs by utilizing users’ existing brand knowledge, resulting in a more effective return on investment.
3. Enhanced Brand Recall: By exposing people to personalized advertisements on a regular basis, remarketing strengthens brand awareness and improves recall. many exposures to the brand’s message through strategic ad placement across many web channels strengthens memory.
4. Personalized Engagement: Remarketing enhances relevance and engagement by providing targeted advertisements based on prior user interactions. Based on user activity, dynamic advertising content changes in real-time to encourage users to return and finish desired tasks. All things considered, customized remarketing strengthens long-term client connections and loyalty to the brand.
5. Better Audience Targeting: Remarketing gives advertisers the ability to target particular audience groups according to their interests, demographics, and prior interactions. Advertisers can more effectively engage and convert consumers by accurately targeting these audiences and crafting advertising that resonates to their interests.
6. Increased ROI: Advertisers may spend less on ineffective audiences by directing their money toward users who have previously expressed interest thanks to remarketing. Remarketing efforts ensure a greater return on investment by increasing the possibility of conversions by focusing on these warm leads.
1. Set Up Remarketing Tags: Installing code samples from advertising networks, such as Google Ads or Facebook Ads, on your application or site is the first step in setting up advertising tags. By analyzing user interactions like page visits and product views, these tags let you create remarketing audiences based on particular activities.
2. Define Audience Segments: Remarketing audience segmentation is grouping users according to a range of factors, such as previous purchases, demographics, and website activities. By breaking down your audience into discrete groups, you may better customize your messaging to each group’s requirements and preferences. This tailored strategy raises the possibility of interaction and conversions while improving the relevancy of your advertisements.
3. Create Compelling Ads: Crafting customized, captivating material that speaks to the interests of those who read is essential to create effective remarketing advertising. One may draw them in and persuade them to return to the website or app by emphasizing deals or goods that are relevant to them.
4. Set Campaign Goals: Establishing campaign goals for remarketing involves deciding on certain targets like boosting brand recognition, encouraging customers to return, or promoting purchases. By making these objectives clear, one can make sure that their remarketing campaigns are targeted and measurable and that they support their larger marketing plans.
5. Choose Ad Platforms: Selecting channels such as Google Advertising, Facebook Advertising, or display advertising networks that fit your target audience and campaign goals is part of the process of selecting ad platforms for remarketing. When choosing, take into account variables including audience demographics, platform reach, and available ad formats.
6. Bidding Strategies: Determining bidding strategies for remarketing involves taking competition, audience value, ad placement, and budget limits into account when optimizing bids. Utilizing performance data and goals to guide strategic bid revisions improves the efficacy of campaigns and return on investment.
1. Conversion Tracking: Remarketing conversion tracking measures the proportion of people who, after seeing remarketing commercials, go on to perform desired actions, like buying something or subscribing to a newsletter. Advertisers may assess how well their remarketing efforts are influencing particular behaviors and accomplishing campaign goals by looking at conversion rates. This information aids in determining which advertising tactics and ad creatives work best to increase user engagement as well as encourage conversions.
2. Click-Through Rate (CTR): The number of people that click on advertisement after viewing them is known as the Click-Through Rate (CTR), and it gives information about the efficacy and engagement of these advertisements. Advertisers may evaluate the attractiveness and significance of ad creatives and messaging to the intended audience by monitoring CTR. While a lower CTR might suggest that changes are needed to increase ad effectiveness, a higher CTR shows more user interest and interaction with the advertising. By identifying efficient ad pieces and improving techniques to increase user engagement and generate conversions, CTR analysis aids in the optimization of remarketing campaigns.
3. Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) measures the average cost of acquiring each conversion in remarketing campaigns. In remarketing efforts, cost per acquisition, or CPA, calculates the average cost of getting each become customers. Campaigns with a lower CPA are considered to be more economical. Marketers may evaluate campaign effectiveness, implement changes to improve performance, and optimize return on investment by keeping an eye on CPA. This includes improving marketing parameters, target sites, advertising artists, and bidding tactics. Optimizing CPA guarantees optimal use of advertising funds and raises the efficacy of campaigns.
4. Return on Investment (ROI): ROI, which compares revenue to expenses invested, is a crucial indicator for evaluating the success of remarketing campaigns. Profitable results are shown by positive ROI, whilst losses are suggested by negative ROI. It helps with resource optimization and effective allocation of funds by pointing out profitable initiatives that need further funding. ROI analysis also makes it possible to clearly evaluate profits per dollar invested and to justify marketing expenditures to stakeholders. In general, ROI directs strategic choices to optimize profits and encourage company expansion.
5. Audience Engagement: Metrics of audience engagement including time on site, number of pages viewed, and frequency of visits offer insights into the efficacy of remarketing campaigns. Recurring visits demonstrate effective re-engagement, while longer site visits and more page views are indicative of engaging ad content. By examining these data, one may improve performance, hone tactics, and increase conversion rates.
Conclusion
To sum up, remarketing is an effective digital marketing tactic that enables companies to get back in touch with customers who have already interacted with their website or brand. Remarketing seeks to nurture leads, increase conversions, and optimize return on investment by carefully focusing on these users with tailored advertisements, emails, or other communications. In an increasingly competitive online environment, organizations may improve their remarketing efforts to successfully re-engage users, build brand loyalty, and ultimately accomplish their marketing goals through ongoing optimization and analysis of key performance data.
How do I set up a remarketing campaign for my business?
To set up a remarketing campaign for your business, you’ll need to install remarketing tags on your website to track user interactions and create remarketing audiences. Then, create compelling ad creatives and target these audiences with personalized messaging on ad platforms like Google Ads or Facebook Ads.
Is remarketing effective for all types of businesses?
Remarketing can be effective for various types of businesses, particularly those with online presence or e-commerce platforms. It allows businesses to re-engage with interested users, increase brand awareness, and drive conversions, making it a valuable strategy across industries.
How much does remarketing typically cost?
The cost of remarketing can vary depending on factors such as the advertising platform used, the size of the remarketing audience, bidding strategies, and the competitiveness of the industry.
Are there any privacy concerns associated with remarketing?
Yes, there are some privacy concerns associated with remarketing. Users may feel that their online behavior is being tracked and targeted with ads, which can raise privacy issues. Additionally, there may be concerns about the collection and use of personal data for remarketing purposes, leading to potential regulatory scrutiny and compliance requirements.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...