What is Organizational Culture?
Organizational Culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors that characterize a company or institution. It encompasses the norms and practices that shape how individuals within the organization interact with each other, approach their work, and perceive the organization’s mission and objectives. Organizational Culture is often considered the personality of a company, influencing employee engagement, decision-making processes, and overall performance.
Geeky Takeaways:
- Organizational Culture encompasses shared values, beliefs, and behaviors within a company.
- It influences how employees interact, make decisions, and perceive the organization.
- A positive culture fosters employee engagement, productivity, and satisfaction.
- Culture impacts organizational performance, innovation, and ability to adapt to change.
- Investing in understanding, nurturing, and evolving organizational culture is crucial for long-term success and resilience.
Importance of Organizational Culture
1. Employee Engagement: A positive organizational culture fosters a sense of belonging and purpose among employees. When employees feel valued, supported, and aligned with the company’s values and goals, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work.
2. Performance and Productivity: A strong organizational culture can enhance employee motivation, morale, and productivity. When employees are motivated by shared values and a sense of camaraderie, they are more likely to collaborate effectively, communicate openly, and strive for excellence in their roles. This contributes to higher levels of performance and overall organizational success.
3. Innovation and Adaptability: Organizational Culture plays a crucial role in fostering innovation and adaptability. A culture that encourages creativity, risk-taking, and continuous learning empowers employees to experiment with new ideas, challenge the existing situation, and adapt to changing market conditions. This enables the organization to stay competitive and agile in an ever-evolving business environment.
4. Decision-Making and Problem-Solving: Decision-making and problem-solving are vital for achieving organizational success. A conducive work environment fosters open communication, allowing individuals to express their thoughts and ideas freely without reservation. Ultimately, promoting an open work culture enhances the quality of decision-making by allowing for the input of various alternative solutions, thereby increasing efficiency and ensuring the implementation of the most effective one.
5. Customer Satisfaction: A customer-centric culture affects the level of customer satisfaction positively. By motivating employees to provide excellent service and creating a work environment that shows them value and interest, it contributes to a higher level of satisfaction and loyalty, as employees provide excellent service. Moreover, it also allows businesses to remain up to date with customers’ changing needs.
Characteristics of Organizational Culture
1. Shared Values: These are the basic assumptions and operational norms that an organization employs to guide its members. The primary objective of these values is to unite individuals by regulating their actions, to direct and support its operations, and to enable people to trust each other.
2. Norms and Expectations: These are the unwritten guidelines that let employees understand how they need to behave and interact with other employees. Some of the most common elements of these norms include communication style, ethics, and collaboration model. They are essential for the organization as they create unity and consistency while helping to remind the employees of the goal the organization is trying to achieve.
3. Communication Style: It relates to how information is transferred among employees of a company and the organizational hierarchy. It denotes both the frequency and the means of communication, as well as the tone and language used. It can vary from more open and transparent to more hierarchical and formal.
4. Leadership Style: It is the way in which the managers interact with their team members and the manner in which decisions are made. There are several approaches to this notion, such as autocratic, democratic, transformational, or laissez-faire. The leadership style adopted with the organization is likely to affect its organizational culture.
5. Work Environment: Work Environment refers to the physical, social, and psychological atmosphere, in which employees carry out their tasks. Therefore, it includes the layout and design of the office, the facilities provided for the staff, the extent to which interpersonal relationships are encouraged on the premises, and the overall “vibe”.
6. Rituals and Traditions: These are defined as recurring symbolic practices, either formal or informal, through which the company articulates and stabilizes its values and identity. They improve connection and create an affiliation between employees. Traditions also allow determining continuity shifts and the possibility of building relationships with others.
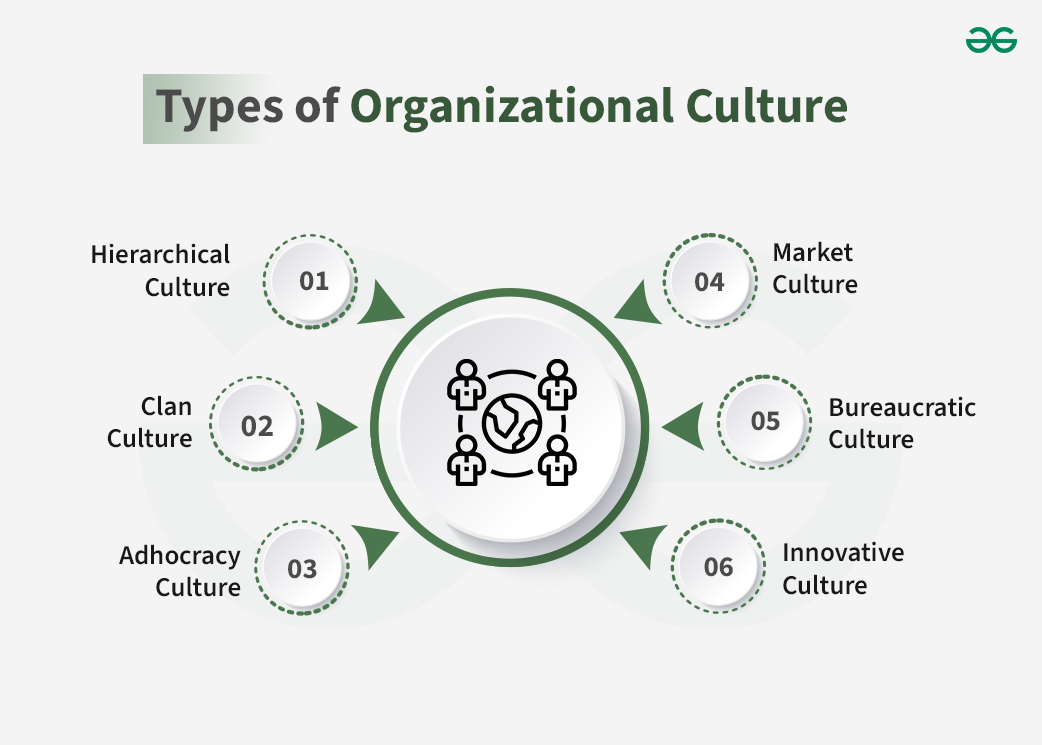
Types of Organizational Culture
1. Hierarchical Culture: Hierarchical Culture can be characterized by the rigid organizational structure where decision-making is centralized, communication goes from the top down, and strict adherence to the prescribed procedure is encouraged. The power is concentrated in the hands of the most senior leaders. This can provide the stability and efficiency needed to compete in some markets, but it can be very inflexible.
2. Clan Culture: A clan culture involves the organization functioning as an extended family. A clan culture is one in which employees work together as they support one another with a touch of a feeling of belongingness. The leaders work as coaches as they promote the spirit of open communication and trust. Members of the culture are motivated as they feel that they are being appreciated by their leaders.
3. Adhocracy Culture: Adhocracy Culture is a kind of corporate culture that focuses on innovation, flexibility, and creativity. It is a dynamic and entrepreneurial culture, typical for organizations that operate in a stable environment with little hierarchy. Adhocracy Culture is characterized by a dynamic and entrepreneurial place where employees are encouraged to take risks for the benefit of the organization. This culture is focused on external flexibility, with employees encouraged to challenge the prevailing situation and innovate .
4. Market Culture: A market culture is associated with the organization’s focus on competitiveness, results, and goal achievement. In a market culture, organizations have a strong external orientation and are actively focused on meeting needs and exceeding competitors. Employees are motivated by metrics, goals, and market share, and a strong emphasis is put on their accountability.
5. Bureaucratic Culture: Bureaucratic Culture is a term that is used to refer to a type of organizational culture that is characterized by formalized procedures or rules, hierarchical structures and adherence to rules and regulations. In a bureaucratic culture, the one who has the power to make decisions is the management and the lower employees are bound up by the protocol and the process set.
6. Innovative Culture: Innovative Culture is a work environment designed to promote creativity, experimentation, and the provision of new ideas. This type of culture allows employees to think outside the box, take risks, and deviate from the existing conditions. It is focused on the development of collaborative practices and an open-minded approach to multiple views.
How to Improve Organizational Culture?
1. Define Core Values: Core Values are the principles and beliefs behind one’s behavior and decision-making. Moreover, these values are the company’s identity, defining the culture and philosophy of the organization. In other words, core values are the main tool for guiding the staff in making the right decisions and carrying out their communication with customers, partners, and each other.
2. Foster Open Communication: Fostering Open Communication entails creating an environment where employees feel comfortable in expressing their ideas, concerns, and feedback without fear of judgment or rejection. This involves establishing channels for two-way communication, such as regular team meetings, suggestion boxes, anonymous feedback mechanisms, and open-door policies. Effective communication enables employees to share information, collaborate on projects, resolve conflicts, and contribute to organizational goals more effectively.
3. Promote Collaboration: Collaboration is a principle of encouraging teamwork, and cooperation among workers aimed at attaining common goals and objectives. This practice can be encouraged through a number of strategies such as team building, cross-functional, or departmental projects, collaborative tools among others. Organizations should encourage a culture where individual employees take the credit to share the ideas, knowledge, or resources they have.
4. Provide Training and Development: To enhance organizational culture, it is essential to provide training and development opportunities. This means giving employees opportunities to improve their skills and knowledge. The organizations’ support for personal growth encourages their workers and raises a continuous improvement culture.
5. Encourage Work-Life Balance: It involves creating an environment that allows employees to keep up with work duties while ensuring their personal and family wellness. This is often done via flexible schedules and friendly policies. The advantages of work life balance are decreased levels of stress, higher morale and productivity and retention.
Qualities of a Great Organizational Culture
1. Clear Mission and Values: A well-defined mission and values in an organization articulate its purpose, aspirations, direction, and guiding principles. When clearly defined and well communicated, these have the ability to set a tone and provide a sense of purpose, alignment and direction for the group of individuals committed to serving the organization in pursuit of certain objectives.
2. Transparency: Open communication is essential for fostering trust, collaboration, and accountability within the organization. A great culture encourages transparent communication at all levels, allowing employees to voice their opinions, share feedback, and contribute to the organization’s success.
3. Collaboration and Teamwork: Collaboration in organizational culture is the practice of promoting an environment where employees work as a team to achieve common goals. It includes sharing knowledge and resources and helping each other to succeed at the workplace. This system also fosters an optimistic and efficient working atmosphere that increases team members’ productivity and performance.
4. Employee Development: A great culture values learning and development as essential components of personal and professional growth. Opportunities for training, skill-building, and career advancement are provided to employees, enabling them to enhance their capabilities and reach their full potential.
5. Recognition and Appreciation: Recognition and appreciation in the workplace revolve around acknowledging and rewarding employees for their contributions and pace of work. They are essential for boosting employees’ morale, motivating them and maintaining positive behaviors and values in the organization.
Challenges to a Good Organizational Culture
1. Leadership Alignment: Ensuring that leaders at all levels of the organization are aligned with and actively promote the desired culture can be challenging. Misalignment or inconsistent messaging from leadership can undermine efforts to cultivate a positive culture.
2. Diversity and Inclusion: Creating an inclusive culture that values diversity and fosters a sense of belonging for all employees requires ongoing effort and commitment. Challenges may arise in addressing unconscious bias, promoting equitable opportunities, and ensuring that diverse voices are heard and valued.
3. Work-Life Balance: Balancing the demands of work with personal responsibilities and well-being is essential for maintaining a healthy organizational culture. Long hours, burnout, and excessive workload can undermine employee morale, engagement, and overall satisfaction.
4. Communication Breakdowns: Poor communication can hinder efforts to cultivate a positive culture by fostering misunderstandings, rumors, and lack of clarity. Clear, transparent communication channels and regular feedback mechanisms are essential for fostering trust and alignment.
5. Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes to the organizational culture, particularly if they perceive it as a departure from familiar norms or values. Overcoming resistance to change requires effective change in management strategies, communication, and involvement of stakeholders.
Factors that Shape an Organization’s Culture
1. Leadership: Leadership within an organization typically consists of guiding, motivating, and influencing others to accomplish shared goals. An effective leader will also define roles and responsibilities, set clear goals, make decisions that enhance the strategic direction of the organization, and create a positive work environment. Organizational culture is thus directly influenced by leaders through their guidance and example.
2. Values and Beliefs: The values and beliefs in an organization are the guiding principles and ideals that are essential to the behavior and decisions made. They define the organization’s culture by establishing what is important and acceptable, and guide norms and priorities. Furthermore, they are in line with the organization’s mission and vision to promote unity and purpose among the employees.
3. Communication: Employee communication in an organization indicates the process of information, opinions, and feedback exchange among the staff, teams, and managers. Effective communication is one of the key elements encouraging transparency, clarity, and understanding; open communication and sharing of information provides employees with opportunities for effective collaboration and decision-making.
4. Employee Behavior: Employee Behavior comprises actions or attitudes demonstrated by workers of a certain company or employer. While positive employee behavior includes all the forms of professionalism and cooperation between coworkers and management, negative factors are absenteeism or interpersonal conflict.
How to Identify Your Organizational Culture?
1. Observe Behaviors: Pay attention to how employees interact with each other, how decisions are made, and how conflicts are resolved. These observable behaviors provide clues about the underlying culture.
2. Analyze Symbols and Artifacts: Examine the physical environment, such as office layout, decor, and symbols used in branding or communication. These can reflect the values and priorities of the organization.
3. Listen to Stories and Language: Pay attention to the stories employees tell about their experiences within the organization. Listen to the language they use, including commonly used phrases or expressions. This can reveal cultural norms and attitudes.
4. Assess Organizational Structure and Processes: Evaluate the formal structure of the organization, including reporting lines, decision-making processes, and performance evaluation systems. This can shed light on the organization’s priorities and values.
5. Review Mission, Vision, and Values Statements: Examine the official statements that articulate the organization’s mission, vision, and values. Compare these with the actual behaviors and practices within the organization to identify any discrepancies.
6. Conduct Surveys and Interviews: Gather feedback from employees through surveys or interviews to understand their perceptions of the organizational culture. Ask questions about what they believe is valued within the organization and how they experience the culture in their day-to-day work.
Organizational Culture – FAQs
What role does communication play in shaping organizational culture?
Communication plays a crucial role in shaping organizational culture by facilitating the transmission of values, norms, and expectations, fostering transparency, and promoting collaboration among employees.
How can organizational culture impact business performance?
Organizational Culture can impact business performance by influencing employee engagement, productivity, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
What are the challenges in maintaining a positive organizational culture?
Maintaining a positive organizational culture can be challenging due to changes in leadership, rapid growth, fostering inclusivity, and addressing conflicts.
What are the signs of a strong organizational culture?
Signs of a strong organizational culture include high employee engagement and satisfaction, clear alignment with company values, effective communication channels, strong teamwork and collaboration, and a positive work environment where employees feel valued and supported in their roles.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...