Kano Model | Introduction, Working, and Benefits
Last Updated :
22 Jan, 2024
Kano Model is a method for ranking features on a product roadmap according to how probable they are to satisfy customers. Product teams can assess if it makes strategic sense to add a high-satisfaction feature to the roadmap by comparing its implementation costs to those of the feature.
The Kano Model in product management is a valuable device that may assist businesses in perceiving, prioritizing, and delivering the capabilities that surely retain their customers. This this article, we will delve into the Kano Model, overlaying its introduction, creation, operating principles, characteristic categories, implementation eventualities, benefits, and actual-world examples.

Kano Model | Introduction, Working, and Benefits
What is the Kano Model?
The Kano Model is a framework developed by Professor Noriaki Kano to prioritize and analyze customer needs and preferences. It was introduced in the 1980s and has been widely used in product development and customer satisfaction research. The model categorizes features or attributes of a product into five distinct categories based on how they impact customer satisfaction.
Professor Noriaki Kano, a Japanese researcher and representative, brought the Kano Model as a way to research purchaser satisfaction and product attributes. His paintings has had a widespread effect on exceptional control and product improvement, making the Kano Model a fundamental idea in those fields.
What is the History of the Kano Model?
The Kano Model was developed by Professor Noriaki Kano in the 1980s. Noriaki Kano, a Japanese professor of quality management, introduced the model in his article titled “Attractive Quality and Must-be Quality,” which was published in the Japanese magazine “Nikkei Business” in 1984. The model was later popularized in the English-speaking world through its inclusion in the Harvard Business Review in 1986.
The Kano Model was initially created to provide a more nuanced understanding of customer satisfaction and product development. Professor Kano sought to go beyond traditional methods of measuring customer satisfaction, which often focused solely on meeting or exceeding customer expectations. The model was designed to capture the dynamic and evolving nature of customer preferences.
How Does the Kano Model Work?

Kano Model
The Kano Model is often represented graphically as a two-dimensional graph, where the x-axis represents the level of a particular attribute or feature, and the y-axis represents customer satisfaction. The model helps businesses prioritize product features and allocate resources more effectively by understanding how different attributes impact customer satisfaction. It emphasizes the importance of considering both basic expectations and unexpected delights in product development and improvement. The Kano Model is a treasured device for information consumer possibilities and prioritizing functions in product development and carrier delivery. It turned into advanced by using Professor Noriaki Kano inside the 1980s and classifies patron possibilities into 5 categories primarily based on their impact on consumer pride. These classes are as follows:
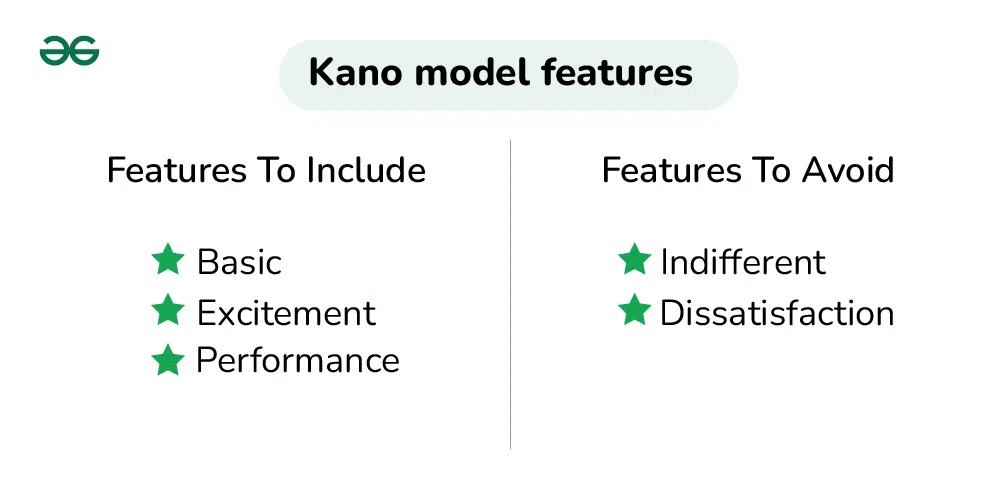
Kano model Features
1. Basic Needs (Must-Have):
- Description: Basic needs are essential functions that clients anticipate as a minimum requirement. These are the vital, non-negotiable features or attributes of a services or products. When those functions are present, clients do not longer grow to be pretty happy, however their absence can cause dissatisfaction.
- Working Principle: The presence of primary needs does now not substantially increase consumer pride, but their absence can lead to a decline in delight. Meeting those necessities is crucial to prevent dissatisfaction, however exceeding them does now not create a substantial growth in purchaser pleasure.
- Example: In the context of a telephone, primary needs would possibly include the potential to make calls and send textual content messages. Customers assume these capabilities, and if a smartphone can’t carry out those basic duties, it results in dissatisfaction.
2. Performance Needs (More is Better):
- Description: Performance needs are functions which have a linear relationship with patron pleasure. This method that as you improve these capabilities, customer pride increases proportionally. However, the absence of these features does now not always lead to dissatisfaction.
- Working Principle: The more you beautify overall performance wishes, the more happy customers come to be. These are the capabilities where “greater is higher.” Customers appreciate enhancements in those areas however aren’t upset if they’re no longer present.
- Example: In a cellphone, a bigger display or a quicker processor could be taken into consideration performance desires. While clients may be more glad with a bigger display screen or faster overall performance, the absence of these functions by myself would not cause dissatisfaction.
3. Excitement Needs (Delighters):
- Description: Excitement needs are sudden or delightful functions which have the ability to seriously beautify purchaser satisfaction. They are the features that set a product aside from its competition.
- Working Principle: The presence of pleasure wishes can result in a enormous boom in client delight and might differentiate a product in the market. Customers may not have explicitly anticipated those capabilities, but they may be pleasantly amazed after they come upon them.
- Example: A phone supplying a voice-managed digital assistant, like Siri or Google Assistant, could be considered an exhilaration need. Customers may not have predicted this feature, however its presence can delight them.
4. Indifferent Needs (Take It or Leave It):
- Description: Indifferent desires are capabilities that don’t substantially effect patron pride. Whether these functions are gift or absent, client pleasure remains pretty constant.
- Working Principle: These are functions that customers are in large part detached to. Their presence or absence would not substantially have an effect on how glad clients are with the product or service.
- Example: Some smartphones may additionally offer customization alternatives for the device’s look, including the shade of the telephone case. However, maximum clients are detached to this selection, and it does not substantially have an effect on their ordinary satisfaction with the phone.
5. Reverse Needs (Dissatisfaction When Present):
- Description: Reverse desires are functions that, when gift, can in reality cause dissatisfaction. However, when they may be absent, they do not necessarily increase consumer satisfaction.
- Working Principle: These features can be sudden in a poor way. Customers might not have anticipated them and may be disenchanted after they encounter them.
- Example: In the context of a smartphone, pre-set up bloatware or intrusive advertisements can be taken into consideration opposite wishes. Their presence can result in dissatisfaction amongst customers, but their absence does no longer always make customers happier.
When Should You Use the Kano Model?
Implementing the Kano Model is useful in numerous situations:

When Should You Use the Kano Model
- Limited Time: When we have limited time to build any product, Kano model is fruitful in that case.
- Limited Resources: When we have limited time to buld a product, There is no need to worry about time and implement the Kano model.
- Product Improvement: For present products or services, it aids in identifying regions for enhancement.
- Competitive Analysis: It can reveal how your product compares to competition in terms of consumer delight.
- Customer Feedback Analysis: Use the Kano Model to categorize and prioritize patron comments and suggestions.
Benefits of the Kano Model
The Kano Model offers numerous blessings to corporations:
- Prioritization: It helps businesses prioritize feature improvement or enhancement efforts primarily based on patron impact.
- Differentiation: Delighters can be a unique promoting factor that sets a services or products other than competition.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By addressing simple needs and delighters, groups can improve universal client satisfaction.
Examples of Kano Model
Let’s keep in mind a cellphone. A lengthy battery lifestyles (More is Better) can beautify customer pride. However, the absence of a physical keyboard (Must-Have) would possibly result in dissatisfaction. Now, imagine the smartphone offers a voice-controlled digital assistant (Delighter) – clients may be extremely joyful by this sudden function.
Conclusion : Kano Model
The Kano Model is a treasured framework for expertise consumer alternatives and prioritizing features in product improvement and carrier shipping. By categorizing functions into 5 wonderful groups, companies can align their efforts with patron expectancies, in the end leading to extended purchaser satisfaction and success within the market. Whether you are growing new merchandise, enhancing present ones, or aiming to stand out in a competitive market, the Kano Model is a effective tool to guide your selection-making and approach.
FAQs On Kano Model
1. What are the three levels of Kano Model?
Noriaki Kano isolated and identified three levels of customer expectations: that is, what it takes to positively impact customer satisfaction. The figure below portrays the three levels of need: expected, normal, and exciting.
2. What is the Kano requirement model?
Based on performance improvement and customer happiness, the kano model ranks your feature ideas in order of priority and creates a detailed development plan. In order to satisfy customers more quickly, the kano model steers clear of feature development on concepts that won’t improve customer happiness.
3. What are the 5 features of Kano Model?
- Basic Needs (Must-Have)
- Performance Needs (More is Better)
- Excitement Needs (Delighters)
- Indifferent Needs (Take It or Leave It)
- Reverse Needs (Dissatisfaction When Present)
4. Why is Kano Model used?
Kano Model is useful in numerous situations:
- Limited Time: When we have limited time to build any product, Kano model is fruitful in that case.
- Limited Resources: When we have limited time to buld a product, There is no need to worry about time and implement the Kano model.
5. Who invented Kano Model?
The kano Model is a theory for product development and customer satisfaction developed in 1980s by Professor Noriaki Kano.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...