How to Convert String to Date Time in Scala?
Last Updated :
08 Apr, 2024
In this article, we will learn how to convert String to DateTime in Scala. Converting String to DateTime consists of parsing a textual representation of date and time into a structured DateTime object for further manipulation and processing in Scala programs.
- In this approach, we are using the SimpleDateFormat class from Java’s standard library to parse a user-inputted date and time string (userInput) in the format “yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss” into a Date object (res).
- The SimpleDateFormat object (dFormat) is initialized with the desired date-time format, and the parse method is used to convert the string into a Date object based on this format.
- Finally, the parsed Date object is printed to the console using println.
In the below example, the SimpleDateFormat library is used to convert String to date time.
Scala
// importing necessary classes from Java
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
import java.util.Date
// Creating object GFG
object GFG {
// Main method
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Input string representing date and time
val userInput = "2024-03-27 13:30:00"
// Creating SimpleDateFormat object with the desired date-time format
val dFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
// Parsing the input string to obtain a Date object
val res = dFormat.parse(userInput)
// Printing the parsed Date
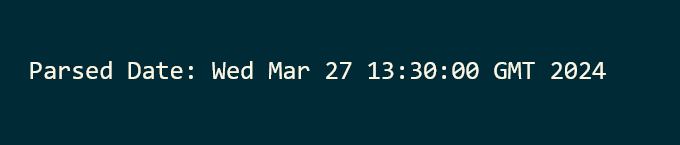
println("Parsed Date: " + res)
}
}
Output:
- In this approach, we are using a combination of SimpleDateFormat and Calendar classes from the Java standard library to parse a date and time string (“yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss“) into a Date object.
- The SimpleDateFormat instance dFormat is used to specify the date-time format for parsing.
- The Calendar instance cal is then used to set the parsed date and time values, which are obtained as a Date object (res) and printed to the console.
In the below example, the SimpleDateFormat with Calender is used to convert String to date time.
Scala
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
import java.util.Calendar
// Creating Objext
object GFG {
// Main Method
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Input string representing date and time
val dInput = "2024-03-27 13:30:00"
// Creating a SimpleDateFormat object to parse the input string
val dFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
// Creating a Calendar instance to work with date and time
val cal = Calendar.getInstance()
// Parsing the input string to obtain a Date object
cal.setTime(dFormat.parse(dInput))
// Getting the Date object from the Calendar instance
val res = cal.getTime()
// Printing the parsed date
println("Parsed Date: " + res)
}
}
Output:

Using Simple Parsing
- In this approach, we are using simple parsing techniques in Scala to convert a string representing a date (“2024-03-27”) into a GregorianCalendar object.
- The simpleParse method splits the input string by hyphens and attempts to create a calendar object based on the parsed components (year, month, day).
- If successful, it returns an Option[GregorianCalendar] representing the parsed date; otherwise, it returns None.
In the below example, the Simple Parsing is used to convert String to date time.
Scala
import java.util.{Calendar, GregorianCalendar}
class GFG {
def simpleParse(dateString: String): Option[GregorianCalendar] = {
dateString.split("-").toList match {
case yyyy :: mm :: dd :: Nil =>
try {
Some(new GregorianCalendar(yyyy.toInt, mm.toInt - 1, dd.toInt))
} catch {
case _: NumberFormatException => None
}
case _ => None
}
}
}
object GFG extends App {
val parser = new GFG
// Input string representing date
val dInput = "2024-03-27"
// Parse the input string using simple parsing
val maybeDate = parser.simpleParse(dInput)
// Print the parsed DateTime object
maybeDate match {
case Some(date) =>
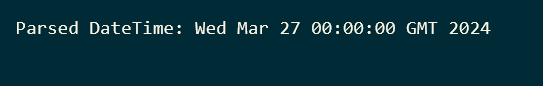
println("Parsed DateTime: " + date.getTime)
case None =>
println("Invalid date format")
}
}
Output:
Using Regular Expressions
- In this approach, we are using regular expressions (Regex) in Scala to match and extract date components from a string with a specific format (yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss).
- The parseDate method checks if the input string matches the regex pattern and extracts the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second components.
- If the format is valid, it constructs a GregorianCalendar object based on the extracted components, otherwise returning None.
In the below example, the Regular Expressions is used to convert String to date time.
Scala
import java.util.{Calendar, GregorianCalendar}
import scala.util.matching.Regex
object GFG {
def parseDate(dateString: String): Option[GregorianCalendar] = {
val dateRegex = """(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2}) (\d{2}):(\d{2}):(\d{2})""".r
dateString match {
case dateRegex(year, month, day, hour, minute, second) =>
try {
Some(new GregorianCalendar(year.toInt, month.toInt - 1, day.toInt))
} catch {
case _: NumberFormatException => None
}
case _ => None
}
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val dInput = "2024-03-27 13:30:00"
val maybeDate = parseDate(dInput)
maybeDate match {
case Some(date) =>
println("Parsed DateTime: " + date.getTime)
case None =>
println("Invalid date format")
}
}
}
Output:

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...