What is Cost Accounting?
Cost Accounting is defined as how costs of products or services are ascertained and controlled. Cost Accounting deals with all those areas that remain unturned by financial accounting, it is a part of management accounting that helps to make informed business decisions, and rather than only translating financial health to stakeholders. It also provides proper information and data to management for planning and better decision-making. Cost Accounting gathers the cost information which helps the management to understand and account the costs involved in operations, processes, and other activities, which helps the management to determine the cost of the product.
As defined by CIMA, “Cost Accounting is the process of accounting for cost from the point at which expenditure is incurred or committed to the establishment of its ultimate relationship with cost center and cost units.
Objectives of Cost Accounting
1. Determining Cost: Cost accounting helps to determine the cost of producing goods or services. It identifies and measures various costs associated with production, such as direct materials, direct labour, and manufacturing overhead.
2. Fixation of Selling Price: Cost accounting allows management to understand the cost of each product. With the right data of cost included, the management can fix the correct selling price per unit of production, it will not only help the manufacturing sector but will also help the service sector to determine the price for there service offering.
3. Controlling Costs: One of the main objective of cost accounting is that it will help management with proper data about cost in all the aspects be it material, labour or overheads. Management can analyse the data further to establish cost control by taking proper decisions in order to minimise costs and increase profits.
4. Valuation of Inventory: Cost Accounting plays an important role in valuing the most important asset for any business concern i.e. there inventory. Proper valuation of inventory allows management to determine value of there stocks for the purpose of financial accounting. Cost accounting uses several methods of inventory valuation like FIFO, LIFO, etc.
5. Comparison of Performance: Cost Accounting compares actual performance with the pre set standards and targets, in case any deviation arises such variances are reported to management for proper action to be taken against adverse result or outputs. Either the reason of variance is identified and corrected for future, or standards are re-checked if they stand correct for the business process.
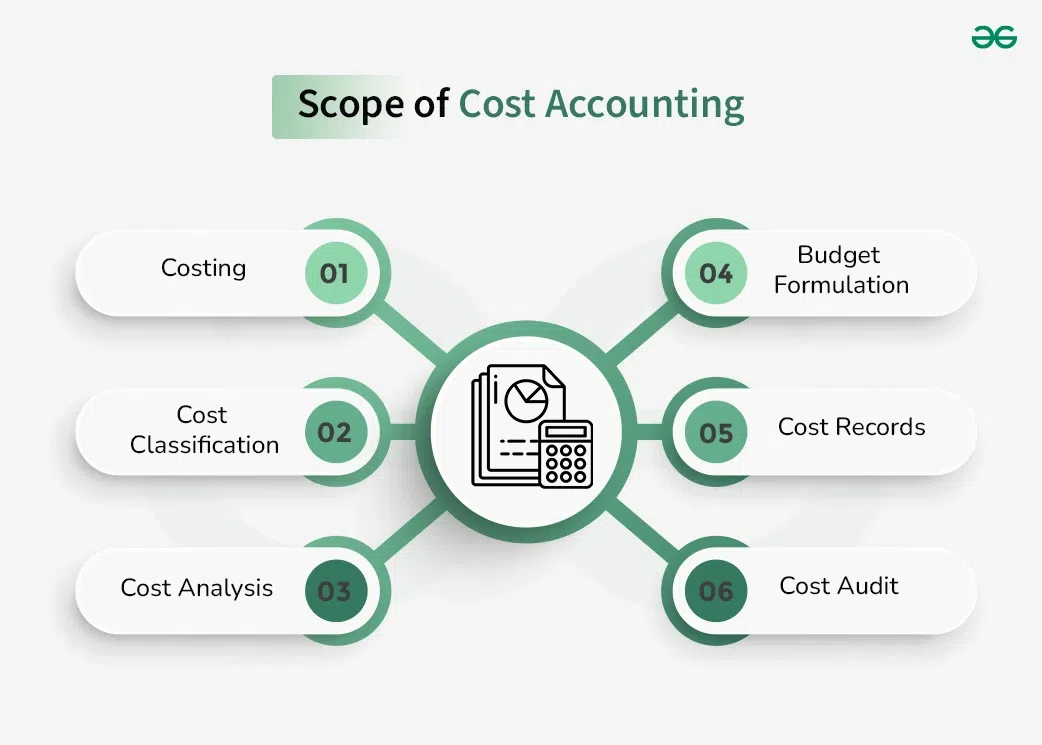
Scope of Cost Accounting
1. Costing: Costing is the process of ascertainment of costs of any product or service. Costing is governed by several principals, rules and guidelines. Cost can be ascertained by using standard, operation, process cost. When the word accounting is connected to cost, it gets extended to accounting of costs with formal methodology in order to provide better insights to the management.
2. Cost Classification: Cost Accounting classify the costs associated with the production of goods and services. Cost Classification involves identifying both the direct costs such as materials and labor and the indirect costs such as overhead and administrative expenses, and allocating them to specific products or services in order to gather true results.
3. Cost Analysis: Cost Accounting deals with the factor of finding the variance and analysis of reason for such variances between actual and pre-established standards. It helps to take better cost management decisions and strategic decisions.
3. Budget Formulation: Cost accounting is also used to develop budgets and forecasts for future. By analysing historical cost data and current market environment, cost accountants can develop realistic projections of future costs and revenues, which can help businesses make informed decisions about their business operations.
4. Cost Records: In some instances, there is a statutory obligation to keep cost records available with the management as notified by the statutory and regulatory authorities. Cost records might be required to gather information regarding material, labor and overhead usage in business.
5. Cost Audit: Cost Audit involves a detailed examination of the cost accounting records of a business, as conducted and checked by an independent auditor. The cost audit aims to verify the accuracy and validity of the cost accounting information and ensure that the business is complying with relevant regulations and standards. The auditor provides a report of the audit findings and recommendations for changes as well.
Users of Cost Accounting
I. Internal Users of Cost Accounting
1. Managers: Managers are the one of the important internal users of cost accounting. They use cost accounting to gather information about cost centers and cost objects, to gather information about the pricing of the product, to evaluate and measure performance of responsibility centres, and to evaluate and calculate profitability- product wise, department wise, customer wise.
2. Operational Level Staff: Operational level staff uses cost accounting to know the objectives and goals set on them, to understand the specifications like volume, quality, process, etc., to understand the parameters of performance by which there performance will be measured, and to Know the profitability and variances under different divisions.
3. Employees: Employees use cost accounting to know thier work efficiency, to understand the different bonus plan in action by the organisation like Rowan or Halsey bonus plan, and to understand the variances in there performance, and increase there efficiency.
II. External Users of Cost Accounting
1. Regulatory Authorities: Authorities use cost audit data, to ensure that they comply with the cost accounting principals, and the records shows true and fair view. Cost accountings also helps regulatory authorities to determine the tariff, subsidies, and fixation of rate.
2. Shareholders: Shareholders consume cost accounting information that might have significant bearing on their investment in the organisation. Shareholders require information regarding the new work orders, market expansion, cost share, etc. to make informed investing decisions. Management periodically communicates all the ongoing via meetings, annual reports, etc.
3. Creditors and Lenders: Creditors and Lenders consume the cost information to analyse the key factors which might effect the organisation’s ability to pay off it’s lenders and creditors. Creditors and Lender also consume other costing info to understand the business, in order for mergers and acquisition so that they will get the information about the business.
Limitations of Cost Accounting
1. Expensive: Cost Accounting is an expensive task, as it will require hiring of additional workforce other than one who manages financial accounts and cost accounting needs wide knowledge of costing aspects.
2. Requirement of Reconciliation: Information recorded in financial and cost accounts is totally different as both are based on their own principals and rules. Treatment of same transaction can be different is both these form of accounting and hence, it will show different results, in order to prepare any report a reconciliation will be required to verify the accuracy.
3. Promote Duplication: Preparation of cost accounting leads to duplication of work, as for the same transaction two different books are to be maintained, which creates duplication of same task and deployment of additional workforce.
4. Narrowed Approach: Cost accounting only focus on one aspect that is cost reduction and cost cutting, which might not be beneficial in all business environment and in current dynamic business environment relying on single strategy might not result in gains and does not fit all the businesses.
Difference Between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
|
Basis
|
Cost Accounting
|
Financial Accounting
|
|
Objective
|
Cost accounting provides with ascertainment of cost for the purpose of strategic decision making and deciding the price of product or service.
|
Financial accounting provides information about financial performance of any business to its stakeholders.
|
|
Recording of Data
|
It records both historical and pre-determined costs.
|
It records historical data.
|
|
Main Analysis
|
It provides the user with basic cost details like process cost, operation cost, job cost, etc.
|
It provides the profit and loss of the business, either individually or as a whole.
|
|
Timeline of Preparation
|
Cost records are prepared as an when required by management, authorities or stakeholders.
|
Financial records are prepared every year, after the end of financial year.
|
|
Users of Information
|
Main users are internal management, but sometimes might be required by stakeholders and government authorities.
|
Creditors, shareholders, government authorities, banks, etc.
|
|
Set of Guidelines Followed
|
Cost principals, cost rules and cost standards are followed while drafting cost records.
|
Accounting standards or Indian accounting standards are followed.
|
|
Valuation of Stock
|
Valuation is always done at cost.
|
Valuation of stock is based on cost or net realisable value whichever is lower.
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...