Angular has become widely popular in the field of web development for its capacity to create adaptable applications. A major reason behind Angular's success is its reliance on TypeScript as the programming language.
TypeScript, which extends JavaScript by adding typing and extra functionalities is favoured for building Angular applications. This piece will delve into the reasons why TypeScript is favoured over JavaScript in Angular development and compare the distinctions, between the two languages.
Table of Content
TypeScript
TypeScript, a programming language created by Microsoft is the source. It extends JavaScript by incorporating typing, classes, interfaces and other enhanced functionalities. In TypeScript the code is transformed into JavaScript for execution, in JavaScript runtime environments.
TypeScript enhances the quality of JavaScript code by incorporating typing and performing error validations during the compilation phase. It mandates the declaration of types, variables function parameters and return values enabling developers to detect mistakes in the development stage instead of at runtime.
Application of TypeScript:
function sum(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
console.log(sum(5, 5));

Ts Output
In TypeScript we clearly state the types of the function parameters and the expected return type. This practice aids in reducing errors related to types and enhancing the dependability of the code.
Features of TypeScript
TypeScript has various advantages that make it a better option for Angular development:
- Static typing: TypeScript mandates static typing, which aids in identifying problems during the development process and offers enhanced tools assistance.
- Classes and interfaces: TypeScript adds classes and interfaces to support the paradigm of object-oriented programming. Better code organization and reusability are made possible by this.
- Code navigation and Intellisense: Better IDE support, such as code navigation and IntelliSense, is offered by TypeScript. Developers can now comprehend and work with big codebases more easily.
- Advanced JavaScript features: The most recent ECMAScript standards are supported, along with all the features of JavaScript, by TypeScript. It also offers more functionality, such as decorators and generics.
Example in TypeScript:
- Create a new Directory for the typescript project by following command:
mkdir typescript-project- Enter your project directory now:
cd typescript-project- After creating your project directory, install TypeScript:
npm i typescript --save-dev- Once TypeScript is installed, use the following command to initialize your TypeScript project:
npx tsc --init- When starting your project you can set it up by making a tsconfig.json file in the directory of your typescript project project using the --init option in the command mentioned. You have the flexibility, to tune and customize how TypeScript and the tsc compiler collaborate by editing this tsconfig.json file. Inside this file you'll find settings that're adjustable – allowing you to include exclude or change them according to your requirements.
- Create two new files called index.html and index.ts and paste the below code snippet.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="greeting"></h1>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
var Greeter = /** @class */ (function () {
function Greeter(message) {
this.greeting = message;
}
Greeter.prototype.greet = function () {
return "Hello, " + this.greeting;
};
return Greeter;
}());
var greetingContainer = document
.getElementById("greeting");
if (greetingContainer) {
var greeter = new Greeter("Geeksforgeeks");
greetingContainer
.textContent = greeter.greet();
}
- Compile the TypeScript code by following command:
npx tsc index.ts- After compiling your code a new file will be created called index.js which will generate below code snippet
var Greeter = /** @class */ (function () {
function Greeter(message) {
this.greeting = message;
}
Greeter.prototype.greet = function () {
return "Hello, " + this.greeting;
};
return Greeter;
}());
var greetingContainer = document.getElementById("greeting");
if (greetingContainer) {
var greeter = new Greeter("Geeksforgeeks");
greetingContainer.textContent = greeter.greet();
}
dependencies:
//package.json
{
"dependencies": {
"typescript": "^5.4.2"
}
}
Output in Ts :

Ts Output
Javascript
JavaScript serves as a level-interpreted programming language predominantly utilized for client-side scripting in web development. Known for its loosely typed nature it enables developers to swiftly and effortlessly write code. Compatible with all leading web browsers JavaScript finds applications, in both end and back-end development.
JavaScript is popular, in web development because of its ease and flexibility. It features a syntax and offers a versatile programming setting. Here's a basic JavaScript function that adds two numbers together:
Example code in JavaScript:
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(sum(5, 5));
Output In Js:

JS Output
In JavaScript variables can store values of types due, to dynamic typing. This flexibility might cause issues and complicate code maintenance in extensive programs.
Features of JavaScript
JavaScript provides several features that make it a powerful language for web development:
- Flexibility: JavaScripts dynamic typing fosters adaptable and nimble development. Variables have the flexibility to store value types without the requirement, for explicit type declarations.
- Large Ecosystem: JavaScript has a vast ecosystem of libraries, frameworks, and tools that support web development. It provides developers with a wide range of options for building robust and scalable applications.
- Browser Compatibility: JavaScript is compatible with all the web browsers and boasts a wide array of libraries and frameworks, in its ecosystem.
Example in JavaScript:
- Create a new project by following command:
ng new my-greeting-project- Enter your project directory now:
cd <Project-Name>- Edit the app.component.html and use the below code snippet:
<div id="greeting">
{{ greeter.greet() }}
</div>
- Use the below code in app.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-greeting',
templateUrl: './greeting.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./greeting.component.css']
})
export class GreetingComponent implements OnInit {
greeter; // No type declaration
ngOnInit() {
this.greeter = {
greetingMessage: "Geeksforgeeks" // Changed property name
};
}
}
- Open the project by following command:
ng serveOutput in Js:
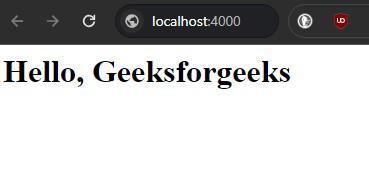
JavaScript Output
Difference between TypeScript and JavaScript:
Feature | TypeScript | JavaScript |
|---|---|---|
Typing | Statically typed | Dynamically typed |
Variables | Must be declared with a type | Can be declared without a type |
Functions | Must be declared with types for arguments and return value | Can be declared without types for arguments and return value |
Classes | Supports classes | Does not natively support classes |
Tooling Support | Better tooling support, including code completion and type checking | Limited tooling support |
Learning Curve | Requires learning TypeScript syntax and features | Familiar for JavaScript developers |
ES6+ Support | Full support for modern JavaScript features | Supports modern JavaScript features |
TypeScript has emerged as the go to language for development because of its static typing improved tooling support and features like classes and interfaces. It provides a development environment that helps developers identify possible errors at an early stage. Despite this JavaScript continues to be a choice for Angular development offering flexibility and access, to a wide range of libraries and frameworks.