Nowadays, website speed and user experience are most important. that's where Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) come in. It helps to speed up the delivery of web content to users all over the world. In this article, you will understand the concept of CDNs in system design, exploring their importance, functionality, benefits, and challenges.

Important Topics for Content Delivery Network(CDN)
- What is Content Delivery Network(CDN)?
- Importance of Content Delivery Network(CDN)
- Type of Content Delivery Network(CDN)
- How does Content Delivery Network(CDN) Work?
- Components of Content Delivery Network(CDN)
- Content Delivery Network(CDN) Use Cases
- How to Incorporate Content Delivery Network(CDN) into Web Application Design
- Benefits of using Content Delivery Network(CDN)
- Challenges of using Content Delivery Network(CDN)
What is Content Delivery Network(CDN)?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed network of servers that work together to deliver content (like images, videos, and static files) to users faster and more efficiently.
- These servers, called edge servers, which are strategically positioned across various geographical locations.
- CDNs help improve the performance, reliability, and scalability of websites and web applications by caching content closer to users, reducing latency, and offloading traffic from origin servers.
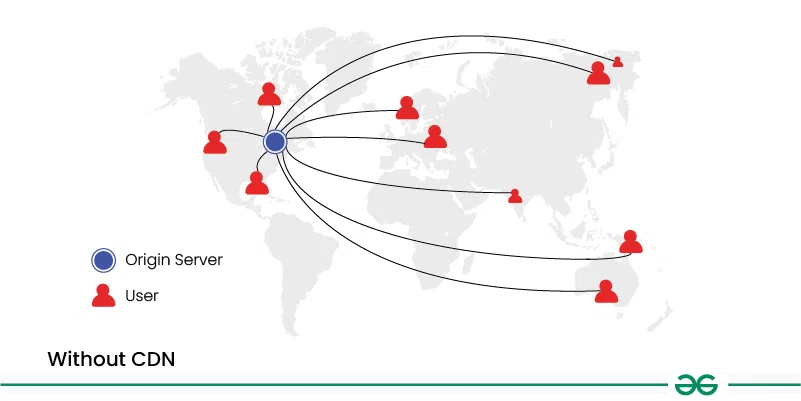
1. Without CDN
When a user requests content from a website without a CDN, the request is sent directly to the origin server where the website is hosted. The origin server processes the request and sends back the requested content to the user's device.
- If the origin server is located far away from the user, it may result in longer loading times due to increased latency.
- High traffic volumes or server overload can lead to slower response times and even server downtime, negatively impacting user experience.
2. With CDN
When a user requests content from a website with a CDN, the CDN identifies the user's location and routes the request to the nearest edge server. The edge server, which stores cached copies of the website's content, quickly delivers the requested content to the user.
- Since edge servers are distributed globally, content delivery is faster, resulting in reduced latency and faster load times.
- The CDN also helps to offload traffic from the origin server, reducing the risk of server overload and ensuring consistent performance even during traffic spikes.
- Additionally, CDNs often include built-in security features such as DDoS protection and web application firewalls, enhancing website security and protecting against cyber threats.

Importance of Content Delivery Network(CDN)
CDNs offer several key benefits that make them important for delivering content over the internet:
- Faster Content Delivery: By caching content in servers located closer to end users, CDNs reduce the physical distance that data must travel, thereby decreasing latency and improving load times.
- Improved Website Performance: Faster load times lead to better overall website performance, which can result in higher user engagement, longer visit durations, and increased conversion rates.
- Scalability: CDNs help websites handle traffic spikes and high loads by distributing the load across multiple servers. This scalability is especially crucial for websites with global audiences or those experiencing sudden surges in traffic.
- Redundancy and Reliability: CDNs offer redundancy by storing copies of content across multiple servers. If one server fails, another server can seamlessly take over, ensuring continuous availability of the content.
- Cost Savings: By reducing the load on origin servers and optimizing content delivery, CDNs can help lower bandwidth costs and infrastructure expenses for website owners.
- Security: CDNs provide additional security features, such as DDoS protection, SSL/TLS encryption, and web application firewalls, helping to protect websites from various online threats.
- Global Reach: CDNs have servers located around the world, allowing websites to reach users in different geographic locations with reduced latency and improved performance.
Overall, CDNs play a crucial role in optimizing content delivery, improving website performance, and enhancing the user experience on the internet.
Type of Content Delivery Network(CDN)
CDNs can be classified into several types based on their architecture and functionality:
1. Public CDNs
A public CDN is a CDN that is available for use by anyone on the internet. These CDNs typically have a large network of servers located around the world and are used to deliver content, such as images, videos, and other static files, to users quickly and efficiently.
For example: Cloudflare, Akamai, and Amazon CloudFront.
2. Private CDNs
A private CDN is a CDN that is used exclusively by a single organization or company. These CDNs are often deployed within a company's own infrastructure or on a private cloud and are used to deliver content to internal users or customers. Private CDNs offer more control over content delivery and can be customized to meet specific security and performance requirements.
For example: Google Cloud CDN, Netflix Open Connect.
3. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) CDNs
These CDNs utilize peer-to-peer networking technology to distribute content directly between users, reducing reliance on centralized servers.
For example: BitTorrent, webTorrent.
4. Hybrid CDNs
A hybrid CDN combines elements of both public and private CDNs. In a hybrid CDN, some content is delivered using a public CDN, while other content is delivered using a private CDN. This approach allows organizations to optimize content delivery based on factors such as cost, performance, and security requirements.
For example: Microsoft Azure CDN
5. Push CDNs
In a push CDN, content is uploaded or "pushed" to the CDN's servers in advance of when it is needed. This can help improve performance by ensuring that content is available closer to end users when they request it. Push CDNs are often used for caching large files or content that is not frequently updated.
For example: KeyCDN, CDN77
6. Pull CDNs
In a pull CDN, content is requested or "pulled" from the CDN's servers when it is needed. This approach is more efficient for delivering content that is frequently updated or dynamically generated. Pull CDNs are often used for delivering dynamic content, such as web pages or API responses.
For example: Amazon CloudFront, Cloudflare
How does Content Delivery Network(CDN) Work?

Below is the simple step-by-step working of a CDN:
- User sends a request for content (e.g., an image) from a website.
- CDN identifies the user's location and routes the request to the nearest edge server.
- If the content is cached at the edge server, it is delivered directly to the user.
- If the content is not cached, the edge server retrieves it from the origin server, caches it locally, and delivers it to the user.
- Cached content is stored at the edge server for future requests, optimizing performance and reducing latency.
Components of Content Delivery Network(CDN)
A typical CDN consists of the following key elements:
- Edge Servers: Distributed servers located in proximity to end-users, responsible for caching and delivering content quickly.
- Origin Server: It is the central repository where original content is stored and managed, and serving as the source for content distribution.
- Content Distribution Nodes: Network nodes responsible for routing and optimizing content delivery within the CDN, ensuring efficient traffic management.
- Control Plane: Software or services that manage and orchestrate the CDN's operations, including content caching, routing, and load balancing.
Content Delivery Network(CDN) Use Cases
CDNs are not limited to websites and can be used for various purposes, including:
- Streaming media delivery: Delivering video and audio content with minimal buffering and lag.
- Software Distribution: It helps in distributing software updates and patches efficiently to global users. And also Providing faster and more reliable downloads for software applications.
- E-commerce: It helful to optimizing online shopping experiences by ensuring fast and reliable content delivery for product images and descriptions.
- Gaming: In Minimizing latency and providing seamless gameplay experiences for online gaming platforms.
- API delivery: To Improving the performance and scalability of APIs used by mobile apps and other services.
How to Incorporate Content Delivery Network(CDN) into Web Application Design
To use a CDN in your website, you just need to:
- Pick a CDN provider.
- Set up the CDN to work with your website.
- Make sure everything is running smoothly.
For Example:
Here is the example below to apply the steps to include Bootstrap via CDN to style a button.
Step 1: Choose a CDN Provider: Bootstrap offers its own CDN. We'll use it by linking to the Bootstrap CSS file hosted on their servers.
Step 2: Link to Bootstrap CSS: Add the following line in the <head> section of your HTML file:
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.0/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">