In Python, Stack, and collections. deque is a foundational data structure used for managing elements in a Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) order. In this article, we will learn to create a stack using collections. deque in Python.
Example :
Input : Stack : 1 2 4
Push(5)
Output : Stack : 1 2 4 5
Input : Stack : 1 2 4
Pop()
Output : Stack : 1 2
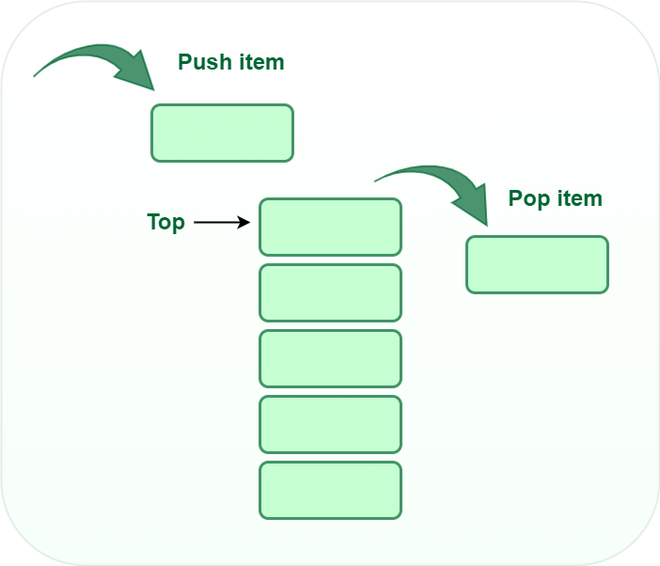
Basic Operations on Stack
In order to make manipulations in a stack, there are certain operations provided to us:
- push() to insert an element into the stack
- pop() to remove an element from the stack
- top() Returns the top element of the stack.
- isEmpty() returns true if the stack is empty else false.
- size() returns the size of stack.
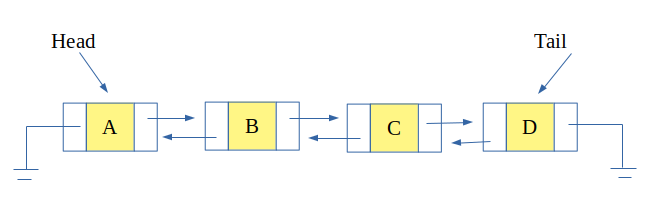
A link-list representation of deque is such that each node points to the next node as well as the previous node. So that insertion and deletions take constant time at both the beginning and the last.
Implement Stack Using Collections.Deque() in Python
Below, is the step-by-step Implementation of Stack using Collections. Deque in Python:
Illustration
In this example, below code defines a doubly linked list (
Deque) and a stack (Stack) implemented using this doubly linked list.
Dequeclass provides methods for basic operations like insertion (insert_first,insert_last), removal (remove_first,remove_last), size computation (size), and display (display).
Operations on Stack
Below, are the stack Operations which perform in below code.
Stackclass wraps aroundDequeand provides stack-specific operations likepush,pop, andsize.- We create a
Stackinstancestk. - We push elements
7and8onto the stack using thepushmethod. - We display the stack contents using the
displaymethod. - We pop an element from the stack using the
popmethod. - We display the updated stack contents.
- Finally, we print the size of the stack using the
sizemethod.
Implementation of Stack Using Collections.Deque in Python
class node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class Deque:
def __init__(self):
self.head = self.tail = None
def isEmpty(self):
if (self.head == None):
return True
return False
def insert_first(self, element):
newP = node(element)
if self.head == None:
self.head = self.tail = newP
return
newP.next = self.head
self.head.prev = newP
self.head = newP
def insert_last(self, element):
newP = node(element)
if self.head == None:
self.head = self.tail = newP
return
newP.prev = self.tail
self.tail.next = newP
self.tail = newP
def size(self):
curr = self.head
len = 0
while curr != None:
len += 1
curr = curr.next
return len
def remove_first(self):
if self.isEmpty():
print('List is Empty')
return
self.head = self.head.next
if self.head != None:
self.head.prev = None
def remove_last(self):
if self.isEmpty():
print('List is Empty')
return
self.tail = self.tail.prev
if self.tail != None:
self.tail.next = None
def display(self):
if self.isEmpty():
print('List is Empty')
return
curr = self.head
while curr != None:
print(curr.val, end=' ')
curr = curr.next
print()
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = Deque()
def push(self, element):
self.stack.insert_last(element)
def pop(self):
self.stack.remove_last()
def size(self):
return self.stack.size()
def display(self):
self.stack.display()
stk = Stack()
# push 7 and 8 at top of stack
stk.push(7)
stk.push(8)
print("Stack: ")
stk.display()
# pop an element
stk.pop()
print("Stack: ")
stk.display()
print("Size of stack is ", stk.size())
Output
Stack: 7 8 Stack: 7 Size of stack is 1
Time Complexity : O(1)
Space Complexity : O(n)